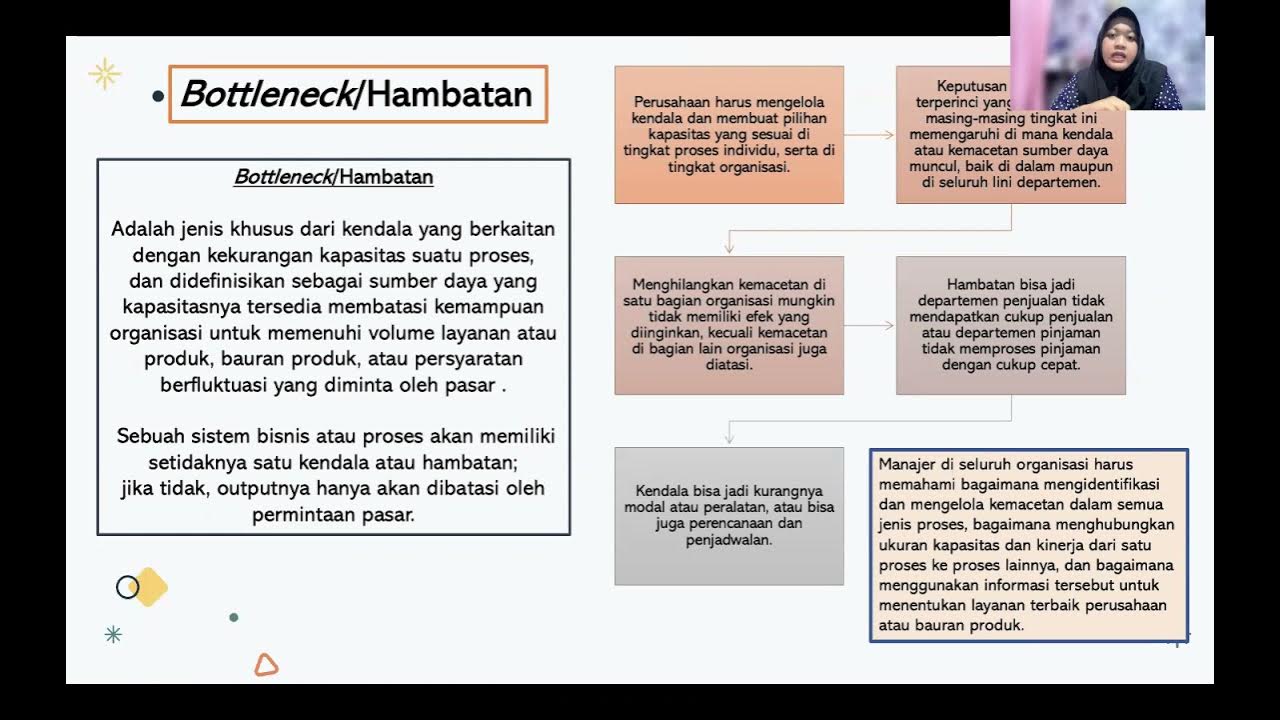
Theory of Constraints
Summary
TLDRThe Theory of Constraints (TOC) is a management philosophy that focuses on identifying and improving the primary limiting factor, or bottleneck, in a process to enhance overall throughput and efficiency. Established by Eliyahu Goldratt, TOC emphasizes that efforts to improve non-constraint areas are often wasteful. Key concepts include the drum-buffer-rope system, which synchronizes production flow with the bottleneck, and the importance of continuous improvement through the cyclical identification of new constraints. Practical applications in healthcare and a Microsoft case study illustrate the effectiveness of TOC in driving productivity gains and operational efficiency.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Theory of Constraints (TOC) is a methodology for identifying and addressing the biggest limiting factor (bottleneck) in a system to improve goal achievement.
- 😀 Improving throughput requires focusing efforts on the constraint rather than enhancing non-constraint processes, as this can waste time and resources.
- 😀 TOC concepts were popularized by Eliyahu Goldratt in his 1984 novel 'The Goal', which illustrates the logical problem-solving approach to production management.
- 😀 The chain analogy explains that a system's overall strength is determined by its weakest link, emphasizing the importance of identifying and strengthening the bottleneck.
- 😀 In healthcare, improving patient flow requires understanding the relationship between operating room efficiency and inpatient bed utilization to avoid creating flow issues.
- 😀 It's essential to consider both local and macro-level constraints in process improvement efforts to avoid exacerbating existing issues within the system.
- 😀 Process capacity analysis involves determining bottleneck times and throughput times, which are critical for understanding system capacity.
- 😀 The 'Drum Buffer Rope' concept is used to balance production flow, with the bottleneck setting the pace and buffers preventing downstream delays.
- 😀 Lean principles and TOC can be complementary, but they have differences in how they handle bottlenecks and overall production flow.
- 😀 A case study from Microsoft demonstrates how TOC principles can significantly improve productivity and reduce lead times in non-manufacturing environments.
Q & A
What is the Theory of Constraints (TOC)?
-The Theory of Constraints is a methodology for identifying the biggest limiting factor that hinders achieving a goal, commonly referred to as the bottleneck of a system.
Who introduced the Theory of Constraints, and in what context?
-Eliyahu Goldratt introduced TOC in his 1984 novel *The Goal*, where he illustrated the methodology through the story of a production manager learning to think logically about operational problems.
How does TOC relate to the concept of a bottleneck in a system?
-TOC posits that every process has a limiting factor, or bottleneck, and improving process throughput can only occur by addressing this constraint.
What is the significance of focusing efforts on the constraint?
-Focusing efforts on the constraint is crucial because working to improve steps in the process that are not the constraint is considered a waste of time, money, or effort.
How is the chain analogy used in TOC?
-The chain analogy illustrates that no chain is stronger than its weakest link; therefore, efforts to strengthen any link other than the weakest one are futile.
Can you give an example of TOC in a non-manufacturing setting?
-An example of TOC in a non-manufacturing context is patient flow in hospitals, where bottlenecks can occur in operating room efficiency or inpatient bed utilization.
What are the five steps of the TOC process for improvement?
-The five steps include: 1) identifying the constraint, 2) developing a plan for the constraint, 3) focusing resources on the plan, 4) reducing the effects of the constraint, and 5) going back to identify the new constraint.
What is the difference between bottleneck time and throughput time?
-Bottleneck time refers to the time of the slowest workstation, while throughput time is the total time it takes for a unit to pass through the entire production process.
How does the drum-buffer-rope system function in TOC?
-In the drum-buffer-rope system, the bottleneck (the drum) sets the pace for the entire production flow, while a buffer of inventory ensures that the bottleneck can operate continuously despite variations in upstream processes.
What are the key differences between TOC and lean thinking?
-While both TOC and lean seek to identify and break bottlenecks, lean does not allow the bottleneck to dictate the pace of production exclusively, emphasizing continuous flow and minimizing waste.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Aprenda TUDO sobre TEORIA DAS RESTRIÇÕES (TOC) e GARGALOS
Session 7 OM Managing Process Constraints

What is Operations Management and the Transformation Model

Scientific Management Theory || Class 12 Business Studies || Chapter 2 || NEB - Gurubaa
Metodología Kanban

Gestão de compras - Prefeitura de Itaquaquecetuba-SP
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)