How To Draw The Lewis Structures of Ionic Compounds
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial explains how to draw Lewis structures for various ionic compounds. It begins with sodium chloride, illustrating the transfer of an electron from sodium to chlorine, resulting in positive and negative charges. The tutorial continues with magnesium fluoride, showing how magnesium donates two electrons to two fluorine atoms. It also covers potassium oxide, detailing the donation of electrons from potassium to oxygen, and aluminum oxide, which involves the transfer of electrons from aluminum to multiple oxygen atoms. Each example emphasizes the electron transfer process and the resulting charges, helping viewers understand ionic bonding.
Takeaways
- 😀 Sodium (Na) has 1 valence electron, while chlorine (Cl) has 7 valence electrons.
- 😀 Sodium donates its electron to chlorine, forming a Na⁺ cation and a Cl⁻ anion.
- 😀 Lewis structures for ionic compounds use brackets to represent ions and their charges.
- 😀 Magnesium (Mg) has 2 valence electrons, and each fluorine (F) has 7 valence electrons.
- 😀 In magnesium fluoride (MgF₂), Mg donates 1 electron to each of the two fluorine atoms.
- 😀 Each fluorine becomes a F⁻ ion, while magnesium becomes a Mg²⁺ ion.
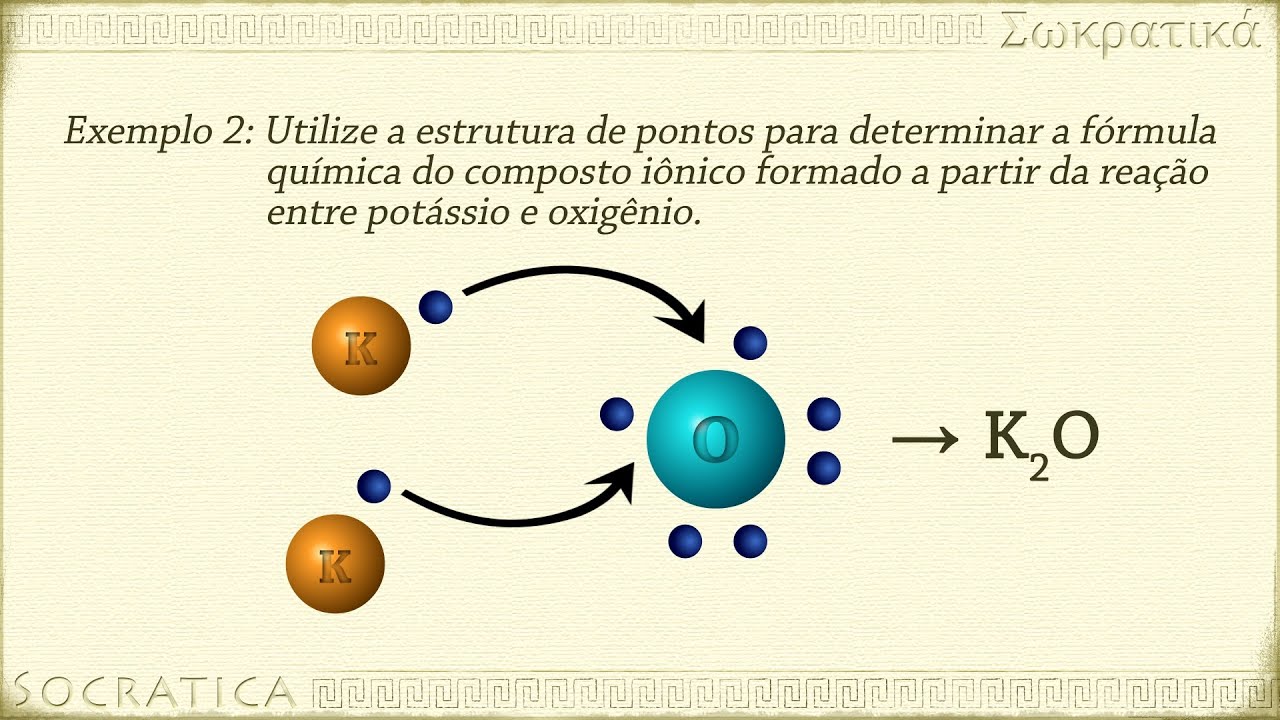
- 😀 Potassium (K) has 1 valence electron, while oxygen (O) has 6 valence electrons.
- 😀 In potassium oxide (K₂O), each of the two K atoms donates 1 electron to the O atom.
- 😀 Oxygen acquires 2 electrons, resulting in an O²⁻ ion, while each K atom becomes a K⁺ ion.
- 😀 Aluminum (Al) has 3 valence electrons, and each of the three oxygen (O) atoms has 6 valence electrons.
Q & A
What is the first step in drawing the Lewis structure of an ionic compound?
-The first step is to identify the atoms involved and determine their valence electrons.
How does sodium behave in the formation of sodium chloride?
-Sodium donates its one valence electron to chlorine, resulting in sodium becoming a cation (Na⁺).
What happens to chlorine when it receives an electron from sodium?
-Chlorine gains an electron, becoming an anion (Cl⁻), and achieves a full octet with eight valence electrons.
In magnesium fluoride, how many electrons does magnesium donate?
-Magnesium donates two electrons, one to each of the two fluorine atoms.
What is represented by a full arrow in Lewis structures?
-A full arrow represents the transfer of two electrons, while a half arrow represents the transfer of one electron.
How are the charges indicated in the Lewis structure for potassium oxide?
-Potassium ions become K⁺ after donating one electron, while oxygen becomes O²⁻ after accepting two electrons.
Why does oxygen need to acquire electrons in potassium oxide?
-Oxygen needs to acquire electrons to achieve a full octet, which is eight valence electrons.
What is the charge of aluminum ions in aluminum oxide?
-Each aluminum ion becomes Al³⁺ after donating three electrons to oxygen atoms.
How many oxygen atoms are involved in the Lewis structure of aluminum oxide?
-There are three oxygen atoms involved, each gaining two electrons.
What do lone pairs represent in the Lewis structure?
-Lone pairs represent unshared pairs of electrons surrounding the ions that help indicate the complete electron configuration.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)