PLANT BREEDING AND SELECTION USING MOLECULAR MARKERS
Summary
TLDRThis module explores the application of DNA-based molecular markers in plant breeding to select hybrids with desired phenotypes and genotypes. It highlights the efficiency of using molecular markers over traditional phenotypic selection, significantly reducing costs and improving accuracy. Through methods like PCR, breeders can identify desirable traits early in the plant's development. The complexity of selecting for polygenic traits, the effects of genetic linkage, and environmental factors are also discussed. A case study illustrates the practical use of identified genes linked to starch content in rice to develop new hybrids, emphasizing the innovative approaches in modern plant breeding.
Takeaways
- 🌱 Molecular markers are essential tools in plant breeding, allowing for the selection of hybrids based on desired phenotypes and genotypes.
- 🔬 The application of DNA-based molecular markers significantly reduces the cost and increases the accuracy of developing novel F1 hybrids.
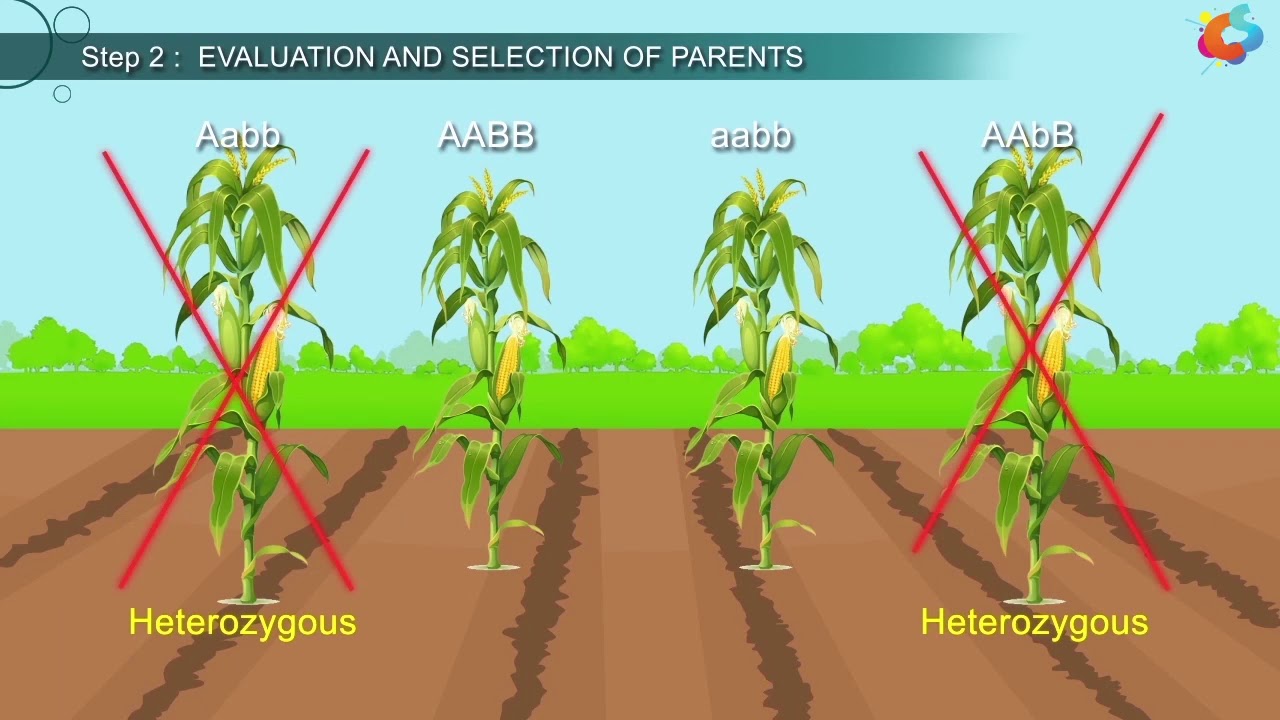
- 📊 Conventional breeding relies heavily on phenotype observation, which can be time-consuming and inefficient compared to molecular marker techniques.
- ⏳ Molecular markers enable early selection of plants by using PCR on seedlings, thus avoiding lengthy growth periods to observe phenotypes.
- 🧬 Selecting for polygenic traits (traits linked to multiple genes) requires the development of multiple molecular markers to confirm desired characteristics.
- 🔗 Understanding genetic linkage and recombination is critical for effective selection; tightly linked genes are less likely to be separated during breeding.
- ⚠️ Mutations in primer binding sites can hinder the detection of specific genes during PCR, which complicates the selection process.
- 🌍 Environmental factors can greatly influence gene expression and trait manifestation, impacting the reliability of molecular markers.
- 💡 The use of molecular markers allows researchers to conduct selections based on genotypes rather than phenotypes, improving efficiency.
- 📚 The module concludes with a case study exercise, encouraging researchers to apply their knowledge of genes linked to specific traits in developing hybrids.
Q & A
What are molecular markers, and why are they important in plant breeding?
-Molecular markers are DNA sequences linked to specific traits in plants. They are important in plant breeding because they allow for the selection of hybrids based on genetic information rather than solely on observable traits, improving accuracy and reducing costs.
How does the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) contribute to the application of molecular markers?
-PCR is a method used to amplify specific DNA sequences, allowing breeders to trace the inheritance of desired genotypes. This technique enables early selection of plants based on their genetic makeup.
What are the advantages of using molecular markers over conventional breeding methods?
-Molecular markers significantly reduce the time and cost associated with breeding, provide greater accuracy in selecting plants with desired traits, and allow for the selection of plants at an early developmental stage.
What challenges do breeders face when using conventional selection methods?
-Breeders face challenges such as lengthy growth cycles, the need for large planting areas, and the risk of losing desirable plants among many hybrids when selecting based on phenotype alone.
What does the term 'polygenic trait' mean in the context of plant breeding?
-A polygenic trait is influenced by multiple genes, making it more complex to select for in breeding. Breeders must develop markers for each relevant gene to ensure accurate trait expression.
How do environmental factors impact the expression of traits in plants?
-Environmental factors, such as nutrient availability and growing conditions, can significantly affect how genes are expressed, potentially leading to variations in phenotype that complicate selection.
Why is it necessary to consider gene linkage when developing molecular markers?
-Understanding gene linkage is crucial because tightly linked genes are inherited together, while genes that can recombine may separate during meiosis. This knowledge helps breeders predict trait inheritance more accurately.
What happens if there is a mutation in the primer binding site of a gene?
-If a mutation occurs in the primer binding site, the PCR process may fail to amplify the target gene, rendering it undetectable. This can hinder the selection process for specific traits.
How does the case study mentioned in the module illustrate the application of molecular markers?
-The case study involves using knowledge of six genes linked to starch content in rice to develop molecular markers for a new hybrid, demonstrating the practical application of molecular markers in improving crop traits.
What is the significance of conducting PCR at the seedling stage?
-Conducting PCR at the seedling stage allows breeders to select plants based on their genotype early in development, significantly reducing the time and resources spent on growing plants that may not exhibit the desired traits.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)