6 Electrical Substation Bus Schemes Explained
Summary
TLDRThe video explains the critical role of electrical substations as junctions for multiple transmission lines, emphasizing the importance of various bus schemes. It outlines six common configurations: Single Bus, Main and Transfer Bus, Double Bus Double Breaker, Double Bus Single Breaker, Ring Bus, and Breaker and Half. Each scheme has its pros and cons regarding reliability, maintenance flexibility, and complexity. The choice of bus scheme significantly impacts operational efficiency and reliability, making careful planning essential to prevent total outages and ensure continuous service.
Takeaways
- 🔌 A substation is a junction point where multiple transmission lines converge, often involving many lines terminating.
- ⚙️ The bus scheme in a substation includes overhead bus bars and switching equipment like circuit breakers and isolators, crucial for operational reliability.
- 🔒 Total shutdown of a substation for maintenance or fault is to be avoided, especially in critical transmission substations.
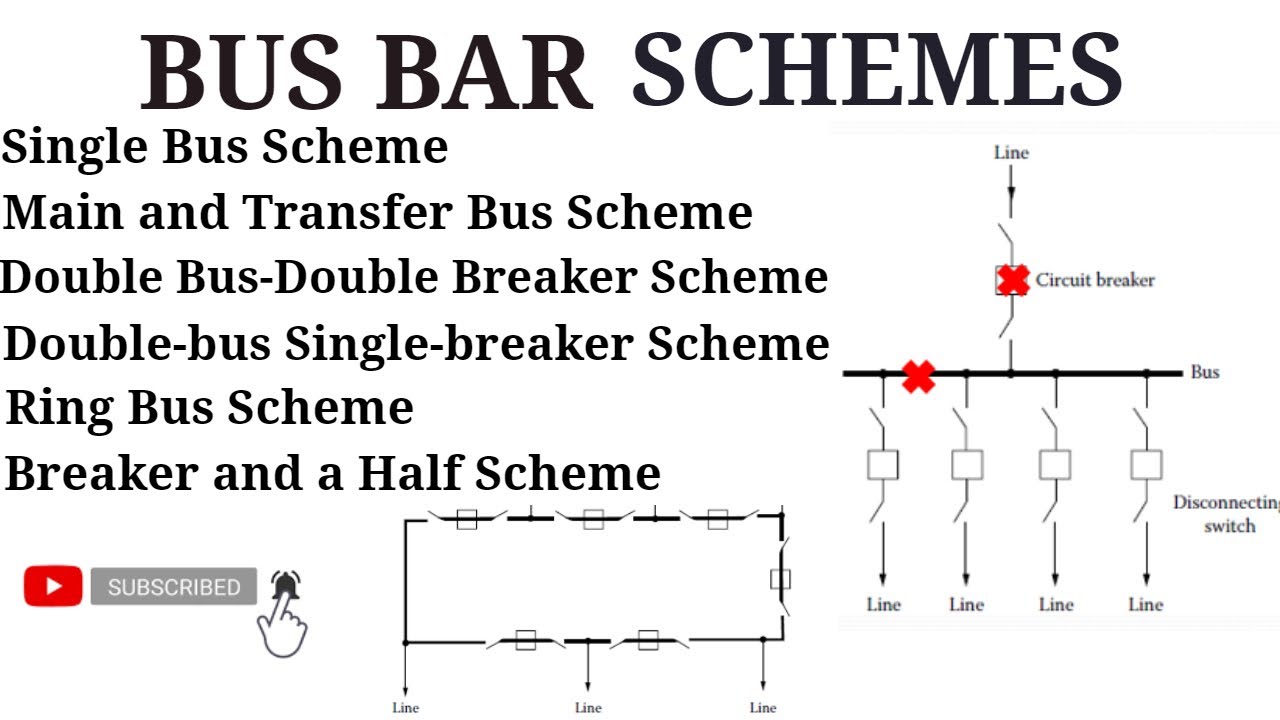
- ⚡ There are six common substation bus schemes, each with its advantages and disadvantages that technicians should understand.
- 🔄 The single bus configuration is the simplest and least expensive, but not very reliable, requiring complete shutdown for maintenance.
- 🔗 The main bus and transfer bus arrangement enhances reliability by allowing maintenance without complete shutdown through circuit breaker management.
- 📊 Double bus double breaker configuration offers high reliability, allowing maintenance of circuits without service interruption, but requires more equipment.
- ⚙️ Double bus single breaker schemes provide flexibility, allowing circuit maintenance with isolation, but are more expensive than single bus configurations.
- 🔄 The ring bus configuration allows for high operational flexibility and reliability, enabling maintenance without service interruption, though careful planning is needed for expansion.
- 🔧 The breaker and a half configuration allows for the easy expansion of substations while maintaining service continuity, offering flexibility and reliability.
Q & A
What is the primary function of an electrical substation?
-An electrical substation serves as a junction point where two or more transmission lines terminate, facilitating the distribution of electricity.
What are the key components of a substation bus scheme?
-The substation bus scheme includes overhead bus bars and associated switching equipment such as circuit breakers and isolators.
Why is it important to avoid a total shutdown of a substation?
-Avoiding a total shutdown is crucial because it prevents complete service disruption to all lines connected to the substation during maintenance or faults.
What is the simplest substation configuration?
-The simplest configuration is the single bus scheme, where all circuits connect to a single bus, but it is not considered reliable for critical applications.
How does the main bus and transfer bus arrangement improve reliability?
-The main bus and transfer bus arrangement allows for maintenance on circuit breakers without shutting down the entire system by transferring circuits to an energized transfer bus.
What advantage does the double bus double breaker configuration provide?
-This configuration allows any circuit to be removed for maintenance without interrupting service, as both buses are normally energized.
What is the disadvantage of the ring bus configuration?
-The main disadvantage of the ring bus system is that if a fault occurs, it can split the ring into two isolated sections, which may not have the correct source and load circuit combinations.
Describe the breaker and half configuration.
-The breaker and half configuration uses two main buses and three breakers connected between them, allowing for maintenance without interrupting service to other circuits.
Why are single bus configurations not recommended for critical substations?
-Single bus configurations lack reliability and can lead to complete outages if a fault occurs, making them unsuitable for critical transmission substations.
How can substation bus schemes be expanded?
-Substation bus schemes can be expanded by adding more buses or switching equipment, allowing for increased capacity and flexibility in operations.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
All Bus Bar Schemes in Substation | Electrical power system | With Advantages and Disadvantages

What are TRANSMISSION LINES? Because the TRANSMISSION LINES operate at HIGH VOLTAGE.

What is Electrical Substation

TRANSMISSÃO SINÁPTICA ELÉTRICA: SINAPSE ELÉTRICA | MK Fisiologia

What is Substation | Function of Substation | Hindi

Why 3 Phase Power? Why not 6 or 12?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)