Nā ʻĀina Kumu Wai - Hawaiʻi's Watersheds
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explores the journey of freshwater in Hawaii, highlighting the essential role of watersheds. It details how trade winds (moai) carry moisture from the ocean, leading to rainfall (ooa) that nourishes native forests, which act as natural sponges. The water percolates into the ground, forming aquifers (moanaliha) that serve as vital underground reservoirs. The video emphasizes the interconnectedness of Hawaii's ecosystems and the importance of native forests in sustaining freshwater supplies, even for those using catchment systems. Understanding this process fosters appreciation for Hawaii's natural water sources.
Takeaways
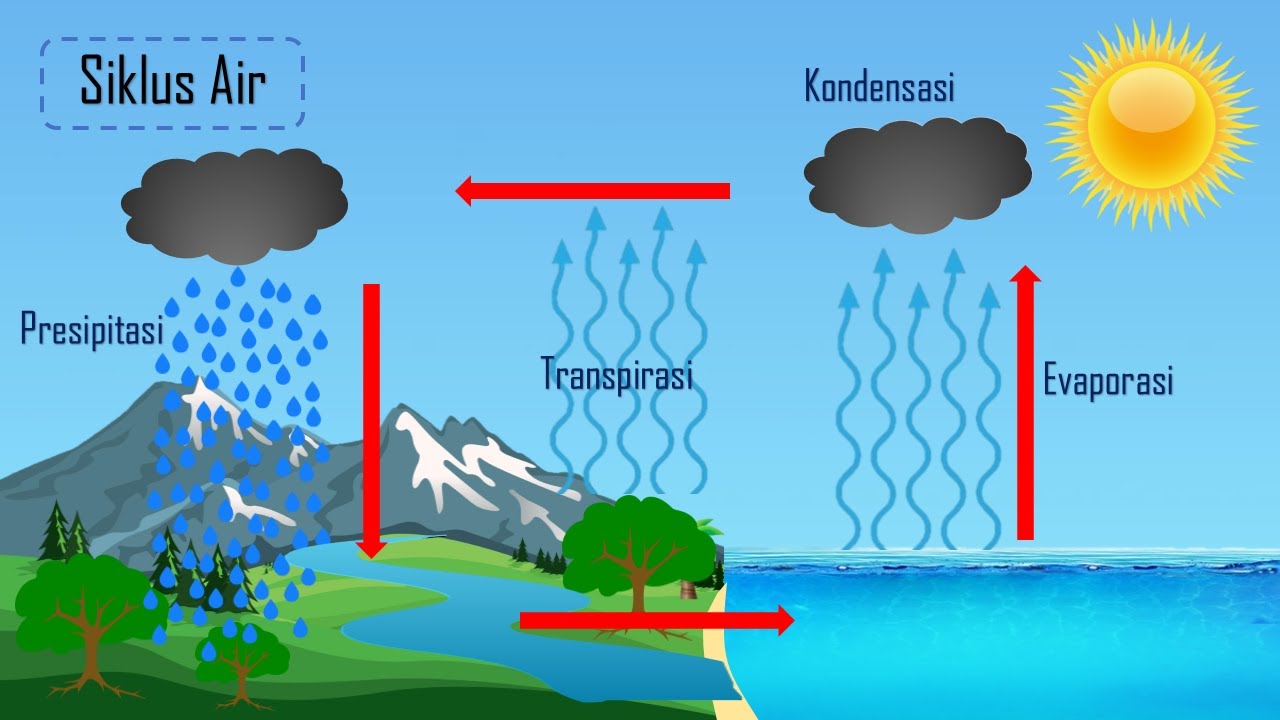
- 🌊 Water in Hawaii comes from a journey that includes oceans, the atmosphere, and watersheds.
- 💨 The moai (trade winds) are crucial for transporting moisture from the ocean to the islands.
- ☀️ Evaporation of ocean water, driven by the sun, converts liquid water into vapor, forming clouds.
- 🌧️ Rainfall is essential for replenishing fresh water resources in Hawaii.
- 🌳 Native forests act as sponges, soaking up rainfall and helping to store fresh water.
- 🏞️ Watersheds are defined as areas that collect and store fresh water, primarily in thick rainforest regions.
- 💧 After rainfall, water can either percolate underground as groundwater or flow as surface water into streams.
- 🗺️ Aquifers (moanaliha) are underground reservoirs formed by lava, storing fresh water above saltwater.
- 🔄 The interaction between fresh and salt water occurs underground, maintaining a balance essential for water supply.
- 🚰 Even those using catchment systems rely on the aquifer for their water supply, especially during droughts.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the video?
-The video explores the journey of water from the ocean to the watersheds in Hawaii, detailing how fresh water is collected and stored.
What are the 'moai' or trade winds, and why are they important?
-The 'moai' or trade winds are prevailing winds that blow from the northeast, pushing moist air over Hawaii's mountains, which is crucial for the evaporation process that leads to rainfall.
How does evaporation contribute to the water cycle in Hawaii?
-Evaporation converts ocean water into water vapor, which rises into the atmosphere. This process is driven by the heat from the sun, much like boiling water on a stove.
What role does rain play in Hawaii's fresh water supply?
-Rain is essential for providing fresh water in Hawaii, as it falls when the water vapor condenses in the atmosphere after being pushed over the mountains by the trade winds.
What are watersheds, and why are they significant?
-Watersheds are areas that collect and store fresh water. In Hawaii, they primarily consist of thick rainforest regions that act as natural reservoirs for the islands' water supply.
What happens to rainwater after it falls on healthy native forests?
-In healthy native forests, rainwater is absorbed into the ground, filtering through soil and lava rock, which allows it to replenish underground aquifers.
What is the difference between groundwater and surface water?
-Groundwater is water that seeps into the ground and collects in aquifers, while surface water is water that flows over the ground in streams and rivers, often resulting from runoff.
What are aquifers, and how do they function in Hawaii?
-Aquifers are underground reservoirs formed by lava flows that store fresh water. They are critical for supplying drinking water and can be accessed through wells and tunnels.
How does the interaction between fresh water and salt water occur underground?
-Fresh water from aquifers is less dense than salt water, allowing it to float above the salt water layer, creating a separation that prevents mixing.
How does native forest health impact water availability in Hawaii?
-Healthy native forests increase rainfall by facilitating cloud condensation, which directly affects the amount of fresh water collected in watersheds and ultimately benefits all water systems, including catchment systems.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)