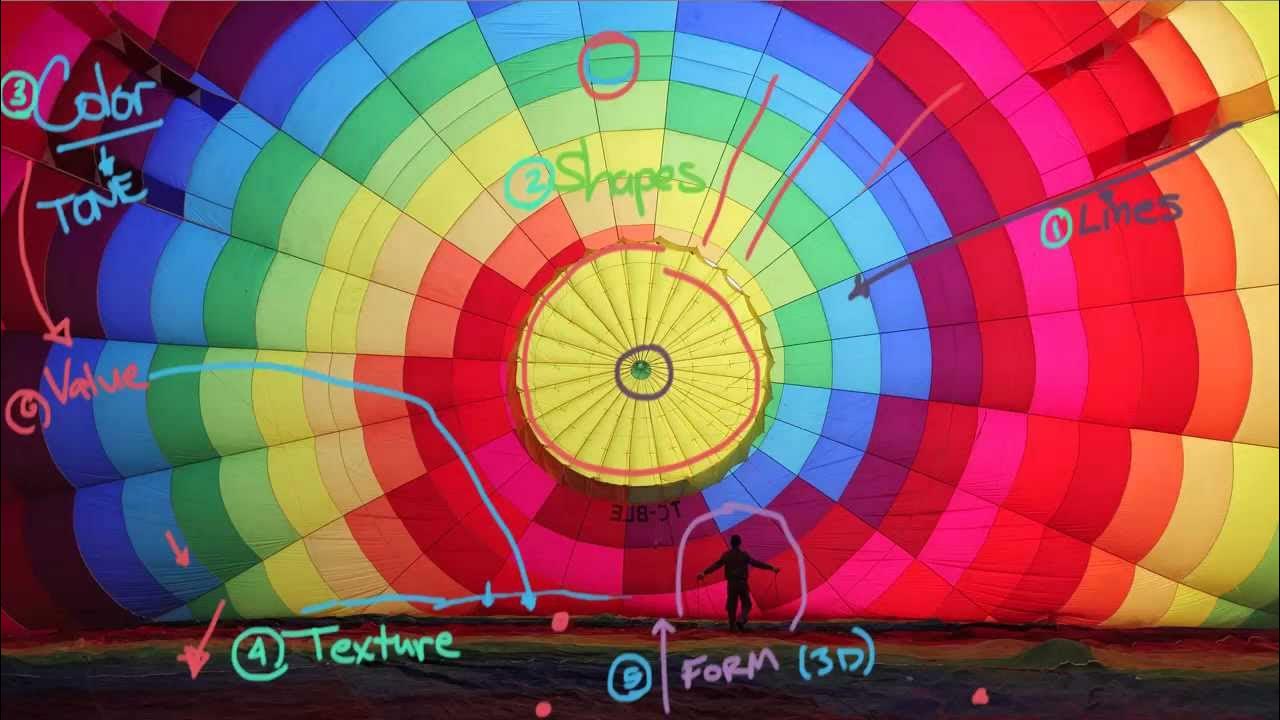
Understanding the Principles of Design
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the presenter explores the principles of design, comparing them to the instructions for a recipe that arranges the elements of art into a compelling composition. Key concepts discussed include movement, balance, unity, variety, rhythm, size, scale, proportion, emphasis, contrast, and juxtaposition. Using examples from renowned artworks, the video illustrates how these principles help to create visually interesting and cohesive art. Viewers will gain a deeper understanding of how to analyze and create artwork effectively, enhancing their appreciation of artistic compositions.
Takeaways
- 🎨 The principles of design serve as instructions for arranging the elements of art, similar to how a recipe guides cooking.
- 🖼️ Composition is the arrangement of elements in an artwork, influencing how the viewer perceives it.
- 📏 The rule of thirds is a key compositional tool that suggests placing points of interest at the intersections of a grid.
- 👁️ Movement refers to the path the viewer's eye takes through the artwork, often guided by lines and shapes.
- ⚖️ Balance involves distributing visual weight, with symmetrical balance featuring equal weight on both sides and asymmetrical balance providing stability through different elements.
- 🤝 Unity creates harmony in an artwork by using similar or repeated elements.
- 🌈 Variety introduces diverse elements to create contrast and maintain viewer interest.
- 🎵 Rhythm in art is akin to musical rhythm, created through the repetition of elements that suggest movement.
- 🔄 Pattern consists of repeated designs that can unify or add visual interest to an artwork.
- 📏 Size and proportion relate to how different objects compare in scale and how parts relate to the whole.
Q & A
What are the principles of design compared to in the video?
-The principles of design are compared to the instructions or directions of a recipe, guiding how to arrange the elements of art.
How is composition defined in the context of art?
-Composition is defined as the way an artwork is arranged, including where everything is placed within the piece.
What is the rule of thirds, and how is it applied in composition?
-The rule of thirds involves dividing an image into a grid and positioning points of interest at the intersections, creating a more dynamic and engaging composition.
What does movement refer to in design principles?
-Movement refers to the path that the viewer's eye takes through an artwork, often directed by lines, shapes, or edges leading to areas of focus.
What are the two types of balance discussed in the video?
-The two types of balance are symmetrical balance, where both sides of the artwork are identical, and asymmetrical balance, where different elements on each side create a sense of stability.
What is unity in the context of design, and how is it achieved?
-Unity, also known as harmony, is the consistency in an artwork achieved through repeated elements, similar colors, or a cohesive theme.
How does variety contribute to an artwork?
-Variety introduces different elements to create interest and contrast in an artwork, preventing it from becoming monotonous.
Can you explain the difference between size and proportion?
-Size refers to the comparison of one object to another, while proportion compares parts of a whole in terms of their relative sizes.
What role does emphasis play in art?
-Emphasis highlights the focal point of an artwork, typically the area that is most detailed or attention-grabbing.
What is juxtaposition, and how is it used in design?
-Juxtaposition involves combining unlike elements to create contrast, which can draw attention and provoke thought within an artwork.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)