Aula 7 Leitura e Interpretação de placas de motores
Summary
TLDRThis video transcript details the interpretation of electric motor nameplates, focusing on how to identify and analyze various specifications. The speaker explains essential concepts such as motor type, voltage, nominal and starting current calculations, protection grades, service factors, speed determination, insulation classes, and construction forms. By providing practical examples and calculations, the speaker emphasizes the importance of understanding these parameters for effective motor selection and operation. This informative guide serves as a valuable resource for those seeking to deepen their knowledge in electrical engineering.
Takeaways
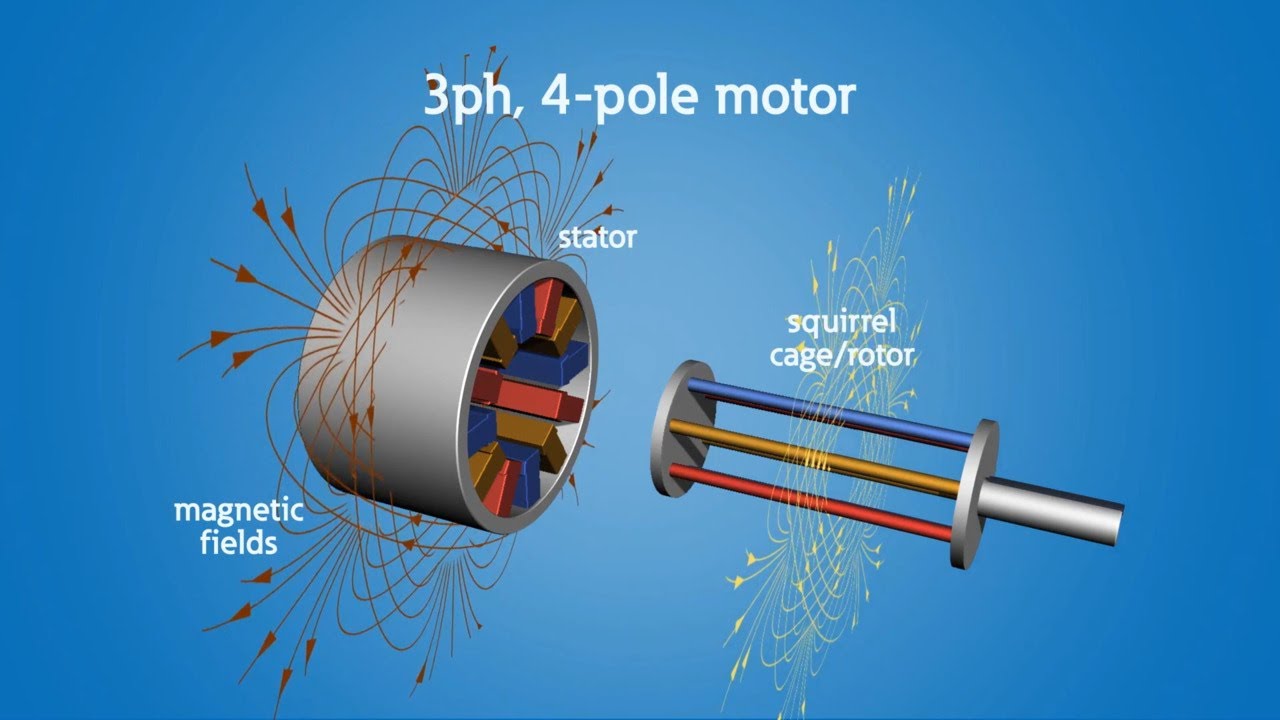
- 🔧 The motor is identified as a three-phase motor based on its nameplate information.
- ⚡ The motor has a single voltage rating, indicating it cannot be operated in star-delta configurations.
- 📊 Two RPM values are provided (10000 and 3600), suggesting that the lower value is half of the higher, confirming its classification under Lander type.
- 📈 The nominal current is specified as 3.5 Amperes, while the calculated starting current can reach up to 22.75 Amperes.
- 🛡️ The motor has an IP54 rating, indicating protection against dust and water splashes from all directions.
- 🔍 The motor is categorized as 'H,' suitable for high-torque applications and capable of handling occasional overloads.
- 🌡️ The insulation class is 'B,' allowing for operation at temperatures up to 130°C, with an ambient temperature limit of 42°C.
- 🔄 The service factor of 1.1 permits a continuous increase of 10% in nominal current without risking damage to the motor.
- ⚙️ The synchronous speed and slip calculations confirm that both provided RPM values are synchronous, with asynchronous speeds of 1728 RPM and 3456 RPM.
- 🔩 The motor uses two bearings: 324 on the coupling side and 334 on the opposite side, indicating the structure's durability.
- 🏗️ The motor's construction type is classified as 'B5,' based on the position of the terminal box and the shaft.
- ⏱️ Operating under service regime 'S2' indicates the motor is designed for limited-time operation.
Q & A
What type of motor is discussed in the transcript?
-The motor discussed is a three-phase asynchronous motor, specifically identified as a Lander model.
How is the starting current calculated for the motor?
-The starting current is calculated by multiplying the nominal current by the starting current factor (IP). For this motor, the starting current is 3.5 A multiplied by 6.5, resulting in 22.75 A.
What does the IP rating of IP54 indicate about the motor?
-The IP54 rating indicates that the motor is protected against dust accumulation (5) and against water splashes from all directions (4).
What is the maximum internal temperature that the motor can handle?
-The maximum internal temperature that the motor can handle is 130°C, according to its insulation class B.
What does a service factor of 1.1 signify?
-A service factor of 1.1 means that the motor can operate continuously with a current or power increase of up to 10% above its nominal rating without sustaining damage.
How can one determine if the given RPM values are synchronous or asynchronous?
-To determine if the RPM values are synchronous, you can use the formula 7200 divided by the number of poles. If the result is an integer, the RPM is synchronous; if not, it can be rounded to the nearest even number to find the corresponding synchronous speed.
What are the calculated asynchronous speeds for the motor based on a 4% slip?
-The calculated asynchronous speeds for the motor are 1728 RPM and 3456 RPM, derived from synchronous speeds of 1800 RPM and 3600 RPM, respectively.
What do the rolling bearing codes '324' and '334' refer to?
-The rolling bearing code '324' refers to the bearing on the side of the coupling (LA), while '334' refers to the bearing on the opposite side of the coupling (LOA).
What is the significance of the motor's structural form B5?
-The structural form B5 indicates that the connection box of the motor is positioned on top, regardless of the direction the shaft is oriented.
What does the service regime S2 mean for the motor's operation?
-The service regime S2 indicates that the motor is designed for limited time operation, meaning it can run continuously for a specified duration but is not intended for indefinite operation.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)