What is Nuclear Medicine | Dr. Paulien Moyaert
Summary
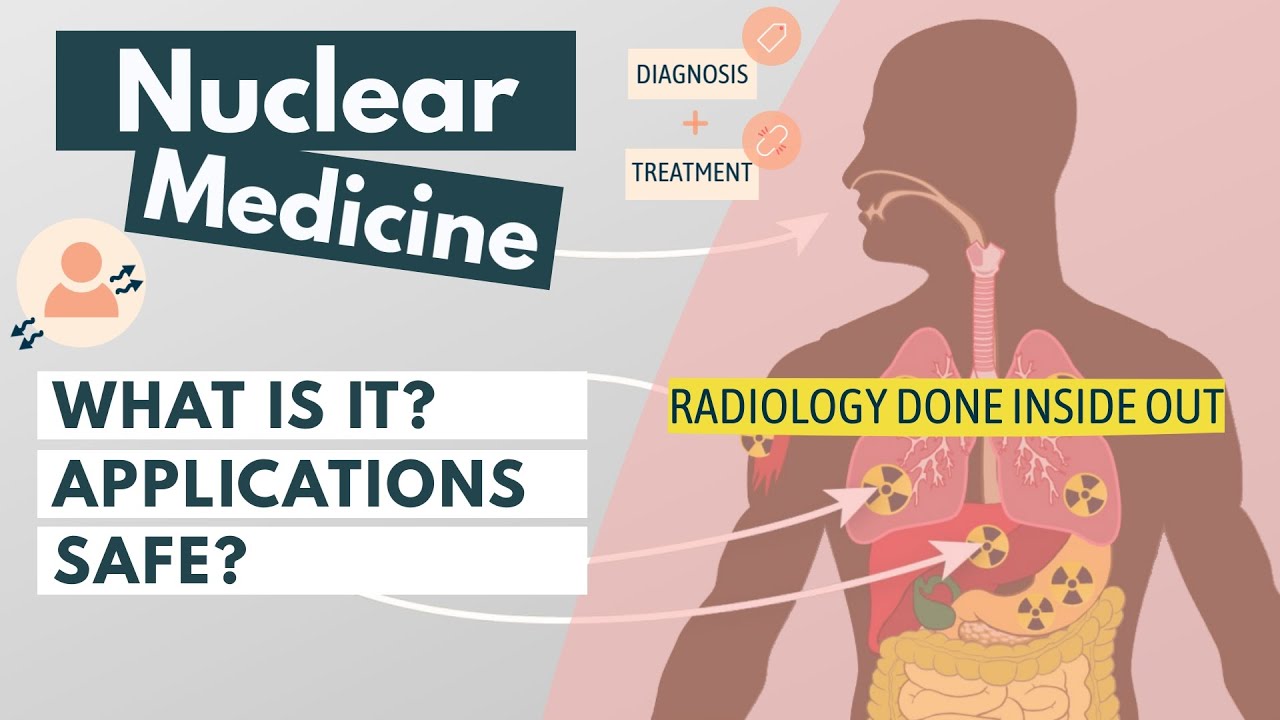
TLDRNuclear medicine is a medical specialty that utilizes small amounts of radioactive materials to diagnose and treat diseases by introducing these substances into the patient's body. Unlike traditional radiology, it focuses on organ function rather than just anatomy. For example, a PET scan can determine whether suspected masses in breast cancer patients are cancerous by using radioactive glucose. While primarily diagnostic, it also offers treatments for conditions like prostate cancer. Despite concerns about radioactivity, nuclear medicine procedures are safe and essential for early disease detection.
Takeaways
- 🩺 Nuclear medicine is a medical specialty that uses small amounts of radioactive materials to diagnose and treat diseases.
- 🔬 Unlike radiology, nuclear medicine introduces radioactive substances into the patient's body to image organ function rather than just anatomy.
- 📊 In a PET scan, radioactive glucose is used to identify cancerous cells by their high metabolic activity.
- 🚨 A CT scan may show masses, but further imaging, like a PET scan, can clarify if they are cancerous.
- 💡 Nuclear medicine can also be used to treat diseases, such as prostate cancer and to relieve pain from bone cancers.
- ⚠️ While the term 'radioactive' can be alarming, nuclear medicine procedures are designed to be safe.
- 📏 A typical bone scan exposes a patient to about 4 millisieverts of radiation, which is often less than a full-body CT scan.
- 🌍 The average American receives about 3 millisieverts of natural radiation exposure annually from natural sources.
- ✈️ Aircrew members experience radiation exposure levels comparable to that of a bone scan due to altitude.
- ✅ Nuclear medicine plays a crucial role in early disease detection and is considered safe when viewed in the context of natural radiation exposure.
Q & A
What is nuclear medicine?
-Nuclear medicine is a medical specialty that uses small amounts of radioactive materials to diagnose and treat diseases.
How does nuclear medicine differ from traditional radiology?
-Unlike radiology, which relies on external sources of radiation, nuclear medicine introduces radioactive substances into the patient's body to image organ function rather than just anatomy.
What methods are used to introduce radioactive substances in nuclear medicine?
-Radioactive substances can be introduced into the body through swallowing, injection, or inhalation.
How do radioactive substances help in diagnosing conditions?
-These substances are attracted to specific organs, bones, or tissues, emitting radiation that is detected by a special camera to provide diagnostic information.
Can you give an example of how nuclear medicine is used in diagnosis?
-In a case of suspected breast cancer spread, a patient received a PET scan after a CT scan showed unclear masses, using radioactive glucose that lights up in cancer cells.
What are the potential treatments provided by nuclear medicine?
-Nuclear medicine can be used to treat diseases such as prostate cancer and to provide pain relief from certain types of bone cancers.
Are nuclear medicine procedures safe?
-Yes, nuclear medicine procedures are designed to be safe. For example, a bone scan typically yields about 4 millisieverts of radiation, which is lower than the radiation dose from a full-body CT scan.
What is the average annual radiation exposure from natural sources for an American?
-The average American receives an annual radiation exposure of about 3 millisieverts from natural sources.
How does altitude affect radiation exposure?
-Higher altitudes result in higher radiation doses; for example, aircrew members receive radiation exposure comparable to a bone scan annually.
What is the key takeaway regarding the safety of nuclear medicine procedures?
-While the term 'radioactive' may sound alarming, nuclear medicine procedures are safe when considered in the context of overall radiation exposure and are vital for early disease detection.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Nuclear medicine explained in 2 minutes

Kedokteran Nuklir itu apa sih? Simak Penjelasannya Disini

Peran Kedokteran Nuklir di Dunia Kesehatan

Introduction To Radiology | What is Radiology | Imaging Modalities | Basics of Radiology

5 Most Disturbing & Barbaric Medical Treatments In History

Teknologi Nuklir Untuk Kesehatan
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)