Connecting Networks
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into Google Cloud's network connectivity options, focusing on VPC peering, Cloud VPN, and Cloud Interconnect. It explains how VPC peering allows private connectivity between VPC networks, while Cloud VPN securely connects on-premises networks via encrypted tunnels, offering options for classic and high availability configurations. The video also outlines Cloud Interconnect, which provides dedicated and partner interconnect options for robust network connections. Key features such as SLA requirements, routing configurations, and MTU considerations are highlighted, along with best practices for setting up reliable connections across diverse cloud architectures.
Takeaways
- 🌐 VPC Peering allows private connectivity between two VPC networks, even if they are in different projects or organizations, provided their subnet ranges do not overlap.
- 🔐 Cloud VPN creates secure connections between on-premises networks and Google Cloud VPC networks through IPsec VPN tunnels, ensuring data encryption during transmission.
- 📈 Cloud VPN offers two configurations: Classic VPN with an SLA of 99.9% and HA VPN with an SLA of 99.99%, depending on your service availability needs.
- 📊 The Classic VPN gateways utilize a single interface and IP address, while HA VPN gateways have two interfaces and IP addresses for high availability.
- 🚧 When configuring Cloud VPN, it's crucial to consider the maximum transmission unit (MTU) of 1,460 bytes for on-premises VPN gateways due to packet encapsulation.
