What is a nucleotide?
Summary
TLDRThis video explains nucleotides, the molecules that make up DNA and RNA. Nucleotides consist of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. These bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine, and uracil) pair in specific ways to form nucleic acids. In DNA, adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine with guanine. In RNA, uracil replaces thymine. Nucleotides also carry energy as ATP, aid in protein synthesis, cellular signaling, and regulate metabolic functions. To learn more about DNA structure and function, watch the next video!
Takeaways
- 🔬 Nucleotides are molecules that make up nucleic acids, the building blocks of DNA and RNA.
- 🧩 Nucleotides are made up of three components: a 5-carbon sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base called a nucleobase.
- 🧬 The 5-carbon sugar is ribose for RNA and deoxyribose for DNA.
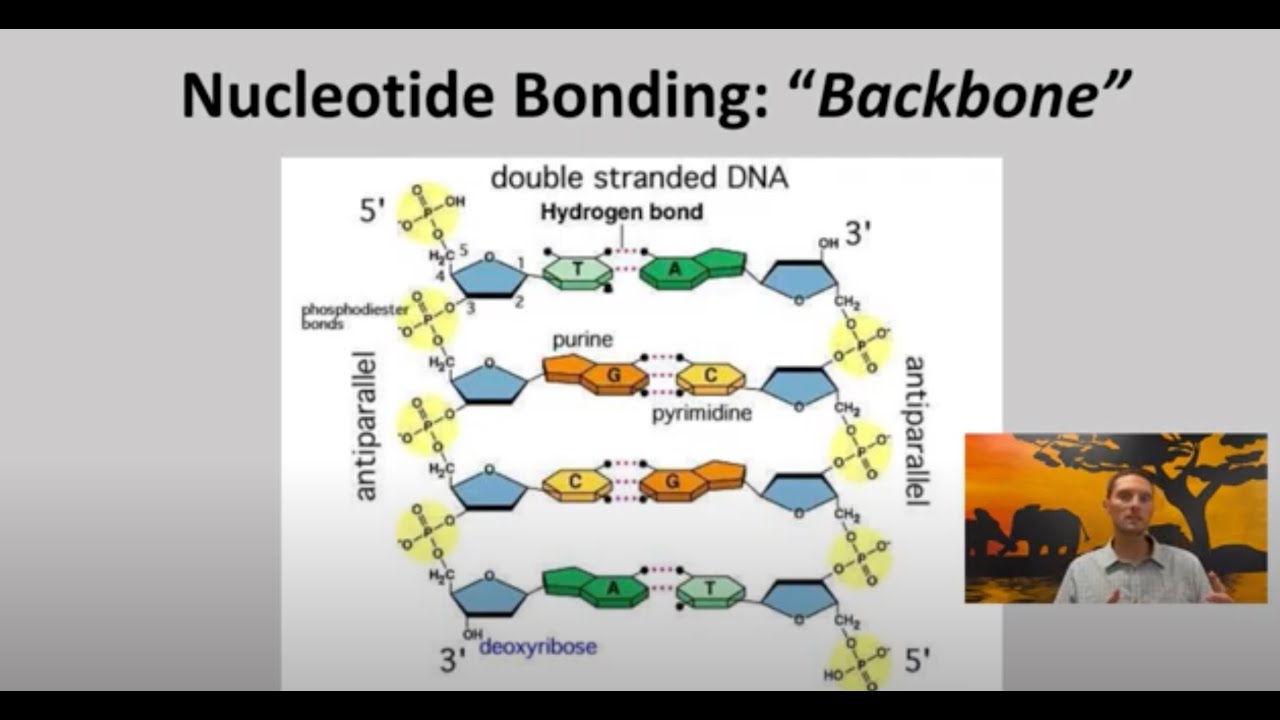
- 🔗 Nucleotides link together through 3' and 5' phosphodiester bonds, connecting the phosphate group and hydroxyl group of two sugars.
- 🧡 There are five main nucleobases: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), thymine (T), and uracil (U).
- 💡 In DNA, adenine pairs with thymine (A-T), and cytosine pairs with guanine (C-G); in RNA, uracil replaces thymine, pairing adenine with uracil (A-U).
- 📜 Purines (adenine and guanine) have two carbon rings, while pyrimidines (thymine, cytosine, and uracil) have one carbon ring.
- 🔑 Purine and pyrimidine bases are essential units of the genetic code.
- ⚡ Nucleotides carry energy in the form of ATP, powering cellular processes like protein and amino acid synthesis.
- 🧪 Nucleotides also act as cofactors in cellular signaling, help regulate metabolism, and send chemical signals between cells.
Q & A
What is a nucleotide?
-A nucleotide is a molecule that makes up nucleic acids like DNA and RNA. It consists of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
What are the three main components of a nucleotide?
-The three main components of a nucleotide are a 5-carbon sugar (ribose in RNA and deoxyribose in DNA), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
What is the difference between RNA and DNA in terms of nucleotide composition?
-The main difference is that RNA contains ribose sugar and uses uracil (U) as a nitrogenous base, while DNA contains deoxyribose sugar and uses thymine (T) instead of uracil.
How are nucleotides linked together to form nucleic acids?
-Nucleotides are linked by 3’ and 5’ phosphodiester linkages, which combine the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the hydroxyl group of another through a condensation reaction.
What are the five nucleobases that make up nucleotides?
-The five nucleobases are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), thymine (T), and uracil (U).
Which nucleobases pair together in DNA and RNA?
-In DNA, adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T), and cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G). In RNA, uracil (U) replaces thymine, so adenine pairs with uracil (A-U), while cytosine (C) still pairs with guanine (G).
What are purine and pyrimidine bases, and how do they differ?
-Purine bases, which include adenine and guanine, have two carbon rings (a pyrimidine ring and an imidazole ring). Pyrimidine bases, which include thymine, uracil, and cytosine, have just one pyrimidine ring.
What role do nucleotides play besides forming nucleic acids?
-Nucleotides also carry energy in the form of Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP), act as cofactors in cellular signaling, regulate metabolic function, and send chemical signals to cells.
What is a phosphodiester bond, and how is it formed?
-A phosphodiester bond links two nucleotides by connecting the phosphate group of one with the hydroxyl group of another sugar molecule. This occurs through a condensation reaction.
Why are nitrogenous base pairings non-negotiable in nucleic acids?
-Nitrogenous base pairings are fixed due to the specific structure and hydrogen bonding patterns of the bases. Adenine only pairs with thymine (or uracil in RNA), and cytosine only pairs with guanine, ensuring accurate genetic coding.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)