CAPÍTULO 2 Robbins: Mecanismos de lesión celular (Estrés oxidativo, daño de membrana, 🧬 y proteínas)
Summary
TLDRThe video explores cellular injury mechanisms, focusing on the consequences of ATP depletion and mitochondrial dysfunction. The speaker explains how reduced ATP levels lead to impaired energy-dependent functions, resulting in reversible or irreversible cell injury and necrosis. Mitochondrial damage triggers the release of apoptosis-inducing proteins, while increased calcium ions and reactive oxygen species contribute to further cellular damage. The video highlights the critical role of lipid peroxidation, misfolded proteins, and DNA damage in the process of cell death, ultimately leading to programmed cell death (apoptosis).
Takeaways
- 😀 Energy depletion, especially a decrease in ATP levels, leads to cellular dysfunction and may cause reversible or irreversible damage.
- 😀 Mitochondrial damage contributes to ATP depletion and can also release apoptosis-inducing proteins like cytochrome c.
- 😀 A disruption in cellular membrane functions, including loss of permeability, can lead to harmful ion imbalances inside the cell.
- 😀 The accumulation of calcium ions within the cell triggers the activation of enzymes that further damage cellular structures.
- 😀 Reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulate, resulting in oxidative stress and peroxidation of lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
- 😀 Damaged proteins that cannot fold properly and DNA damage contribute to irreversible cellular dysfunction.
- 😀 Apoptosis (programmed cell death) can be induced as a result of mitochondrial damage and protein misfolding.
- 😀 Cellular injury often results in necrosis if the damage is too severe or not corrected in time.
- 😀 ATP-dependent cellular functions fail due to energy depletion, leading to cellular death if not reversed.
- 😀 Key processes like biosynthesis and degradation are impaired when ATP levels are low, contributing to cellular breakdown.
- 😀 The video concludes with a summary of these mechanisms, encouraging the audience to comment or ask questions for further understanding.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video script?
-The main focus of the video script is on cellular injury, its mechanisms, and the processes that lead to cell death, such as necrosis and apoptosis, primarily due to ATP depletion and mitochondrial damage.
How does ATP depletion affect cellular functions?
-ATP depletion leads to the failure of energy-dependent functions within the cell, which can result in reversible damage if corrected, or irreversible damage leading to necrosis if not addressed.
What role does mitochondrial damage play in cell death?
-Mitochondrial damage can release apoptotic proteins, such as cytochrome c, that trigger programmed cell death (apoptosis), further exacerbating cellular damage.
What happens when calcium ions accumulate inside the cell?
-Excessive calcium influx activates calcium-dependent enzymes that cause damage, such as lipid peroxidation and protein dysfunction, ultimately contributing to cellular injury.
What are reactive oxygen species (ROS) and how do they impact cells?
-Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive molecules that accumulate in the cell and modify proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, causing oxidative stress and contributing to cell damage and dysfunction.
How does protein misfolding contribute to cellular injury?
-Protein misfolding can lead to dysfunctional proteins that cannot perform their intended tasks, which contributes to cellular damage and can trigger apoptosis if not repaired.
What is lipid peroxidation and how does it relate to cellular damage?
-Lipid peroxidation is the oxidative degradation of lipids, which can damage cellular membranes and other structures, leading to loss of cell integrity and function.
What is necrosis, and how does it relate to ATP depletion?
-Necrosis is the irreversible death of a cell due to severe injury. ATP depletion is a key factor in necrosis, as it leads to a failure in cellular functions and energy-dependent processes.
How does the influx of calcium ions affect enzyme activation?
-Increased calcium ion concentration activates enzymes such as phospholipases and proteases, which then break down cellular structures like lipids and proteins, contributing to cell damage.
What are the key steps in the progression of cellular injury to cell death?
-The key steps include ATP depletion, mitochondrial damage, calcium ion influx, ROS accumulation, lipid peroxidation, protein misfolding, and DNA damage, all leading to either reversible damage or the activation of apoptosis for irreversible damage.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Cell Injury and Cell Death. Causes, mechanism and different types of cell injury - part I

Degenerações - Conceito e Classificação

Does Red Light Therapy stimulate Mitochondria? Not always...
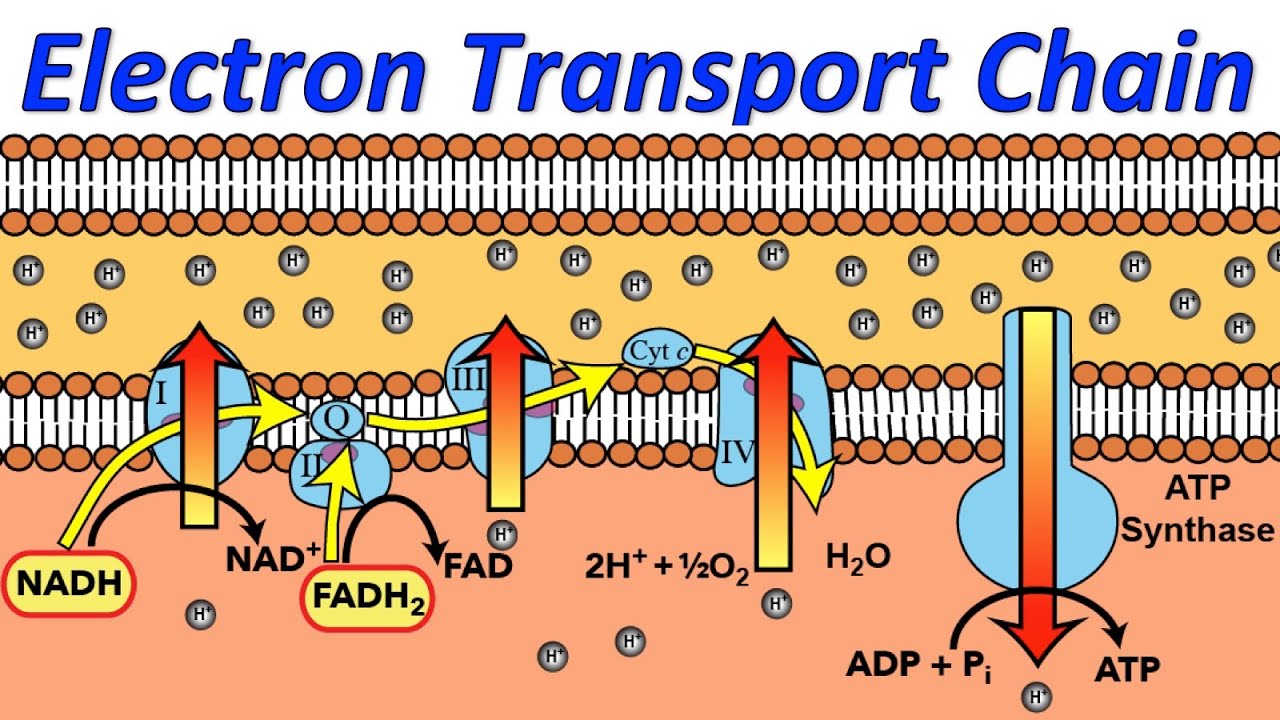
Mysteries of the Electron Transport Chain, Revealed in Rap!

Respiración celular | 4 | Cadena transportadora de electrones

MITOCÔNDRIAS E ATP - Prof. Paulo Jubilut
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)