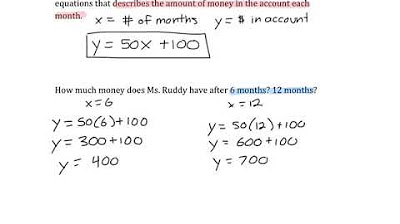ACC 406 - Mixed Costs Part 2 (High Low Method)
Summary
TLDRThe video explains the high-low method for analyzing production costs and outputs using a linear equation format (C = MX + B). It begins with a review of basic math principles, demonstrating how to calculate the slope from two data points (highest and lowest outputs). The slope represents the variable cost per unit, while the intercept indicates the fixed costs. The process is illustrated with an example of car production, highlighting how to derive monthly and annual equations. The video also cautions against potential issues like outliers that could distort the analysis, emphasizing the importance of careful data selection.
Takeaways
- 😀 The high-low method is used to estimate costs based on the highest and lowest output levels and their respective total costs.
- 📊 The equation for total cost is represented as C = MX + B, where C is total cost, M is variable cost per unit, X is output, and B is fixed cost.
- 🔍 To apply the high-low method, first identify the lowest and highest outputs (X values) and their corresponding total costs (Y values).
- 📈 The slope (M) represents the variable cost per unit and is calculated using the formula M = (Y2 - Y1) / (X2 - X1).
- 🛠️ After calculating the slope, you can find the fixed cost (B) by rearranging the total cost equation to B = C - MX.
- 📅 When converting monthly cost estimates to annual costs, the variable cost remains constant, while the fixed cost should be multiplied by the number of months.
- 🚧 The high-low method may ignore middle values, which could provide a more accurate overall picture of cost behavior.
- ⚠️ Outliers in data can skew results; careful consideration is needed when selecting points for the high-low method.
- 🔄 Understanding the difference between variable and fixed costs is crucial for accurate cost estimation and budgeting.
- 💡 The high-low method simplifies cost analysis but is best used alongside other methods to ensure robustness in decision-making.
Q & A
What is the primary objective of using the high-low method in cost analysis?
-The primary objective is to derive an accurate cost equation from production data by identifying the highest and lowest output levels and their respective costs.
How is the basic equation of cost structured in the high-low method?
-The basic equation is structured as C = MX + B, where C is the total cost, M is the variable cost per unit, X is the output, and B is the fixed cost.
What are the two key points needed to apply the high-low method?
-The two key points are the lowest output and its corresponding cost, and the highest output and its corresponding cost.
How do you calculate the slope (M) in the high-low method?
-The slope (M) is calculated using the formula M = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1), which represents the change in cost over the change in output.
What does the variable cost per unit (M) represent in the context of this method?
-The variable cost per unit (M) represents the cost incurred for producing each additional unit, in this case, each car.
How is the fixed cost (B) determined in the high-low method?
-The fixed cost (B) is determined by rearranging the cost equation to isolate B: B = C - MX, where C is the total cost, M is the variable cost, and X is the output.
What is the significance of converting a monthly cost equation to an annual cost equation?
-The conversion is significant because it allows businesses to understand and predict total costs over a longer period, which is essential for budgeting and financial planning.
What must be done to the fixed cost when converting from a monthly to an annual equation?
-The fixed cost must be multiplied by the number of months (e.g., multiplied by 12 for annual) to accurately reflect the total fixed costs over that period.
What are some potential issues with the high-low method?
-Some potential issues include ignoring middle values in the data set and the impact of outliers, which can lead to a misleading representation of the overall cost behavior.
Why is it important to consider outliers when using the high-low method?
-Considering outliers is important because they can skew the results and result in an inaccurate equation that does not represent the overall trend of the data.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)