What is Genomic Sequencing?
Summary
TLDRGenomic sequencing is a process that analyzes DNA samples from blood, extracting and preparing the DNA for sequencing. Each human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, which house about 6 billion paired chemical bases made up of four types: A, T, C, and G. Sequencing involves breaking the DNA into smaller fragments, tagging them, and reading their sequence with specialized instruments. This data is processed by computers and analyzed by medical experts to identify significant variants for medical care. The results are then discussed with healthcare professionals for further understanding and implications.
Takeaways
- 🧬 Genomic sequencing analyzes DNA samples from blood to identify genetic information.
- 🔬 DNA is housed within 23 pairs of chromosomes, which coil into a double helix structure.
- 📏 The double helix can be unwound into a ladder shape made up of paired chemical bases.
- 🧪 DNA contains approximately 6 billion paired bases, represented by the letters A, T, C, and G.
- 🔗 In DNA, base A pairs exclusively with T, while G pairs only with C.
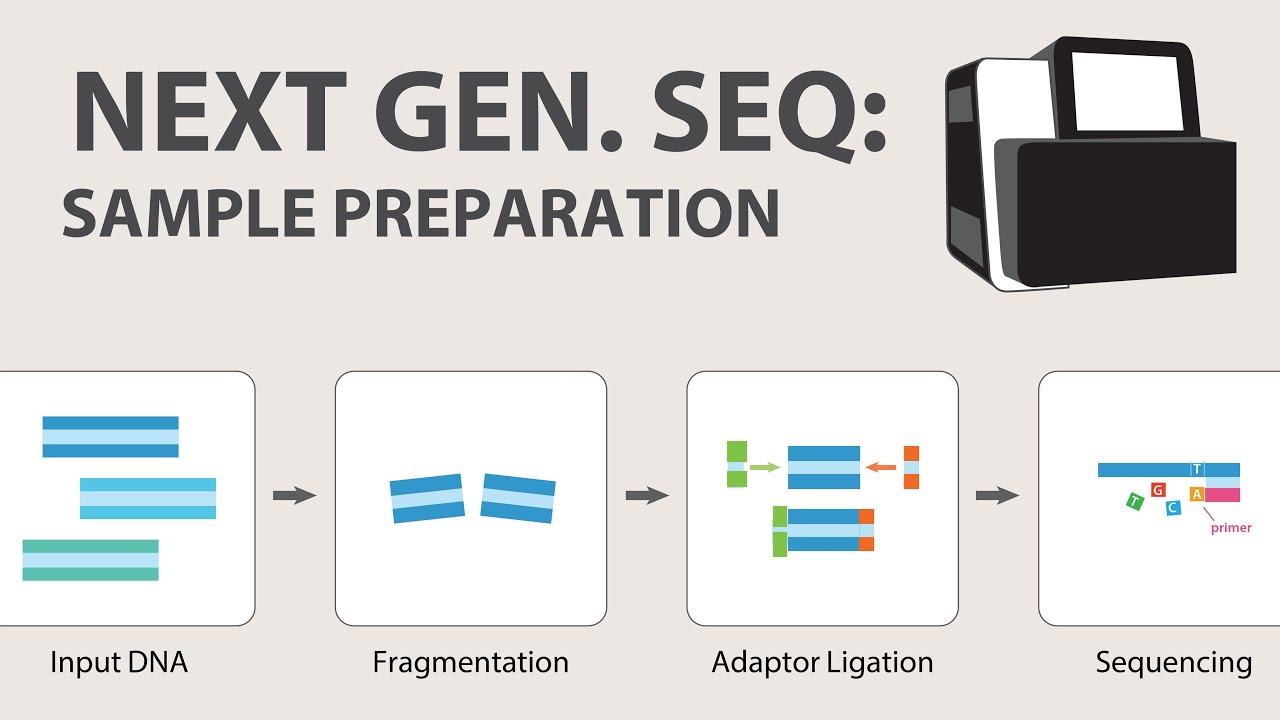
- 💻 Sequencing instruments use high-frequency sound waves to break DNA into smaller fragments, typically around 600-1000 bases long.
- 🏷️ Special tags are added to fragmented DNA strands for identification during sequencing.
- 🔍 The sequencer reads DNA by identifying colored tags corresponding to each base, revealing the DNA sequence.
- 🖥️ Powerful computers compile individual DNA fragments to reconstruct the overall DNA sequence.
- 👨⚕️ Medical experts analyze the sequenced DNA to identify variants important for individual medical care.
Q & A
What is genomic sequencing?
-Genomic sequencing is the process of analyzing a sample of DNA taken from an individual, often extracted from blood, to determine the sequence of its bases.
How many pairs of chromosomes are present in normal human cells?
-There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in each normal human cell.
What shape is DNA coiled into?
-DNA is coiled into a shape known as the double helix.
What makes up the 'ladder' structure of DNA?
-The 'ladder' structure of DNA is made up of paired chemical bases, referred to as bases.
How many bases are there in the DNA alphabet?
-There are four bases in the DNA alphabet: Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C), and Guanine (G).
Which bases pair together in DNA?
-Base A pairs only with base T, and base G pairs only with base C.
How are DNA samples prepared for sequencing?
-DNA samples are prepared by breaking them into smaller pieces, typically around 600 to 1000 bases long, using high-frequency sound waves.
What is the purpose of adding special tags to fragmented DNA?
-Special tags are added to the ends of fragmented DNA to allow them to attach to a glass slide in a sequencer, facilitating the sequencing process.
How does a sequencer read the DNA sequence?
-The sequencer reads the DNA one base at a time using different colored tags for each DNA base, with sensors detecting these colors to reveal the DNA sequence.
What role do computers play in genomic sequencing?
-Powerful computers piece together individual DNA fragments to reveal the overall sequence of an individual's DNA.
Who analyzes the results of the DNA sequencing?
-A team of medical experts uses specialized software to analyze and compare the DNA sequences to identify important variants for medical care.
Why is it important to discuss sequencing results with a doctor?
-Discussing sequencing results with a doctor and a genetic counselor is important to understand the implications of any identified variants for an individual's medical care.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)