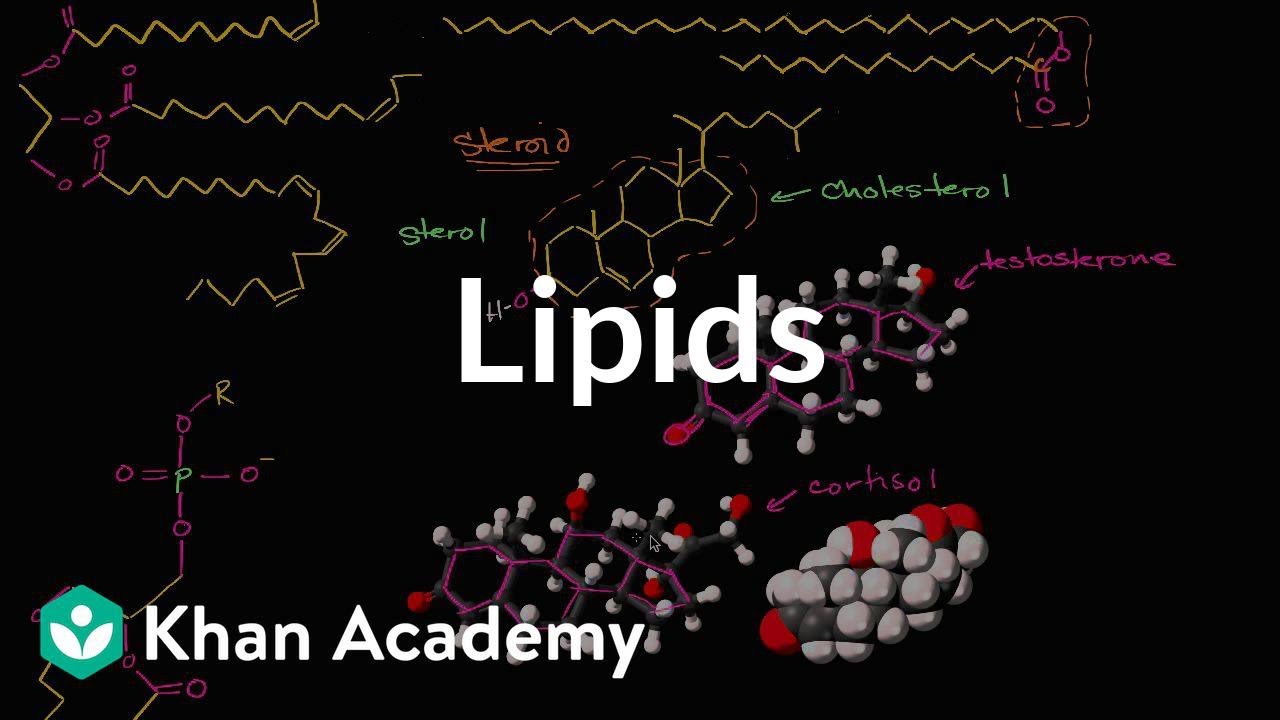
Lipids - General Biology (Updated)
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces lipids as key macromolecules, highlighting their waxy, greasy consistency and hydrophobic properties. It explains three main types: triglycerides, which serve as long-term energy storage; phospholipids, crucial for forming cell membranes with their dual nature of hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails; and steroids, including cholesterol and hormones that regulate cellular functions. The video emphasizes the essential roles lipids play in energy storage, structural integrity of cells, and communication within biological systems.
Takeaways
- 😀 Lipids are generally waxy or greasy and are hydrophobic, meaning they repel water.
- 🧪 The scientific term for lipids' water-repelling nature is 'hydrophobic.'
- 🍟 Common examples of lipids include oils and greases, such as those found on fried foods.
- 🔋 Triglycerides, the most common type of lipid, are essential for long-term energy storage.
- 🧬 Triglycerides consist of a glycerol molecule bonded to three fatty acids.
- ⚖️ Fatty acids can be saturated (solid at room temperature) or unsaturated (liquid at room temperature).
- 🌿 Phospholipids are the primary components of cell membranes, featuring a hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic tails.
- 💧 The unique structure of phospholipids allows them to form a lipid bilayer in cell membranes.
- 💊 Steroids, including cholesterol and hormones like testosterone, serve as important chemical messengers in the body.
- 📈 Steroids can easily diffuse into cells and regulate gene expression, playing crucial roles in various biological processes.
Q & A
What are lipids and how are they generally characterized?
-Lipids are macromolecules that have a waxy or greasy consistency. They are characterized by their hydrophobic nature, meaning they repel water.
What does the term 'hydrophobic' mean in relation to lipids?
-Hydrophobic refers to the fear of water; in the context of lipids, it means that they do not mix with water, as seen when oil floats on water.
What are triglycerides and what is their primary function?
-Triglycerides are a type of lipid composed of glycerol and three fatty acids. Their primary function is long-term energy storage in the body.
What distinguishes saturated fatty acids from unsaturated fatty acids?
-Saturated fatty acids have straight chains of carbon and hydrogen and are solid at room temperature (e.g., butter), while unsaturated fatty acids contain at least one double bond that causes a bend in the chain, making them liquid at room temperature (e.g., olive oil).
How do phospholipids differ from triglycerides?
-Phospholipids are composed of a glycerol, two fatty acid tails, and a phosphate group, whereas triglycerides consist of glycerol and three fatty acids. Phospholipids are crucial for forming cell membranes.
What is the structure of a phospholipid, and what are its characteristics?
-A phospholipid has a hydrophilic phosphate group head that attracts water and two hydrophobic fatty acid tails that repel water, allowing it to form bilayers in cell membranes.
What role does cholesterol play in the body?
-Cholesterol is a type of steroid that helps maintain the fluidity of cell membranes and serves as a precursor for lipid-based hormones.
What are steroid hormones, and how do they interact with cells?
-Steroid hormones, such as testosterone and cortisol, are lipid-based and can easily diffuse through cell membranes to influence gene expression and cellular responses.
Can you give examples of how lipids are used in animals?
-In animals, lipids serve various functions such as energy storage (e.g., blubber in seals), waterproofing (e.g., oils in duck feathers), and hormone production (e.g., steroid hormones).
What are the three main types of lipids discussed in the video?
-The three main types of lipids discussed are triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)