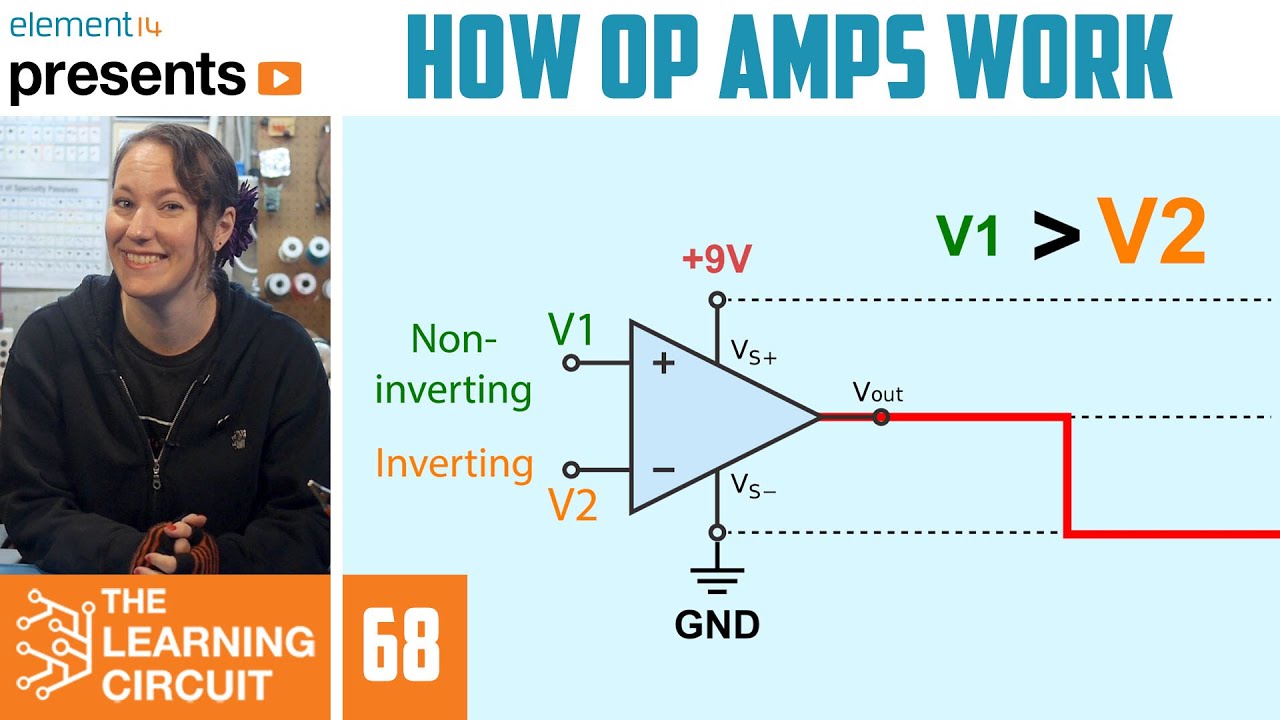
Chapter 6 Non Ideal Op Amp V3
Summary
TLDRThis lecture delves into the principles of operational amplifiers (op-amps) and their behavior with AC signals. Key concepts discussed include the characteristics of open-loop vs. closed-loop systems, the significance of bandwidth in maintaining desired gain, and the critical gain-bandwidth product. The speaker illustrates how variations in gain affect bandwidth and emphasizes the importance of staying within bandwidth limits for optimal performance. By using practical examples and cautioning against common pitfalls, the lecture aims to equip students with a solid understanding of designing effective electronic circuits.
Takeaways
- 😀 Open-loop gain in operational amplifiers (op-amps) refers to the gain without any feedback, which often leads to non-linearities.
- 🔄 Negative feedback is used to improve the linearity and stability of op-amps by regulating the gain.
- 📈 Bandwidth is essential for AC signals, ensuring the op-amp can maintain its designed gain across a specific frequency range.
- 🔍 The gain-bandwidth product (GBP) is a constant that indicates the relationship between gain and bandwidth in an op-amp.
- 📊 The y-axis of the gain vs. frequency graph represents gain in decibels (dB), while the x-axis is a logarithmic scale for frequency.
- 🔗 When the gain is set higher, the bandwidth must decrease to maintain a constant GBP, demonstrating an inverse relationship.
- ⚖️ For unity gain (gain of 1), the op-amp achieves its maximum bandwidth, which is equal to the GBP value.
- 📉 Operating outside the designed bandwidth can lead to reduced gain and output distortion, impacting performance.
- 🔧 Engineers must consider both gain and bandwidth when designing circuits with op-amps to ensure quality signal amplification.
- 💡 Understanding these concepts is crucial for effective circuit design and maintaining signal integrity in audio and other applications.
Q & A
What does AC signal refer to in the context of the discussion?
-AC signal refers to alternating current signals, which vary in frequency. In this context, the focus is on the frequency response of amplifiers (or 'OMs').
What is meant by 'open-loop' in amplifier characteristics?
-'Open-loop' refers to the operational mode of an amplifier where there is no feedback from the output back to the input. This means the amplifier operates solely based on its input without any corrections or adjustments.
How is the gain affected if the input signal exceeds the amplifier's bandwidth?
-If the input signal exceeds the amplifier's bandwidth, the gain will not be constant and will drop below the intended gain. This means that the output signal will be less than what is expected.
What does bandwidth mean in the context of AC signals?
-Bandwidth refers to the range of frequencies that an amplifier can handle without a significant drop in gain. It is critical to ensure that the input signal frequency falls within this range to achieve the desired output.
What is the gain-bandwidth product?
-The gain-bandwidth product is a constant value for an amplifier, representing the product of the amplifier's gain and its bandwidth. It indicates the trade-off between gain and bandwidth.
How can one find the maximum bandwidth of an amplifier?
-To find the maximum bandwidth, you first determine the desired minimum gain of the amplifier. For a unity gain, the maximum bandwidth can be read from the characteristic chart.
What happens to bandwidth when the gain is increased?
-When the gain is increased, the bandwidth decreases to maintain the gain-bandwidth product as a constant value. This means that increasing gain results in a shorter bandwidth.
Why is it important to use the correct scale when interpreting amplifier characteristics?
-Using the correct scale, especially in dB for gain and logarithmic for frequency, is crucial for accurate interpretation of the amplifier's performance and characteristics, as incorrect scaling can lead to significant errors.
What is the relationship between gain and bandwidth as described in the video?
-The relationship is such that as one increases, the other must decrease. This is illustrated by the constant gain-bandwidth product, meaning adjustments in gain will inversely affect bandwidth.
How does one ensure that an amplifier operates within its intended bandwidth?
-To ensure that an amplifier operates within its intended bandwidth, one must input signals that fall within the specified frequency range for which the amplifier was designed, avoiding frequencies that exceed this range.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)