Properties and Grain Structure
Summary
TLDRThe video explores the grain structure of metals, focusing on processes such as etching and cold working. It demonstrates how grains form when metals like aluminum and steel solidify and how manipulating temperatures during heat treatment can alter their properties. Cold working elongates grains, enhancing hardness while reducing ductility, while recrystallization restores softness and ductility. The video compares different carbon content steels, showcasing how heat treatment affects grain structure and mechanical properties, including toughness and hardness, leading to practical applications in engineering.
Takeaways
- 🔍 All metals are composed of grains, which are often not visible without special treatment.
- ⚙️ The grain structure of aluminum can be revealed through a process called etching, involving powerful acids and careful surface preparation.
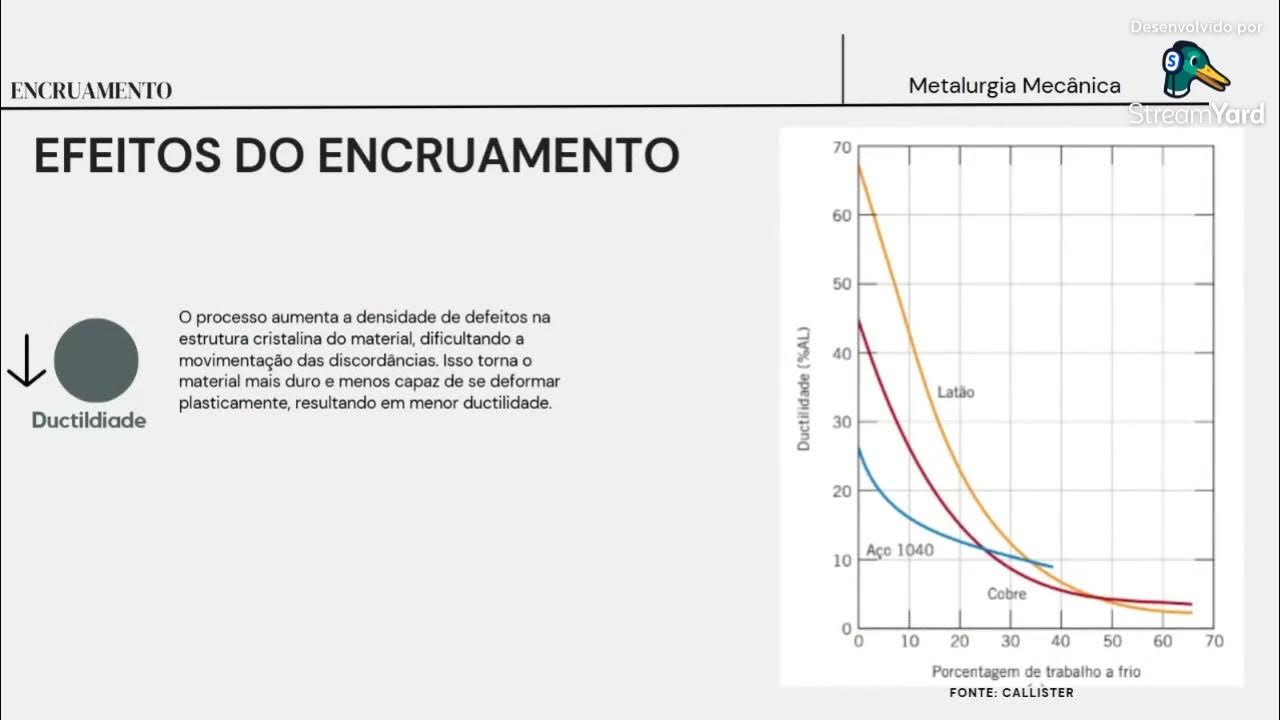
- 📏 Cold working processes elongate and distort the grains of metals, increasing hardness and tensile strength while decreasing ductility.
- 🔥 Recrystallization occurs when cold-worked metal is heated, allowing new grains to form and restoring ductility and softness.
- 🔬 In steel, two types of grains exist: ferrite (ductile) and pearlite (hard and strong), with their proportions varying based on carbon content.
- 🔄 Heat treatment can significantly alter the mechanical properties of steel by controlling the sequence of heating and cooling.
- 🌡️ Normalizing involves heating steel to about 720 degrees Celsius, resulting in a more uniform grain structure.
- 💧 Quenching rapidly cools heated steel, forming a hard but brittle needle-like structure.
- ⚖️ Tempering modifies the structure of quenched steel to reduce brittleness while maintaining hardness.
- 📊 The mechanical properties of metals, including aluminum and steel, are closely tied to their grain structure and the processing methods used.
Q & A
What is the purpose of the zinc coating on safety barriers?
-The zinc coating on safety barriers serves as a protective layer that prevents corrosion and extends the lifespan of the metal.
How are the grains of metal made visible?
-The grains of metal can be made visible by giving the surface a mirror-like finish and then treating it with a powerful acid followed by a second chemical treatment called etching.
What happens to metal grains during the solidification process?
-During the solidification process, tiny crystals begin to form in the molten metal, which grow outward until they meet neighboring crystals, resulting in a structure made up of many grains.
What effect does cold working have on the grain structure of aluminum?
-Cold working elongates and distorts the grains of aluminum, changing their shape in the direction of rolling, which increases the metal's hardness and tensile strength while decreasing its ductility.
What is recrystallization, and how does it affect metal properties?
-Recrystallization is the process where new grains form at the grain boundaries when the metal is heated, which restores softness and ductility while reducing hardness and tensile strength.
What types of grains are present in plain carbon steel?
-Plain carbon steel consists of two types of grains: ferrite, which provides ductility, and pearlite, which consists of alternating layers of iron and iron carbide that provide hardness and strength.
How does the carbon content affect the grain structure of steel?
-Increasing the carbon content in steel leads to a higher number of pearlite grains and a reduction in ferrite grains, thereby altering the mechanical properties of the steel.
What is the effect of heat treatment on the grain structure of steel?
-Heat treatment can refine the grain structure of steel, making it more uniform and smaller, which in turn enhances its mechanical properties such as toughness.
What happens to the grain structure during quenching?
-During quenching, the rapid cooling of steel leads to the formation of a hard needle-like structure, which increases hardness but can also make the steel brittle.
What is the purpose of tempering in the heat treatment process?
-Tempering modifies the brittle needle-like structure formed during quenching, introducing small flakes of carbon and reducing brittleness while maintaining increased hardness.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Metallography Part II - Microscopic Techniques

Understanding Metals

Heat Treatment || Metallurgy || Materials Science

Experiments with the Bubble Model of Metal Structure 1952 - Sir Lawrence Bragg, W.M Lomer, J.F. Nye
Pitch sobre Encruamento

SOLIDIFICATION OF PURE METAL | COOLING CURVE | GIBB'S PHASE RULE | NUCLEI AND GROWTH OF NUCLEI |GATE
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)