- 💡 HA VPN connections require dynamic routing and can be set up with multiple tunnels for increased reliability and performance.
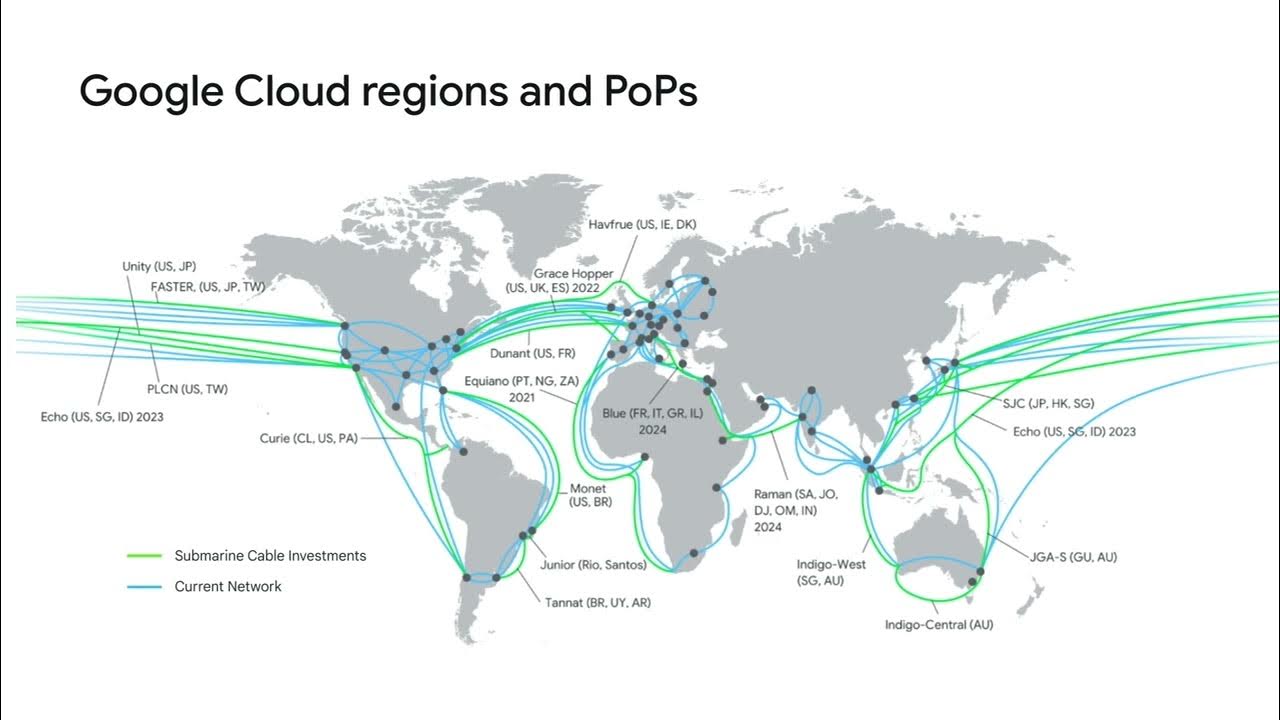
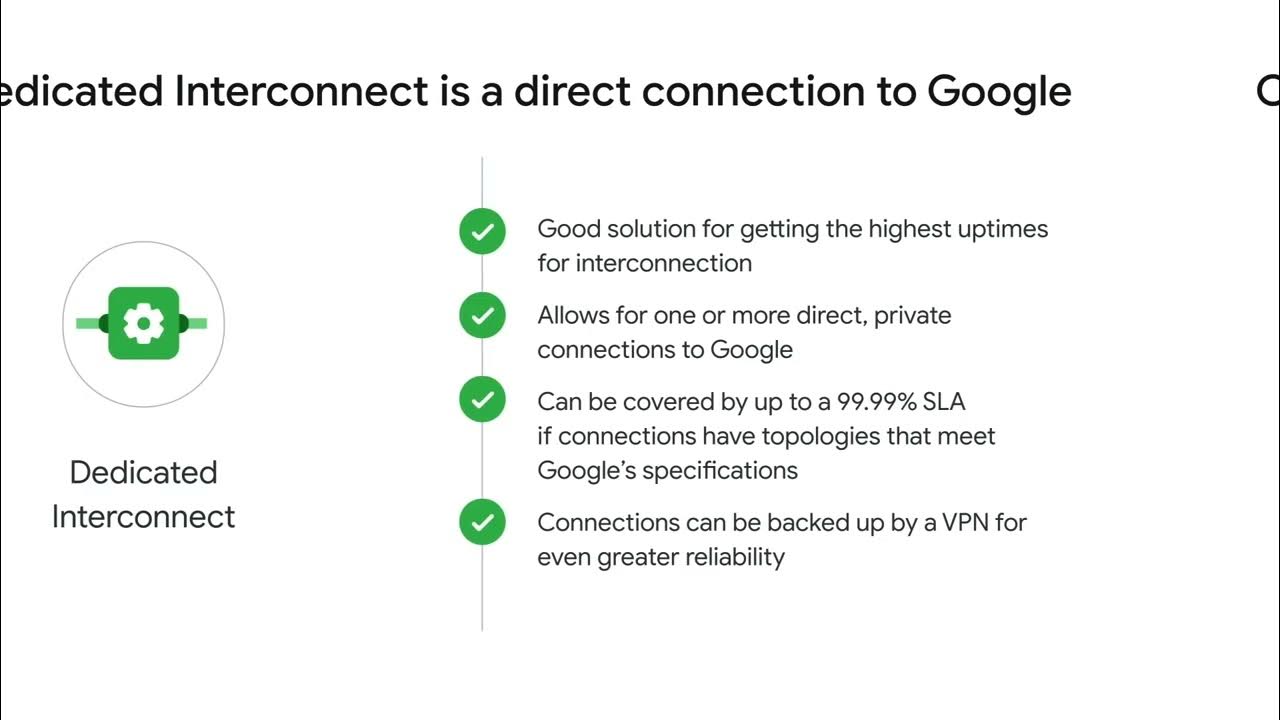
- 🌉 Cloud Interconnect provides dedicated or partner connections for on-premises networks to extend into Google Cloud, with high bandwidth options available.
- 🔄 Dedicated Interconnect requires a direct connection to a co-location facility, allowing for up to 200 gigabits per second of bandwidth.
- 📡 Partner Interconnect is suitable for lower bandwidth requirements and connects through a service provider, offering flexibility for various data needs.
- 🔧 Cloud Routers are necessary for managing dynamic routing in Cloud VPN, facilitating seamless updates and route exchanges between networks.
Q & A
What are the primary products discussed in the video related to Google Cloud's network connectivity?
-The primary products discussed are VPC peering, Cloud VPN, and Cloud Interconnect.
What is VPC peering and what are its requirements?
-VPC peering allows private connectivity between two VPC networks, regardless of project or organization. The subnet ranges of the networks must not overlap for the connection to be established.
How do firewall rules impact VPC peering connections?
-Each VPC network has firewall rules that define what traffic is allowed or denied between the networks, which must be configured to permit the desired communication.
