Copper Cabling - N10-008 CompTIA Network+ : 1.3
Summary
TLDRThis script explains the importance of copper cabling in Ethernet networks, detailing the construction and function of twisted pair cables. It covers different cable categories, their uses, and maximum lengths for various Ethernet standards. It also discusses coaxial and Twinax cables, the role of standards like ISO/IEC 11801 and TIA-568, and the significance of T568A and T568B wiring standards in ensuring consistent and reliable network connections.
Takeaways
- 🌐 Copper cabling is essential for Ethernet networks, commonly used in home networks.
- 🔌 The correct type of cable must be chosen based on the network being installed.
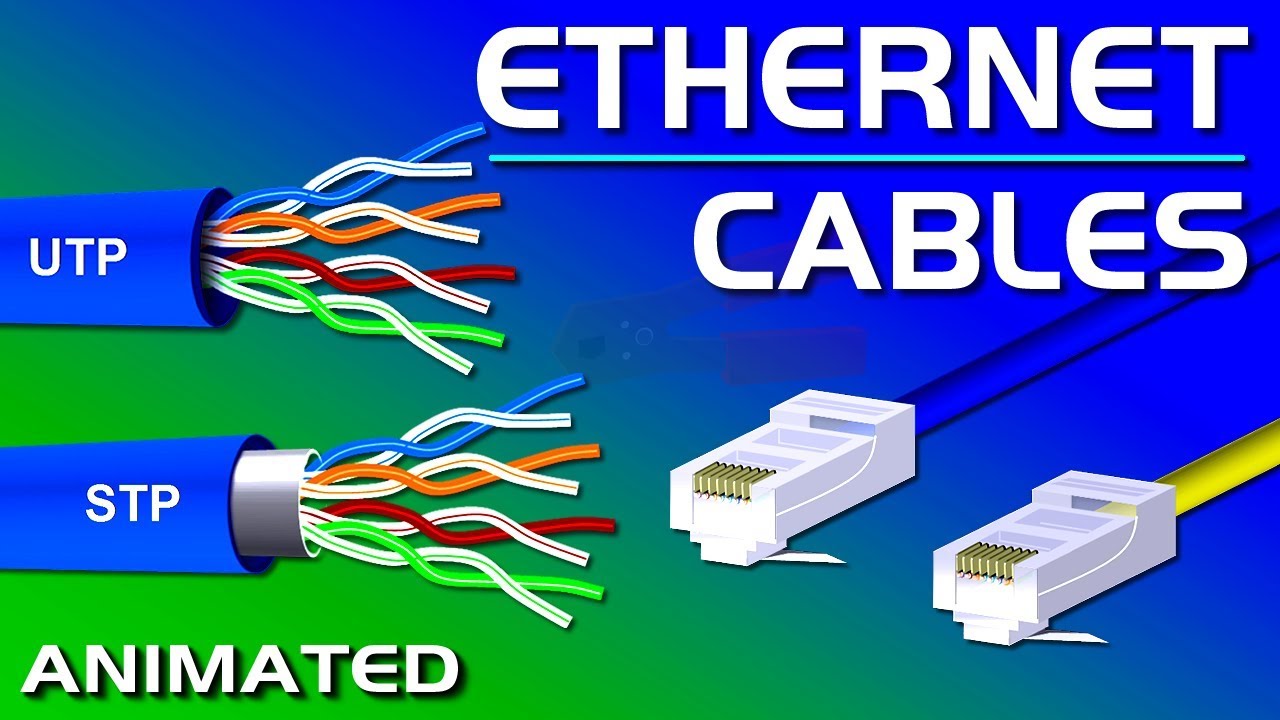
- 🧵 Twisted pair Ethernet cables contain four pairs of wires twisted to reduce interference.
- 🔄 Equal and opposite signals are sent down the twisted wires to combat noise and interference.
- 📏 Different pairs of wires in a cable have different twist rates to help reconstruct signals.
- 📦 Categories of cables are used to determine the appropriate cable for different network types.
- 🚀 For 1000BASE-T Ethernet, a minimum of Category 5e cable is recommended for 100 meters.
- 🔟 For 10GBASE-T Ethernet, a minimum of Category 6 cable is required, with different lengths supported by unshielded and shielded types.
- 🔢 Category 6A and Category 7 cables can support 10GBASE-T up to 100 meters.
- 🔄 Category 8 cable is used for 40GBASE-T Ethernet, but only supports up to 30 meters.
- 📡 Coaxial cables are used for cable modem connectivity and are different from twisted pair cables.
- 🌐 Twinax cables are similar to coaxial but have two conductors for full duplex connections, commonly used with 10G Ethernet.
- 🏢 Structured cabling standards like ISO/IEC 11801 and TIA/EIA-568 ensure consistency across networks.
- 🔢 The T568A and T568B standards dictate the color codes for Ethernet cable connections, important for proper cable installation.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of copper cabling in Ethernet networks?
-Copper cabling serves as the foundation for Ethernet networks, commonly used for home network connections.
Why is it important to use the correct type of cable for the network being installed?
-Using the correct type of cable ensures compatibility and optimal performance for the specific network standards being implemented.
What do the twisted pairs in Ethernet cables signify?
-The twisted pairs in Ethernet cables are designed to reduce interference by sending equal and opposite signals down both sides of the wires, enhancing signal integrity.
How does the twist in twisted pair Ethernet cables help with signal transmission?
-The twist in the cables moves away from noise or interference, allowing for the comparison and reconstruction of signals at the receiving end.
What is the significance of different twist rates in Ethernet cables?
-Different twist rates are used to help reconstruct the signal on the other side of the transmission, improving the quality of the received signal.
What are the categories of cables and how do they determine the type of network they are suitable for?
-Categories of cables are a set of characteristics that determine the type of network they are suitable for, dictating performance and maximum distances for different Ethernet standards.
What is the minimum category of cable required for 1000BASE-T Ethernet?
-For 1000BASE-T Ethernet, a minimum of Category 5e cable is required to support gigabit Ethernet connections up to 100 meters.
What is the difference between unshielded and shielded cables in terms of 10GBASE-T Ethernet?
-Unshielded twisted pair cables support 10GBASE-T up to 55 meters, while shielded cables can support up to 100 meters.
What is the maximum distance supported by Category 8 cables for 40GBASE-T Ethernet?
-Category 8 cables, which are shielded, support 40GBASE-T Ethernet up to a maximum distance of 30 meters.
How does coaxial cable differ from twisted pair cable?
-Coaxial cable consists of a single wire conductor surrounded by a shield, commonly used for cable modem connectivity, whereas twisted pair cables have multiple pairs of twisted wires.
What is Twinax cable and how is it commonly used?
-Twinax cable contains two separate conductors, similar to coax but with two conductors, and is commonly used for 10 Gigabit Ethernet over copper with SFP transceivers, supporting full-duplex connections.
Why is it important for structured cabling to be consistent across different locations within an organization?
-Consistent structured cabling ensures uniformity and simplifies maintenance and troubleshooting, following international standards like ISO/IEC 11801 and TIA/EIA-568.
What are the T568A and T568B standards and how do they relate to Ethernet cable connections?
-The T568A and T568B standards dictate the color coding for the eight wires in an RJ45 connection, ensuring consistent pin and pair assignments for Ethernet connections.
How can one determine if an Ethernet cable is wired to the T568A or T568B standard?
-One can determine the standard by examining the color sequence of the wires in the RJ45 connector and comparing it to the T568A or T568B color codes.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)