Coaxial cables and common connectors
Summary
TLDRIn this informative video, Sunny explores coaxial cables and their significance in networking. The video details the structure of coaxial cables, which includes an outer PVC sheath, metal shielding for EMI reduction, and an inner insulator, making them ideal for high-frequency signal transmission in applications like broadband internet and cable TV. It discusses common connectors such as BNC, F-type, and SMA, emphasizing their uses. Additionally, it compares coaxial cables to twisted pair cables, highlighting their superior distance capabilities and resistance to interference, despite being more expensive and challenging to install.
Takeaways
- 📡 Networking cables connect different devices, with common types including coaxial, twisted pair, optical fiber, and parallel or serial cables.
- 🔗 The specifications of networking cables depend on the networking topology, hardware, software, and network size.
- 📏 Coaxial cables consist of an outer PVC or fire-resistant plastic sheath, metal shielding to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI), and a PVC or Teflon insulator.
- ⚡ Coaxial cables are used for high-frequency electrical signals with low losses, commonly found in telephone systems, broadband internet, cable TV, and databases.
- 🛠️ Coaxial cables are categorized by RG numbers, with RG6 being typical for home cable TV or internet connections.
- 💡 Coaxial cables are rated in ohms for impedance, with 50 ohm and 75 ohm being standard for most applications.
- 🔌 Common coaxial connectors include BNC, F-type, and SMA connectors, each serving specific purposes in signal transmission.
- 🌧️ F-type connectors are weatherproof and used for microwave frequency signals, while SMA connectors are used in high-frequency microwave and Wi-Fi systems.
- 🆚 Compared to twisted pair cables, coaxial cables carry signals further and are better shielded against crosstalk, while twisted pair cables offer higher transmission rates.
- 💰 Coaxial cables are more expensive and harder to install than twisted pair cables, which are more flexible and commonly used in Ethernet networks and telephone systems.
Q & A
What are the main types of networking cables mentioned?
-The main types of networking cables mentioned are coaxial cable, twisted pair cable, optical fiber, and parallel/serial cables.
What factors determine the use of different networking cables?
-The use of different networking cables depends on the networking topology, hardware, software, and the size of the network.
What is the structure of a coaxial cable?
-A coaxial cable consists of an outer PVC or fire-resistant plastic sheath, braided metal shielding to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI), a PVC or Teflon insulator, and a central conductor.
In what applications are coaxial cables commonly used?
-Coaxial cables are commonly used in telephone systems, broadband internet, high-speed computer databases, cable TV, and internet connections.
What does the RG number indicate in coaxial cables?
-The RG number, which stands for Radio Guide, classifies coaxial cables, with RG6 being a common type used for cable TV and internet.
What are the typical impedance ratings for coaxial cables?
-The typical impedance ratings for coaxial cables are 50 ohms and 75 ohms.
What are some common types of coaxial connectors?
-Common types of coaxial connectors include BNC connectors, F-type connectors, and SMA connectors.
What is the purpose of the BNC connector?
-The BNC connector, which stands for British Naval Connector, is used for connecting coaxial cables in various applications.
How do coaxial cables compare to twisted pair cables in terms of signal transmission?
-Coaxial cables carry signals over longer distances and are more resistant to signal interference compared to twisted pair cables, which provide higher transmission rates but are more flexible.
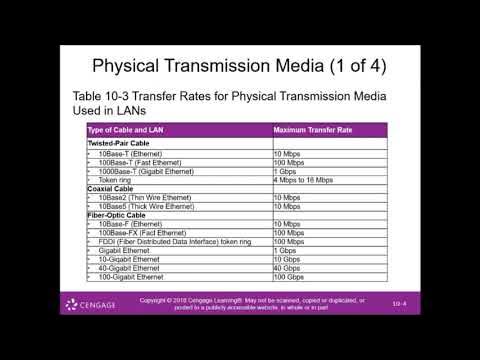
What is the maximum transmission rate for twisted pair cables like Cat 6 and Cat 7?
-Twisted pair cables like Cat 6 and Cat 7 can carry up to 10 gigabits per second.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Computer Network Basics: Understanding the Fundamentals

Network Transmission Media
Module 10 Communicating Digital Content Wired and Wireless Networks and Devices PART5

Lec-4: Physical layer in computer networks in hindi | Functions of Physical layer | OSI

Network Connectors - N10-008 CompTIA Network+ : 1.3

Copper Cabling - N10-008 CompTIA Network+ : 1.3
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)