The Importance of Soil | Essentials of Environmental Science
Summary
TLDRThis informative video clarifies the vital distinction between soil and dirt, emphasizing soil's role as a critical natural resource essential for life. It explains the formation of soil through processes like weathering and decomposition, driven by various factors such as parent material, time, organisms, climate, and topography. The video highlights the significance of soil in agricultural productivity and its ecosystem services, including water filtration and carbon storage. It also addresses the threats posed by unsustainable practices that degrade soil health, underlining the importance of preserving soil to combat climate change and maintain biodiversity.
Takeaways
- 🌱 Soil is a crucial natural resource, distinct from dirt, that supports life and ecosystems.
- 🪨 Soil formation is influenced by five main factors: parent material, time, organisms, climate, and topography.
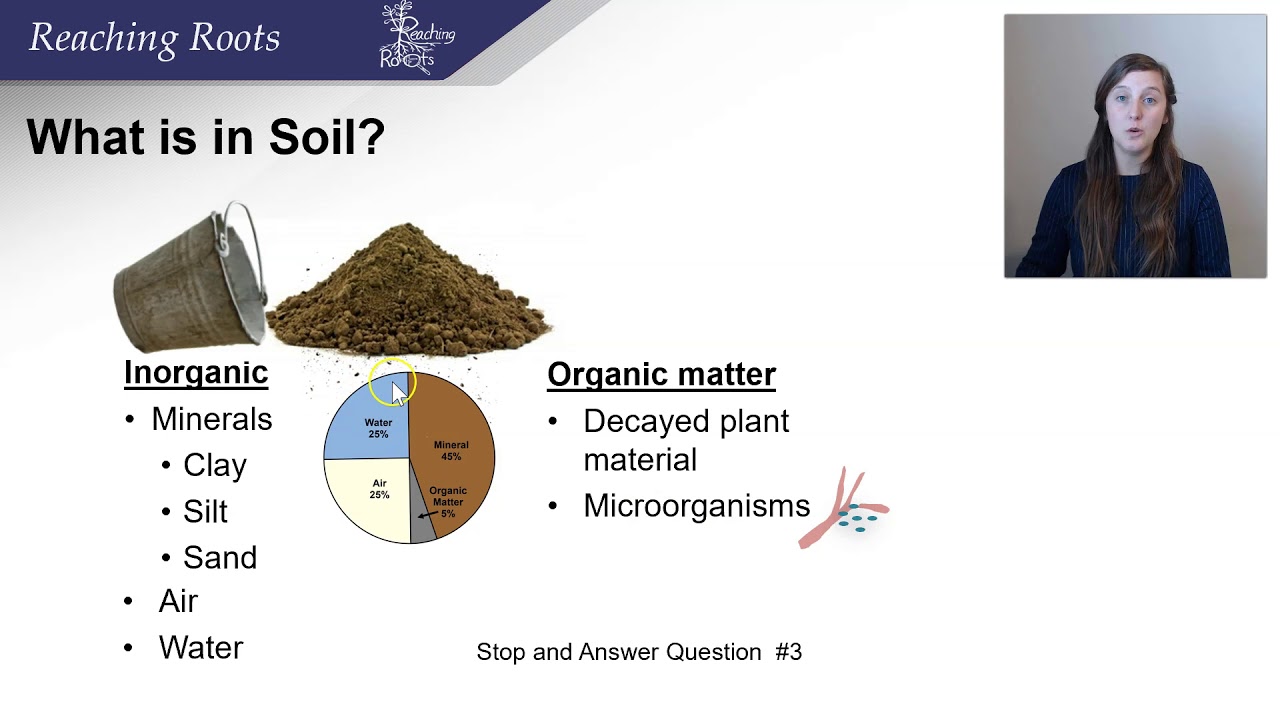
- 💧 Soil is composed of minerals, organic matter, water, and air, each playing a significant role in its functionality.
- 🌍 Different soil types have unique properties, impacting their use in agriculture and environmental health.
- 🌿 Living organisms, including microorganisms and plants, contribute to soil fertility and nutrient cycling.
- 🌡️ Climate affects soil formation; warmer, wetter conditions promote faster decomposition compared to colder, drier climates.
- 🚜 Unsustainable agricultural practices, such as overgrazing and deforestation, can degrade soil quality and lead to erosion.
- 🔄 Soil plays a vital role in biogeochemical cycles, particularly in nitrogen and carbon cycling.
- 💧 Soil acts as a natural filter for groundwater, improving water quality before it enters aquifers.
- 🌍 Healthy soil is essential for food production and mitigating climate change by acting as a carbon sink.
Q & A
What is the primary distinction between soil and dirt?
-Soil is a productive natural resource that supports life and ecosystems, whereas dirt is simply soil that is in the wrong place.
What are the five main components that drive soil formation?
-The five components are parent material, time, organisms, climate, and topography.
How does parent material affect soil characteristics?
-Parent material influences the mineral content and nutrients in the soil, as different types of rock break down into varying soil compositions.
What role do pioneer species play in soil formation?
-Pioneer species, such as lichen, help break down parent material and contribute organic matter to the soil as they die and decompose.
How do temperature and humidity influence soil formation?
-Warm and wet conditions speed up decomposition and soil formation, while cold or dry conditions slow it down.
What is soil texture and how is it determined?
-Soil texture refers to the percentages of sand, silt, and clay in the soil, and it is represented using the 'soil triangle.'
What is loamy soil and why is it important?
-Loamy soil is a balanced mixture of sand, silt, and clay, making it ideal for agricultural uses due to its good structure and nutrient-holding capacity.
What are the consequences of unsustainable agricultural practices on soil?
-Unsustainable practices can lead to loss of soil fertility, increased erosion, and degradation of soil health, making it less able to support life.
In what way does soil function as a carbon sink?
-Soil stores carbon dioxide from the atmosphere as organic matter, helping to mitigate climate change by sequestering carbon underground.
What are the ecosystem services provided by soil?
-Soil provides essential services including water filtration, nutrient cycling, and support for plant growth, which are crucial for agriculture and maintaining ecological balance.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)