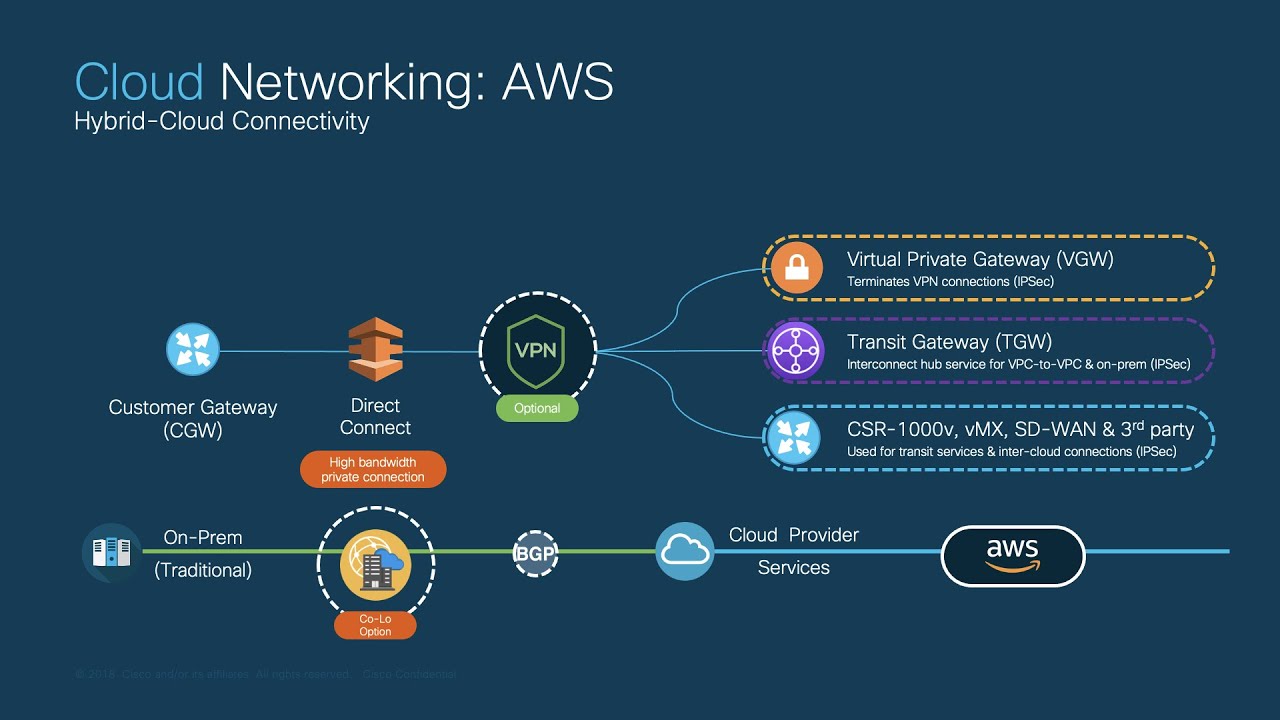
What is the function of Cloud VPN?
-Cloud VPN securely connects on-premises networks to Google Cloud VPC networks through IPsec VPN tunnels, encrypting traffic to protect data over the public Internet.
What are the differences between Classic VPN and HA VPN?
-Classic VPN features a single interface and external IP address with a 99.9% SLA, while HA VPN has two interfaces, two external IPs, and offers a higher SLA of 99.99%.
What are the limitations of Cloud VPN regarding static routes?
-Static routes are only supported by Classic VPN, whereas HA VPN requires the use of dynamic routing.
What does the maximum transmission unit (MTU) limitation imply for Cloud VPN?
-The MTU for on-premises VPN gateways cannot exceed 1,460 bytes due to encryption and packet encapsulation requirements, impacting the size of packets that can be transmitted.
What is Cloud Interconnect and what options does it provide?
-Cloud Interconnect extends on-premises networks and offers two options: Dedicated Interconnect for direct connections with high bandwidth, and Partner Interconnect, which connects through a service provider for lower bandwidth needs.
How does BGP play a role in Cloud Routers for dynamic routing?
-BGP allows for automatic updates and exchanges of routes without needing to change tunnel configurations, facilitating seamless communication between new subnets in the VPC network and peer networks.
What must be configured to use Dedicated Interconnect?
-To use Dedicated Interconnect, a cross connect must be provisioned between the Google network and the on-premises router in a common co-location facility.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)