Module 4 Gender Development
Summary
TLDRThis presentation delves into the development of the gendered self, highlighting how societal perceptions shape gender identity from an early age. Through engaging examples, it illustrates the emergence of rigid gender stereotypes in childhood, with distinctions in traits, roles, and preferences. The speaker discusses the significance of sex versus gender, emphasizing that gender identity involves cultural aspects beyond biology. As children grow, they face social pressures that intensify gender differences, particularly during adolescence. Family and cultural influences play a crucial role in shaping perceptions of masculinity and femininity, ultimately guiding individual identity formation.
Takeaways
- 😀 Gender roles and stereotypes emerge early in childhood and are influenced by societal expectations.
- 👩⚕️ The example of the doctor highlights how gender stereotypes can shape perceptions about roles and professions.
- 🧒 Children as young as two to three years old begin to identify their own gender and label others accordingly.
- 🚼 By three to four years, children exhibit rigid gender stereotypes related to toys, colors, and activities.
- 🎨 Cultural associations of colors, such as pink for girls and blue for boys, can vary over time and across societies.
- 👭 Children typically prefer same-sex playmates during early childhood, reinforcing gendered socialization.
- 🔄 By ages six to seven, children recognize gender stability and understand that it does not change over time.
- 📚 Middle childhood brings an awareness of gender-associated personality traits, with females seen as gentle and males as competitive.
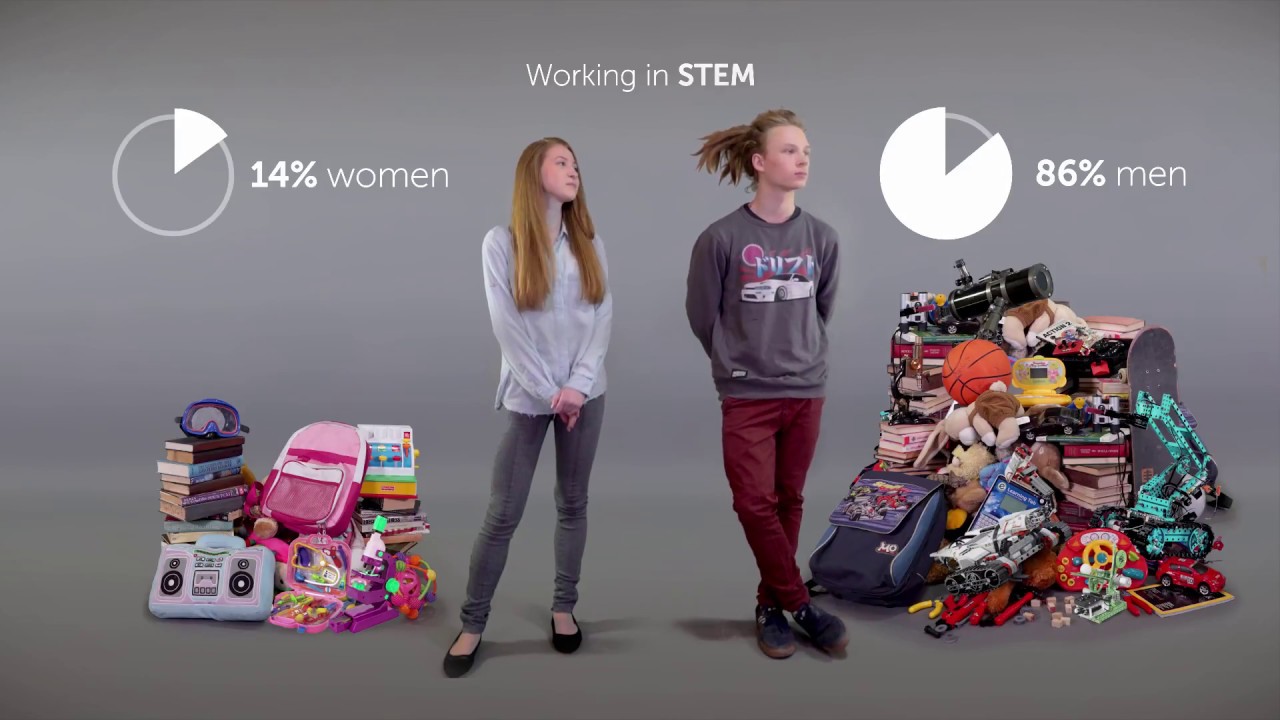
- 🏥 Masculine occupations are perceived as having higher status among children, affecting their career aspirations.
- 📊 Adolescence intensifies gender differences due to social pressures, pushing individuals to conform to traditional masculine and feminine roles.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the presentation?
-The main topic is the development of the gendered self, focusing on how gender roles and stereotypes emerge and evolve throughout childhood and adolescence.
How does the presentation illustrate the concept of gender roles?
-The presentation begins with a thought experiment involving a scenario where a doctor, who is the boy's mother, is unable to operate on her son, highlighting how assumptions about gender can influence perceptions.
At what age do children typically begin to show gender identity?
-Children typically show gender identity around two to three years of age, expressing statements like 'I am a girl' and labeling others' genders.
What are some characteristics associated with typical males and females, according to the presentation?
-Typical females are described as affectionate and gentle, while typical males are seen as independent and assertive, demonstrating societal stereotypes.
What does the term 'gender constancy' refer to?
-Gender constancy refers to the understanding that gender remains stable over time and is not altered by changes in appearance or situation.
How do gender stereotypes evolve in middle childhood?
-In middle childhood, children increasingly associate certain personality traits and occupations with specific genders, often perceiving masculine roles as having higher status.
What impact does adolescence have on gender identity development?
-During adolescence, the gender intensification hypothesis suggests that social pressures heighten, pushing individuals to conform more strictly to traditional gender norms.
How do cultural influences affect the understanding of gender roles?
-Cultural influences, including family and societal expectations, play a significant role in shaping how individuals learn about masculinity and femininity and their importance.
What evidence does the presentation provide regarding the flexibility of gender roles?
-The presentation mentions that females tend to be more flexible than males in considering diverse activities and traits associated with gender.
What role do same-sex friendships play in childhood gender development?
-Same-sex friendships are prevalent during childhood, with boys typically preferring to play with boys and girls with girls, reinforcing gender-specific behaviors and preferences.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)