Multiple sclerosis - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, pathology
Summary
TLDRThis video explains multiple sclerosis (MS), a demyelinating disease affecting the central nervous system. It describes how the immune system mistakenly attacks myelin, leading to communication breakdown between neurons and various sensory, motor, and cognitive issues. The video outlines the four types of MS, their symptoms, and the autoimmune mechanisms involved. Diagnosis is supported by MRI and cerebrospinal fluid analysis. Although there is no cure, treatments focus on managing relapses and symptoms, highlighting the importance of early intervention and therapies such as immunosuppressants and physical rehabilitation. The video emphasizes the chronic nature of MS and its impact on individuals.
Takeaways
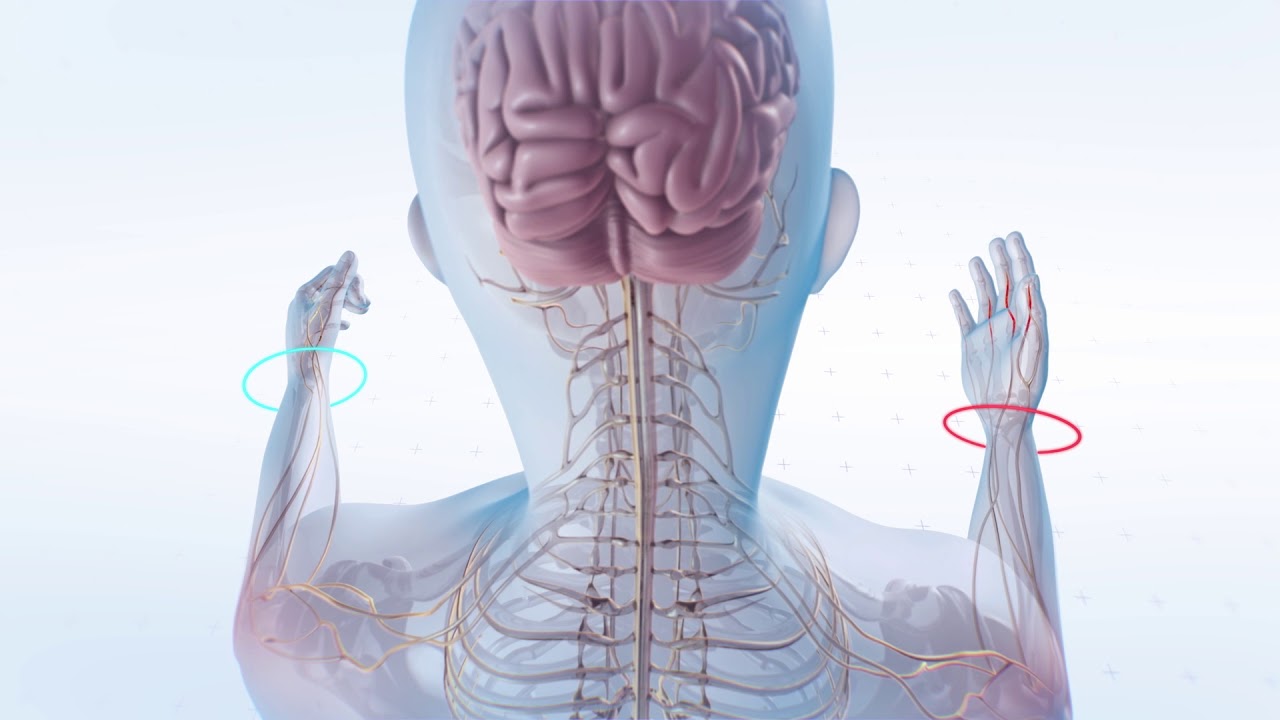
- 🧠 Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a demyelinating disease affecting the central nervous system, leading to communication breakdown between neurons.
- 🔍 Myelin, the protective sheath around neurons, is produced by oligodendrocytes, which are damaged in MS due to immune system attacks.
- 🚨 The immune response in MS is characterized by the inappropriate activation of T cells that attack myelin, leading to inflammation and damage.
- ⚠️ There are four main types of MS: Relapsing-Remitting (RRMS), Secondary Progressive (SPMS), Primary Progressive (PPMS), and Progressive Relapsing (PRMS), each with different patterns of symptoms.
- 📈 RRMS is the most common type, featuring bouts of attacks followed by periods of remission, but often leading to cumulative disability.
- 💔 Symptoms of MS vary widely and can include motor, sensory, and cognitive issues, with a common trio known as Charcot’s neurologic triad: dysarthria, nystagmus, and intention tremor.
- 🔬 Diagnosis of MS typically involves MRI scans showing white matter plaques, cerebrospinal fluid analysis for antibodies, and visual evoked potentials.
- 💊 While there is no cure for MS, treatments like corticosteroids and immunosuppressants can help manage symptoms and reduce the frequency of relapses.
- 🌞 Environmental factors, such as vitamin D deficiency and certain infections, may influence the risk of developing MS, particularly in individuals living further from the equator.
- 📅 MS often affects individuals between the ages of 20 and 40, and early interventions can improve quality of life through therapies addressing various symptoms.
Q & A
What is multiple sclerosis?
-Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a demyelinating disease of the central nervous system that affects the brain and spinal cord, leading to sensory, motor, and cognitive problems.
What role does myelin play in the nervous system?
-Myelin is the protective sheath around axons of neurons, allowing for quick transmission of electrical impulses. In MS, the immune system attacks myelin, disrupting communication between neurons.
How does the immune system contribute to the progression of multiple sclerosis?
-In MS, immune cells like T-cells mistakenly attack myelin. Activated T-cells release cytokines that cause inflammation, leading to damage of oligodendrocytes and subsequent loss of myelin.
What are the four main types of multiple sclerosis?
-The four main types of MS are: 1) Relapsing-Remitting MS (RRMS), 2) Secondary Progressive MS (SPMS), 3) Primary Progressive MS (PPMS), and 4) Progressive Relapsing MS (PRMS).
What is the typical age range for multiple sclerosis onset?
-Multiple sclerosis typically affects individuals between the ages of 20 and 40.
What is Charcot's neurologic triad?
-Charcot's neurologic triad includes dysarthria (unclear speech), nystagmus (rapid involuntary eye movements), and intention tremor (tremors during purposeful movement), which are common symptoms in MS.
How is multiple sclerosis diagnosed?
-Diagnosis of MS is supported by MRI scans showing white matter plaques, analysis of cerebrospinal fluid for high antibody levels, and visual evoked potential tests to measure nervous system response.
What treatment options are available for multiple sclerosis?
-There is no cure for MS, but treatments include corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, plasmapheresis, and therapies to manage symptoms like depression, motor function, and cognitive rehabilitation.
What are some environmental and genetic risk factors for multiple sclerosis?
-Genetic risk factors include being a woman and specific immune-related genes, while environmental factors may involve infections and vitamin D deficiency, particularly in regions with less sunlight.
What happens during a relapse in multiple sclerosis?
-During a relapse, there is an autoimmune attack on oligodendrocytes, leading to inflammation and potentially irreversible damage, which can worsen symptoms and disability over time.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Multiple Sclerosis Nursing | Multiple Sclerosis Treatment, Symptoms, NCLEX Review

What is Multiple Sclerosis (MS)?

How I’m Living My Best Life with Multiple Sclerosis | Robin Brockelsby | TEDxUniversityofNevada

Rebif For Multiple Sclerosis.avi

2022 Pre-RNDS | MOG Antibody Disease (MOGAD)
What is Multiple Sclerosis? An Overview of MS Causes, Symptoms, Treatments & Research
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)