Soil Profile and Soil Horizons
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the essential role of soil in supporting life, highlighting its composition of 45% minerals, 5% organic matter, 25% water, and 25% air. It explores the soil profile, which includes distinct layers known as horizons: O (litter), A (topsoil), E (eluviation), B (subsoil), C (parent material), and R (bedrock). Each layer has unique properties, contributing to soil's fertility and health. The video emphasizes the importance of decomposers in creating nutrient-rich humus and how soil layers interact with water movement. It invites viewers to learn more through additional resources on soil.
Takeaways
- 🌱 Soil is essential for plant growth, supporting grass and trees, and is the foundation for food production.
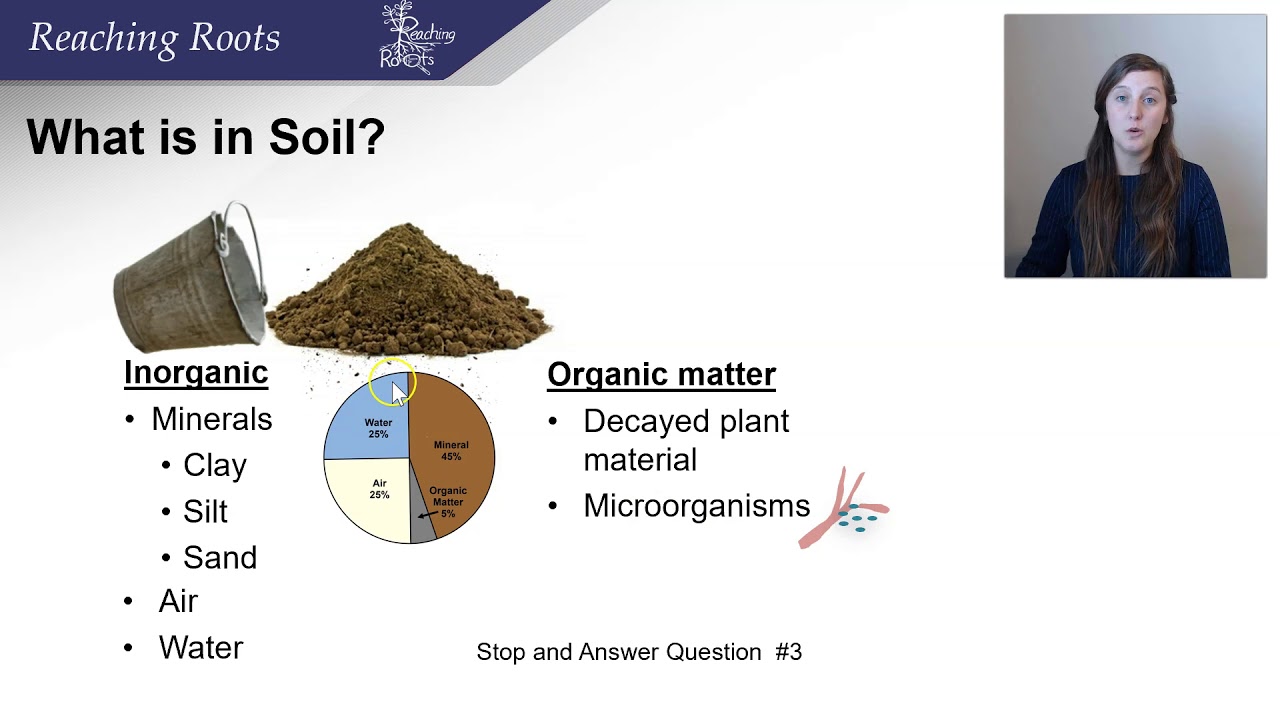
- 🔬 Soil composition consists of approximately 45% minerals, 5% organic matter, 25% water, and 25% air.
