The journey of a biopsy #DiscoverPathology
Summary
TLDRThe video provides an insightful look into the biopsy process, highlighting the roles of various medical professionals, including consultants and biomedical scientists. It details the steps from specimen collection through processing, embedding, and slicing to staining and quality control, culminating in the diagnostic phase. Pathologists examine the stained slides to identify conditions like cancer, offering critical information for patient care. The collaborative nature of pathology is emphasized, showcasing how each step contributes to accurate and timely diagnoses, ultimately impacting patient outcomes.
Takeaways
- 😀 Biopsies are essential for diagnosing irregularities found in imaging, particularly for breast masses.
- 😀 Pathologists work collaboratively with biomedical scientists to process and analyze biopsy specimens.
- 😀 The processing of biopsies involves removing water content and replacing it with wax to preserve the tissue.
- 😀 Training biomedical scientists has become crucial for dissecting small specimens, which was traditionally done by pathologists.
- 😀 Tissues are embedded in wax blocks to protect them and are sliced into thin sections for microscopic examination.
- 😀 Staining samples is vital to enhance visibility of cells under a microscope, allowing for accurate diagnoses.
- 😀 Quality control is an important step to ensure that the slides accurately represent the patient's condition.
- 😀 Diagnoses often involve meticulous review of multiple slides, with some cases requiring extensive analysis.
- 😀 Pathologists play a detective role in diagnosing various cancers, determining the aggressiveness of tumors.
- 😀 The final biopsy results are crucial for patient care, impacting treatment decisions and outcomes.
Q & A
What should a patient do if they find a lump in their breast?
-Patients should seek medical advice and may need to undergo imaging tests to investigate the lump further.
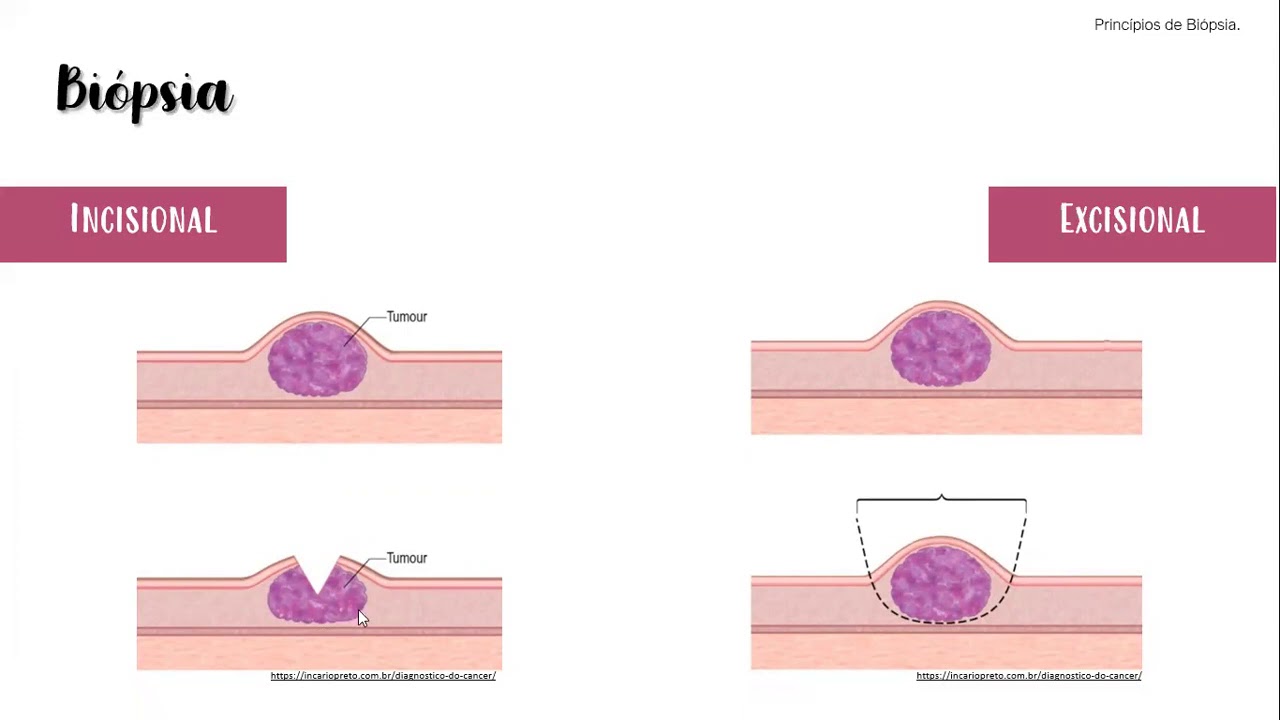
What is the purpose of a biopsy?
-A biopsy is performed to collect tissue samples for examination to determine if there are any abnormalities, such as cancer.
What happens to the biopsy sample after it is collected?
-The sample is processed, which involves removing water content and replacing it with wax to preserve the tissue.
Who is involved in the dissection of biopsy specimens?
-Consultant pathologists and trained biomedical scientists are involved in dissecting and processing biopsy specimens.
What does the embedding process entail?
-Embedding involves impregnating the processed tissue with molten paraffin wax to create a solid block for slicing.
How thick are the slices of tissue taken for examination?
-The slices of tissue are usually cut to about three microns thick to allow for proper examination under a microscope.
Why is staining necessary for biopsy samples?
-Staining enhances the visibility of tissue cells under the microscope, making it easier to identify any abnormalities.
What role does quality control play in the pathology process?
-Quality control ensures that the slides accurately represent the samples and that the staining is of high quality before diagnosis.
What can a pathologist determine from the biopsy results?
-A pathologist can identify the type of cancer, if present, and its aggressiveness, which is critical for treatment decisions.
What happens after the pathologist has examined the slides?
-The results are compiled into a report and communicated to the referring physician, who then informs the patient.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Best DNB Hospitals in Mumbai.
Princípios de Biópsia

Phylum Annelida Part 3: Oligochaeta and Hirudinea (Segmented Terrestrial/Aquatic Worms and Leeches)

A Day in the Life of a Data Analyst (2023)

Data Science Jobs Explained in 5 Minutes

What are the different types of roles in IT | Technology jobs overview
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)