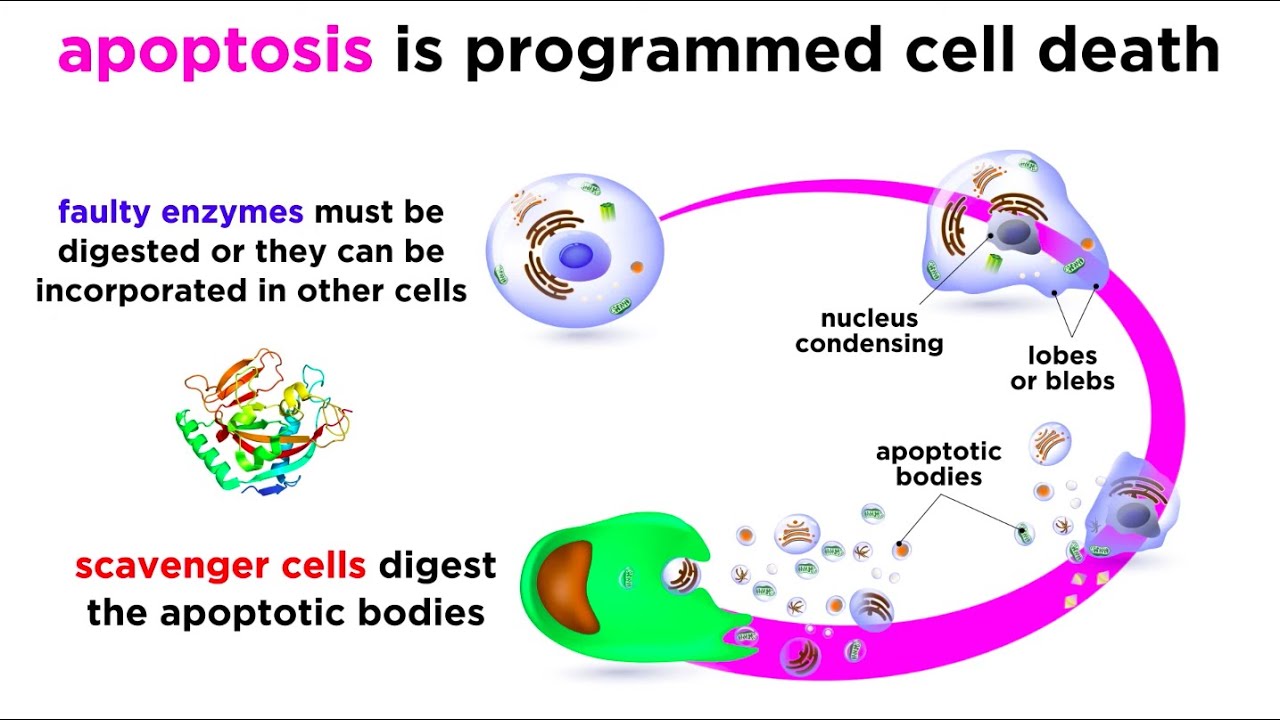
APOPTOSIS (ANIMASI 3D)
Summary
TLDRThe video explains apoptosis, a crucial cellular process that enables programmed cell death essential for growth and development. It highlights two pathways of apoptosis: the extrinsic pathway, initiated by external signals such as T-lymphocytes, and the intrinsic pathway, activated by internal signals related to mitochondrial health. The video also discusses the role of various proteins in regulating apoptosis and how abnormalities in these processes can lead to diseases, such as cancer. Understanding these pathways could lead to better therapeutic strategies targeting apoptosis.
Takeaways
- 🧬 Apoptosis is a vital cellular process that allows programmed cell death, playing an essential role in growth and development.
- 👶 In fetal development, apoptosis helps shape the formation of fingers by eliminating cells between them.
- ⚠️ Apoptosis is crucial for removing damaged cells, preventing pathological processes caused by irreparable cellular DNA.
- 🛡️ The process of apoptosis is initiated by proteins known as caspases, which must be activated for apoptosis to occur.
- 🔗 There are two main pathways for activating apoptosis: the extrinsic pathway and the intrinsic pathway.
- 🌍 The extrinsic pathway is initiated by signals from outside the cell, often through interactions with T-lymphocytes and their Fas ligand.
- 📉 The intrinsic pathway is triggered by internal signals, regulated by the balance of pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins in the mitochondria.
- ⚖️ Proteins like Bcl-2 and Myc help maintain cell survival by blocking pro-apoptotic signals, but they can be inhibited if the cell is damaged.
- 💥 When pro-apoptotic proteins are activated, they can cause mitochondrial membranes to become permeable, leading to the release of cytochrome c.
- 🎯 Understanding the roles of extrinsic and intrinsic pathways in apoptosis allows for better therapeutic strategies to regulate cell death.
Q & A
What is apoptosis?
-Apoptosis is a programmed cell death process that allows cells to die in a controlled manner, playing a crucial role in development and tissue homeostasis.
How does apoptosis contribute to embryonic development?
-During embryonic development, apoptosis helps in shaping tissues by removing unnecessary cells, such as the cells between the fingers, leading to the formation of distinct digits.
What are the two main pathways of apoptosis?
-The two main pathways of apoptosis are the extrinsic pathway, initiated by external signals, and the intrinsic pathway, triggered by internal cellular signals.
What triggers the extrinsic pathway of apoptosis?
-The extrinsic pathway is typically initiated by T-lymphocytes through the binding of the Fas ligand to the Fas receptor on the target cell's surface.
What is the role of proteins in the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis?
-The intrinsic pathway is regulated by a balance of pro-apoptotic proteins, such as Bax, and anti-apoptotic proteins, such as Bcl-2, which determine whether a cell undergoes apoptosis based on survival signals.
What happens when the balance of pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins is disrupted?
-If the balance is disrupted, it can lead to either excessive cell death or the survival of damaged cells, contributing to pathological conditions like cancer.
What is the function of cytochrome c in apoptosis?
-When released from the mitochondria, cytochrome c binds to Apaf-1 to form a complex that activates caspases, leading to the execution phase of apoptosis.
How do cancer cells evade apoptosis?
-Cancer cells often evade apoptosis by upregulating anti-apoptotic proteins or downregulating pro-apoptotic proteins, allowing them to survive and replicate despite DNA damage.
Why is understanding apoptosis important for therapy development?
-Understanding the mechanisms of apoptosis, including the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways, allows for the design of targeted therapies that can regulate apoptosis in diseases like cancer.
What are potential therapeutic implications of targeting apoptosis pathways?
-Targeting apoptosis pathways could lead to the development of treatments that enhance the death of cancer cells or protect normal cells from unintended apoptosis during treatment.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)