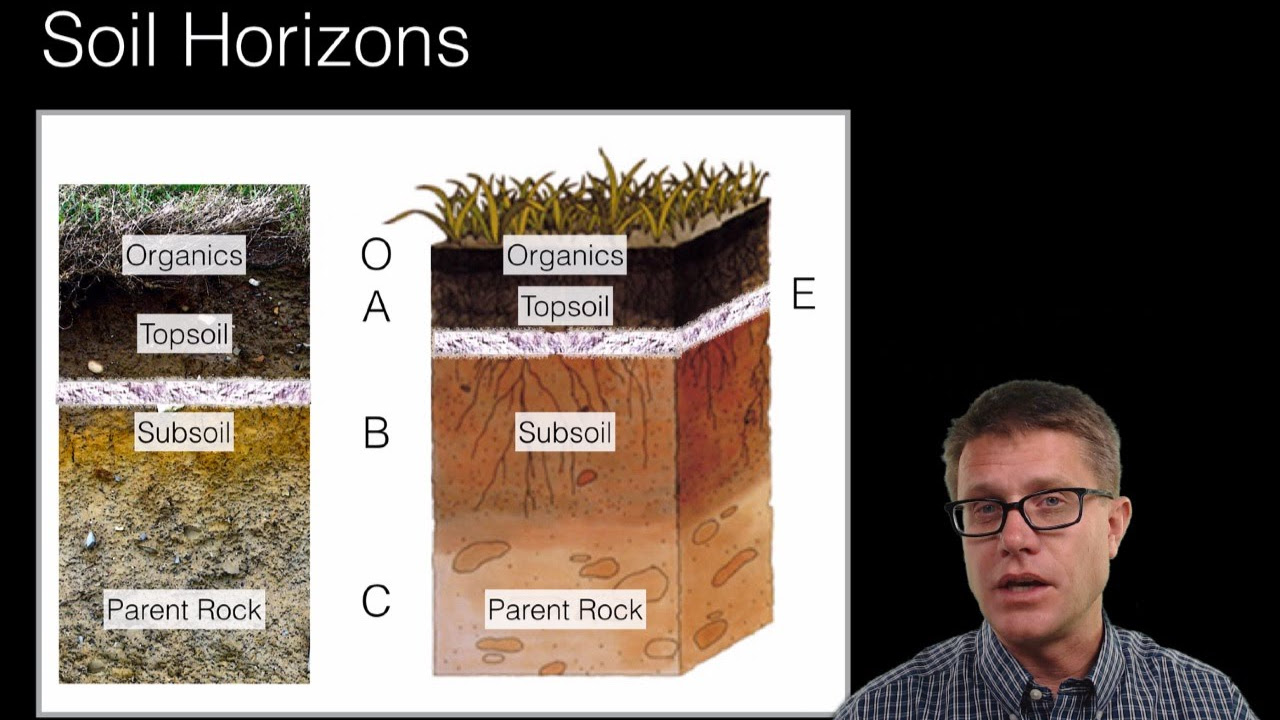
- 📏 A soil profile displays vertical layers of soil, which are referred to as soil horizons.
- 📖 The O horizon, or litter layer, contains dead organic material such as leaves and fallen trees.
- 🌍 The A horizon, or topsoil, is rich in organic matter and is where decomposers break down plants and animals.
- 💧 The E horizon, or eluviation layer, is characterized by the leaching of minerals and can result in sand and silt concentration.
- 🏗️ Horizon B, or subsoil, is often lighter in color and serves as a zone of accumulation for clay and other materials.
- 🪨 The C horizon consists of parent material, which includes rock fragments that break down to form soil.
- 🪨 Horizon R is the bedrock, comprising solid rock such as granite or limestone, forming the base material for soil.
- 📺 For more information on soil, additional educational resources are available through the playlist provided.
Q & A
What is the composition of soil?
-Soil is composed of 45% minerals, 5% organic matter, 25% water, and 25% air.
What does the soil profile represent?
-The soil profile is a vertical layer of soil that shows all the different layers, similar to a profile on social media.
What are the main layers of soil, known as horizons?
-The main layers are O, A, E, B, C, and R horizons.
What is the O horizon, and what does it contain?
-The O horizon, also called the litter layer, contains dead leaves, twigs, sticks, and fallen trees.
What is the A horizon and its significance?
-The A horizon, or topsoil, contains rich organic matter and minerals and is home to decomposers that break down plants and animals.
What happens in the E horizon?
-In the E horizon, water moves down and removes substances, leading to a concentration of sand and silt particles.
What characterizes the B horizon?
-The B horizon, or subsoil, is lighter in color, often reddish or brown, and acts as a zone of accumulation for materials like clay.
What is the composition of the C horizon?
-The C horizon consists of parent material, containing rock fragments that weather into smaller pieces.
What does the R horizon represent?
-The R horizon is the bedrock, which can be made of various types of rock, including granite, basalt, and sandstone.
How do decomposers contribute to soil health?
-Decomposers break down dead plants and animals, creating humus, a dark organic material that enriches the soil.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)