01 INTRODUCCION A LA RM - 1 de 9
Summary
TLDRThe video discusses the critical concepts of material resistance and stability in engineering. It emphasizes the importance of structures that can withstand external forces, highlighting three key properties: resistance, rigidity, and stability. Resistance refers to the ability to bear loads without failure, while rigidity limits shape deformation. Stability is concerned with an element's capacity to resist significant deformations caused by minor disturbances. The analysis of these properties is essential across various engineering fields, influencing the design of everything from buildings and bridges to machinery, ensuring they can perform reliably under expected conditions.
Takeaways
- 🔧 The study of materials resistance is essential for ensuring that structures can withstand external loads effectively.
- 🧱 The concept of 'resistance' refers to a material's ability to withstand and transmit stresses without breaking.
- 📏 Rigidity is crucial for structures to limit deformations and maintain their intended shape under load.
- ⚖️ Stability is defined as a structure's ability to resist large deformations caused by small disturbances.
- 📊 The critical load for stability can be much lower than the load that would cause material failure in tension.
- 🌪️ Pandeo, or buckling, occurs when a slender element under compression exceeds its critical load, leading to potential structural failure.
- 🔍 Understanding the relationship between resistance, rigidity, and stability is key to effective structural design.
- 🏗️ Engineers from various disciplines, including civil and industrial engineering, apply principles of materials resistance in their projects.
- ⚙️ The analysis of structural behavior requires understanding both individual component performance and overall system dynamics.
- 🔗 Applications of materials resistance span across many engineering fields, influencing the design of everything from buildings to machinery.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of material resistance in engineering?
-The primary focus of material resistance is to ensure that structures and objects can withstand external loads without failing, thus providing safety and functionality in various applications.
How is resistance defined in the context of material science?
-Resistance in material science refers to the ability of a material to support and transmit forces without breaking or deforming excessively, ensuring the integrity of structures under load.
What is the significance of rigidity in structural design?
-Rigidity is significant because it determines a structure's ability to maintain its shape and dimensions under load, preventing excessive deformations that could lead to failure or functional issues.
What does the term 'critical load' refer to?
-The 'critical load' is the maximum load that can be applied to a slender structure, like a column, before it experiences instability or buckling.
What is buckling, and how does it affect structural integrity?
-Buckling is a failure mode where a structural member deforms under compressive loads, leading to a sudden change in shape. It can compromise the structural integrity even if the material itself is not broken.
Why is stability important in material resistance?
-Stability is important because it ensures that a structure can resist small perturbations without undergoing large deformations or collapse, thereby maintaining its functionality and safety.
What types of structures are commonly analyzed using material resistance principles?
-Common structures analyzed using material resistance principles include buildings, bridges, tunnels, and various industrial structures, as well as components like beams, columns, and machinery.
How do engineers ensure that structures have adequate resistance and rigidity?
-Engineers ensure adequate resistance and rigidity by selecting appropriate materials and designing dimensions that can withstand expected loads while minimizing deformations.
What role does material science play in different engineering disciplines?
-Material science plays a crucial role in various engineering disciplines, including civil, mechanical, chemical, and industrial engineering, as it informs the selection and application of materials in design and manufacturing processes.
How does the concept of stability in material resistance differ from static stability?
-In material resistance, stability refers to the ability of individual elements to resist deformation under loads, while static stability focuses on the overall configuration of systems and their resistance to changes in position or shape.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
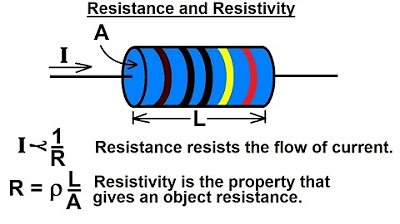
Electrical Engineering: Basic Laws (1 of 31) Resistance and Resistivity

Spenning, strøm og resistans - enkelt forklart

Engineering Ethics Course - Chapter 1 - Part A - General Introduction
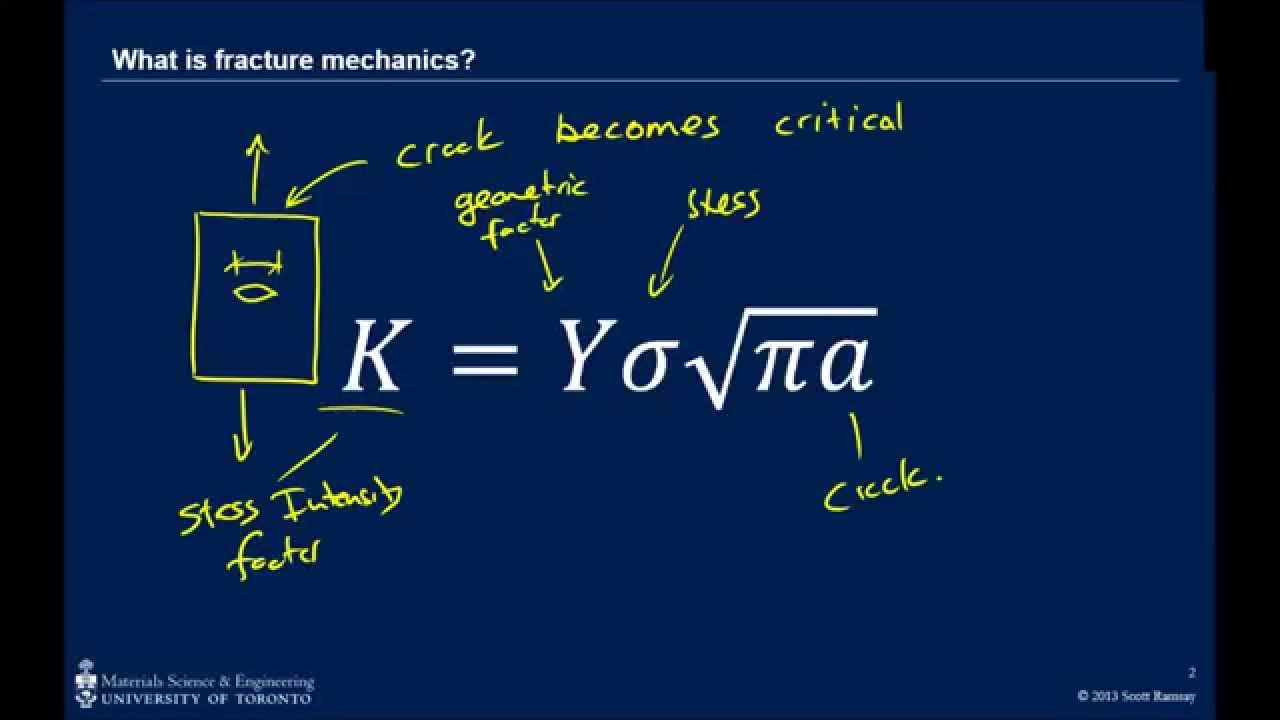
Basic fracture mechanics

Shear Strength of Soils

Konsep Dasar Batang Tekan & Euler Buckling Load | Struktur Baja | Lightboard
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)