NUMERICAL CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS | PLOIDY
Summary
TLDRThis video explores numerical chromosomal aberration, focusing on ploidy variations such as euploidy and aneuploidy. It explains how euploidy involves complete sets of chromosomes, including autopolyploidy and allopolyploidy, while aneuploidy refers to the loss or gain of individual chromosomes. The significance of ploidy is highlighted in plant breeding and horticulture, emphasizing its role in creating larger fruits and flowers, evolving new species, and enhancing disease resistance. The benefits of polyploid varieties, like apples and watermelons, are also discussed, showcasing their economic importance and nutritional advantages.
Takeaways
- 😀 Each organism has a specific number of chromosomes in its somatic cells, usually found in pairs.
- 🔍 During gamete formation, the chromosome number is halved, leading to haploid cells.
- 📊 Numerical chromosomal aberrations, or ploidy, involve variations in chromosome numbers, categorized into euploidy and aneuploidy.
- 🌱 Euploidy refers to changes in complete sets of chromosomes and includes types like diploidy and polyploidy.
- 🔗 Polyploidy can be further divided into autopolyploidy (additional sets from the same species) and allopolyploidy (additional sets from different species).
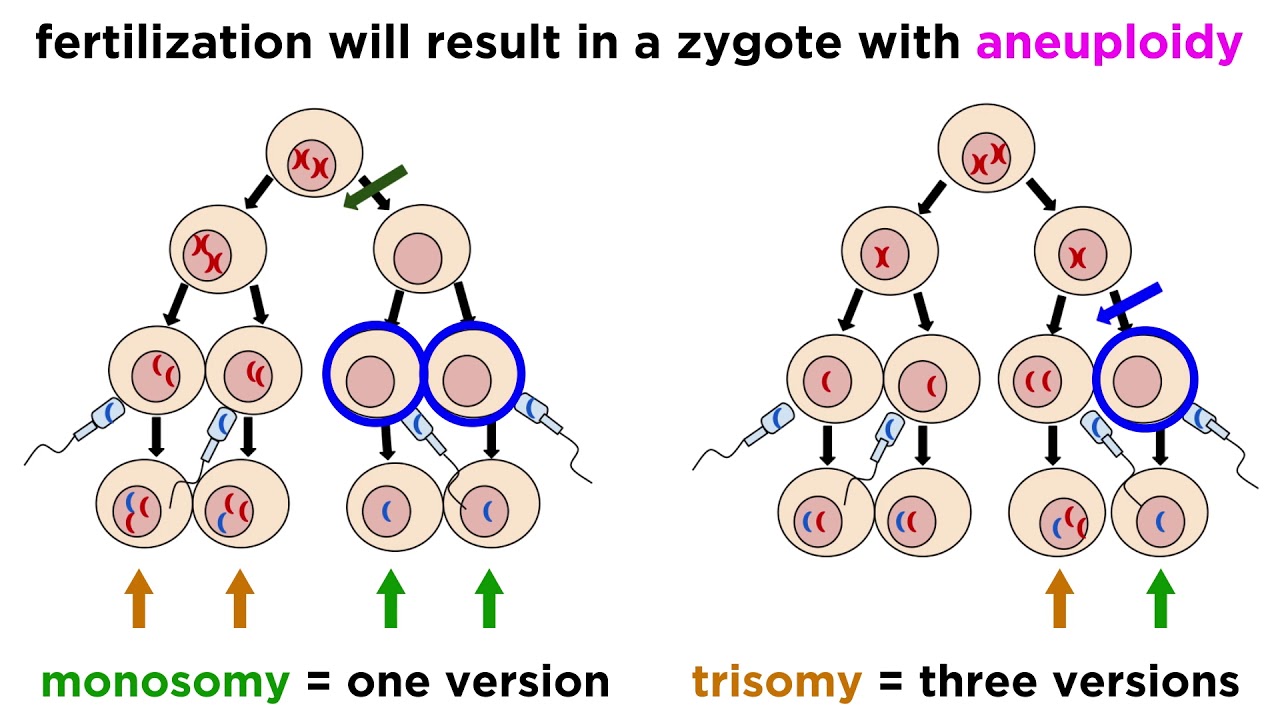
- 🧬 Aneuploidy involves the gain or loss of individual chromosomes and can be classified into hypoploidy and hyperploidy.
- ⚠️ Hypoploidy includes conditions like monosomy (loss of one chromosome) and nullisomy (loss of a homologous pair).
- 📈 Hyperploidy involves the addition of chromosomes, including trisomy (one extra chromosome) and tetrasomy (two extra chromosomes).
- 🌼 Polyploidy plays a significant role in plant breeding, often resulting in larger flowers and fruits.
- 🍏 Nutritional benefits of polyploid crops include higher vitamin content, such as ascorbic acid in tetraploid cabbages and vitamin A in corn.
Q & A
What are numerical chromosomal aberrations?
-Numerical chromosomal aberrations refer to variations in the number of chromosomes within an organism's somatic cells, affecting the diploid set.
What is the difference between euploidy and aneuploidy?
-Euploidy involves a variation in the complete set of chromosomes, while aneuploidy involves changes in the number of individual chromosomes within that set.
What are the two main types of euploidy?
-The two main types of euploidy are diploidy and polyploidy.
What is polyploidy?
-Polyploidy is the condition where an organism has more than two complete sets of chromosomes, which can enhance certain traits in plants and some animals.
What distinguishes autotetraploidy from allopolyploidy?
-Autotetraploidy results from the duplication of an organism's own haploid genome, while allopolyploidy results from the combination of haploid sets from different species.
Can you give examples of organisms that exhibit autotetraploidy?
-Examples of autotetraploid organisms include watermelons, grapes, and bananas.
What is hypoploidy?
-Hypoploidy refers to a condition where there is a decrease in one or two chromosomes from the diploid set, leading to conditions like monosomy or nullisomy.
What is hyperploidy?
-Hyperploidy is characterized by the addition of one or two chromosomes to the diploid set, resulting in conditions like trisomy and tetrasomy.
How does polyploidy contribute to plant breeding?
-Polyploidy can lead to larger flowers and fruits, greater vigor, and increased resistance to diseases, making it significant in horticulture and agriculture.
What congenital diseases can be caused by aneuploidy in humans?
-Aneuploidy can lead to various congenital diseases, including Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and Klinefelter syndrome, which result from chromosomal number abnormalities.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)