The Four Types of Tissues - Epithelial, Connective, Nervous and Muscular
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the four primary types of tissues in the human body: epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissue serves protective and absorptive functions, covering surfaces and lining organs. Nervous tissue, comprising neurons and glial cells, facilitates communication by transmitting signals. Muscular tissue enables movement, with skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscles fulfilling various involuntary and voluntary roles. Lastly, connective tissue supports and connects other tissues, consisting of loose and dense varieties as well as specialized types like blood and bone. Each tissue type is vital for the proper functioning of organs and overall bodily health.
Takeaways
- 😀 A tissue is a group of similar cells working together to perform specific roles in an organ.
- 😀 There are four primary types of tissues: epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissue.
- 😀 Epithelial tissue is made of closely packed cells with minimal matrix, covering body surfaces and lining organs.
- 😀 The functions of epithelial tissue include protection, secretion, absorption, and filtration, especially in glands and kidneys.
- 😀 Nervous tissue consists of neurons and glial cells that transmit signals and information throughout the body.
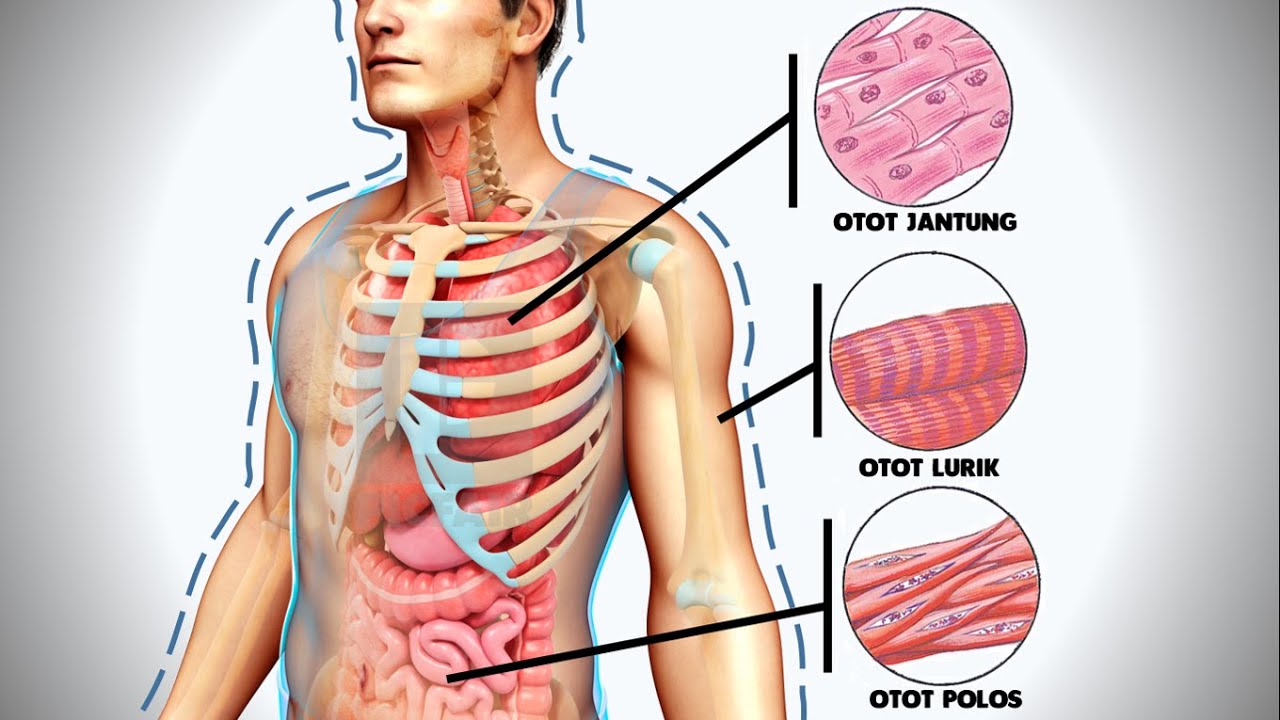
- 😀 Muscular tissue is composed of elongated cells specialized for contraction, enabling movement and various physiological functions.
- 😀 There are three types of muscular tissue: skeletal (voluntary), cardiac (involuntary), and smooth (involuntary).
- 😀 Connective tissue supports and connects other tissues, consisting of loosely packed cells and an extracellular matrix.
- 😀 Connective tissue can be classified into connective tissue proper (loose and dense) and specialized connective tissues (blood, bone, cartilage).
- 😀 Organs are formed from two or more tissue types working together, such as the spleen, skin, and heart.
Q & A
What are the four primary types of tissues in the human body?
-The four primary types of tissues are epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscular tissue, and nervous tissue.
How are epithelial tissues characterized?
-Epithelial tissues are characterized by layers of closely spaced cells with minimal matrix, resembling tightly packed bricks.
What functions do epithelial tissues perform?
-Epithelial tissues perform various functions including protection, secretion, excretion, filtration, and absorption, particularly in glands and kidneys.
What is the main role of nervous tissue?
-The main role of nervous tissue is to transmit signals and information throughout the body via neurons and supporting glial cells.
What distinguishes muscular tissue from other tissue types?
-Muscular tissue is distinguished by elongated, excitable cells specialized for contraction and movement.
What are the three types of muscular tissue?
-The three types of muscular tissue are skeletal muscle (voluntary), cardiac muscle (involuntary), and smooth muscle (involuntary).
What functions do skeletal muscles serve?
-Skeletal muscles serve voluntary functions, such as aiding in movement, including bending limbs.
How does cardiac muscle function in the body?
-Cardiac muscle functions involuntarily to pump blood out of the heart.
What is the purpose of connective tissue?
-Connective tissue connects, separates, and supports all other types of tissues in the body.
How is connective tissue categorized?
-Connective tissue can be categorized into connective tissue proper (which includes loose and dense connective tissues) and specialized connective tissues (such as blood, bone, and cartilage).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)