Penginderaan Jauh
Summary
TLDRIn this discussion on remote sensing (penginderaan jauh), the speaker defines it as the technique for gathering information about objects from a distance without direct contact. Key components include energy sources, atmospheric influence, the objects on Earth's surface, and sensors that capture data. The process distinguishes between passive systems, which rely on natural sunlight, and active systems using electronic waves. Data collected can be visual or digital, serving various applications such as urban planning and environmental monitoring. The session sets the stage for exploring different types of imagery in future discussions.
Takeaways
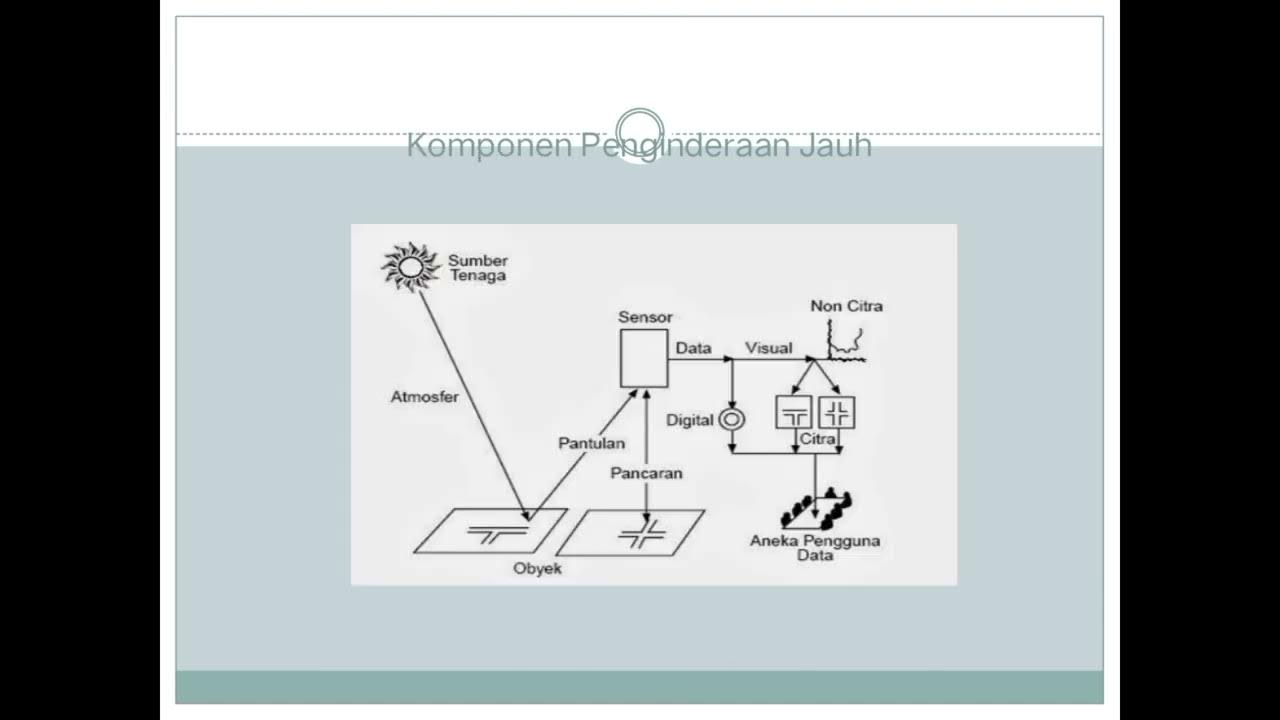
- 🌍 Remote sensing (penginderaan jauh) is the technology of obtaining information about objects or areas from a distance without direct contact.
- 📸 This process is also known as indraja or PJ in Indonesian, and in English, it's referred to as remote sensing.
- 🖼️ An example demonstrates how information about Candi Borobudur can be gathered through images without being physically present at the site.
- 🔋 There are two main types of energy sources in remote sensing: passive (using natural sunlight) and active (using artificial electronic sources).
- ☀️ The atmosphere serves as a medium that transmits sunlight to the Earth's surface, influencing data capture.
- 🌊 Different materials reflect or absorb sunlight variably, impacting how they appear in remote sensing images (e.g., water appears darker than solid surfaces).
- 📡 Sensors in remote sensing are classified into two types: photographic sensors (which use cameras) and electronic sensors (which use scanners).
- 🚀 Platforms (wahana) for remote sensing can include satellites, drones, and aircraft, which allow data collection from various altitudes.
- 📊 Data generated from remote sensing is categorized into visual data (e.g., photographs) and digital data (e.g., processed information like coordinates).
- 👥 Remote sensing data is utilized by various stakeholders for applications like urban planning, flood monitoring, and environmental assessments.
Q & A
What is remote sensing?
-Remote sensing is the science and technology used to acquire information about objects or areas without direct contact, primarily through the analysis of data obtained using various tools.
What are some alternative terms for remote sensing?
-Remote sensing is also known as 'indraja' or 'PJ,' and in English, it is referred to as 'remote sensing.'
How does remote sensing differ from direct observation?
-Remote sensing allows for the collection of information from a distance, meaning observers do not need to be physically present at the location to gather data.
What are the main components of remote sensing?
-The main components include the energy source, atmosphere, objects on the Earth's surface, sensors, platforms, and data.
What types of energy sources are used in remote sensing?
-Remote sensing uses two types of energy sources: passive systems that rely on natural sunlight and active systems that use electronic waves from satellites.
What role does the atmosphere play in remote sensing?
-The atmosphere acts as a medium for sunlight to reach the Earth's surface and is crucial for the transmission of electromagnetic radiation.
What are the two types of sensors mentioned in the transcript?
-The two types of sensors are photographic sensors, which use cameras to capture images, and electronic sensors, which use scanners to gather non-photo data.
What is the significance of the object's reflectivity in remote sensing?
-The reflectivity of an object affects how it appears in remote sensing imagery; bright objects reflect more sunlight and appear lighter, while dark objects absorb more sunlight and appear darker.
What are the different platforms used for remote sensing?
-Platforms for remote sensing include satellites, airplanes, drones, and other vehicles designed to carry sensors above the Earth's surface.
What types of data are generated from remote sensing?
-Remote sensing generates visual data, which can be observed directly, and digital data, which requires processing, such as coordinates and other numerical information.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)