Series & Parallel Circuit, Electrical Safety Devices | Grade 8 Science DepEd MELC Quarter 1 Module 6
Summary
TLDRThis video covers key concepts in electricity, specifically focusing on series and parallel circuits. It explains how these circuits operate, their advantages, disadvantages, and the differences between them in terms of voltage, current, and resistance. The video also highlights safety devices like fuses, circuit breakers, grounding, and double insulation that protect against electrical hazards such as overloading and short circuits. The script emphasizes the importance of handling electricity safely to prevent dangers like electrocution, while concluding with a recap of series and parallel circuits and basic home safety measures.
Takeaways
- ⚡ Electricity is crucial for powering many devices and appliances, making it essential in daily life.
- 🔌 Electrical devices are part of circuits, which come in two types: series and parallel circuits.
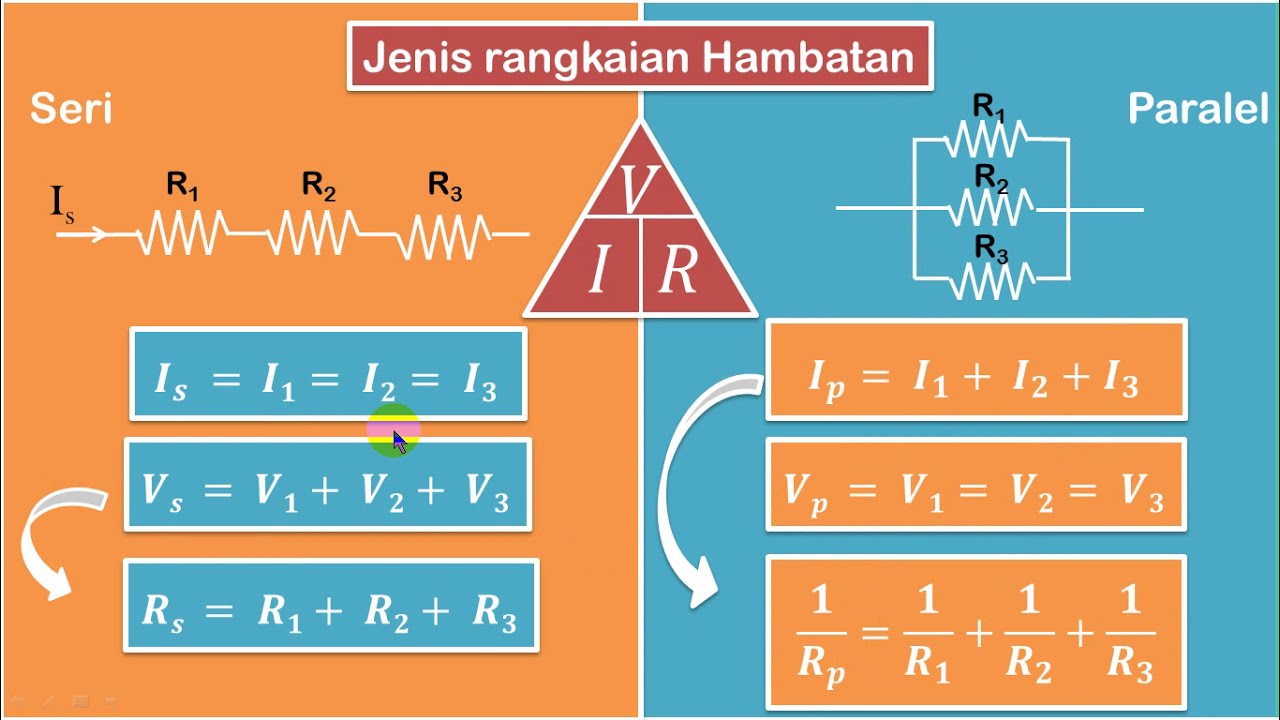
- 🟢 Series circuits connect devices in a single path, making them dependent on each other.
- 🔥 A key advantage of series circuits is that they don't overheat easily, but they fail if one device breaks.
- 🔄 Parallel circuits connect devices on independent paths, allowing them to function separately.
- 📉 Parallel circuits decrease resistance and increase current with more devices added.
- ⚠️ Overloading and short circuits are risks in electrical systems, potentially leading to fires or electrocution.
- 🛡️ Safety devices like fuses, circuit breakers, grounding, and double insulation help prevent electrical hazards.
- 🌍 Grounding creates a safe path for electricity, reducing the risk of electric shocks.
- 🎓 Understanding circuits and safety measures is essential for handling electricity safely in everyday life.
Q & A
What is the key difference between a series circuit and a parallel circuit?
-In a series circuit, devices are connected in a single path, meaning they are dependent on each other. In contrast, a parallel circuit allows each device to have its own independent path, so they function separately.
What are the advantages of using a series circuit?
-The advantages of a series circuit include: it does not overheat easily, it is simple to design and repair, and it can provide higher voltage output by adding more power devices.
What are the disadvantages of a series circuit?
-The disadvantages of a series circuit are: if one device fails, the entire circuit breaks, and the overall resistance increases with more devices, reducing efficiency.
What are the main benefits of using a parallel circuit?
-The advantages of a parallel circuit include: each device gets equal voltage, devices can be connected or disconnected without affecting others, and a fault in one pathway doesn’t stop current from passing through other paths.
What is a common risk in parallel circuits and how can it be dangerous?
-A common risk in parallel circuits is overloading, which can cause excessive current flow. This can lead to overheating and potentially cause fires.
How does current behave in a series circuit compared to a parallel circuit?
-In a series circuit, the same current flows through all devices. In a parallel circuit, the total current is the sum of the currents in each individual branch.
Why does resistance increase in a series circuit but decrease in a parallel circuit?
-In a series circuit, resistance adds up with more devices, increasing overall resistance. In a parallel circuit, the total resistance decreases because the current has multiple paths to flow through, reducing the load on each branch.
What safety devices are commonly used to prevent electrical hazards?
-Common safety devices include fuses, circuit breakers, earthing (grounding), and double insulation. These devices help prevent overcurrent, electric shocks, and short circuits.
What is the role of a fuse in an electrical circuit?
-A fuse is designed to provide over-current protection by melting when the current exceeds a safe level, breaking the circuit and preventing potential damage or fires.
What is the difference between a fuse and a circuit breaker?
-Both a fuse and a circuit breaker protect circuits from over-current, but a fuse needs to be replaced after it melts, while a circuit breaker can be reset without needing replacement after it trips.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

BAB 4 LISTRIK, MAGNET DAN SUMBER ENERGI ALTERNATIF - PART 2 (IPA Kelas 9 Kurikulum Merdeka)

KELISTRIKAN PART 2 : LISTRIK DINAMIS (IPA KELAS 9 SMP)
IPA Kelas 9 : Listrik Dinamis 3 (Rangkaian Hambatan Seri dan Paralel)

RANGKAIAN SERI DAN PARALEL

Kurikulum Merdeka Rangkuman IPA Kelas 9 Bab 4 Listrik Statis dan Listrik Dinamis

energi listrik (sumber energi listrik, rangkaian seri, paralel, campuran)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)