introduction to projectile motion
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the fascinating concepts of projectile motion, highlighting that objects dropped vertically and thrown horizontally from the same height will land at the same time due to gravity acting only on their vertical velocity. The horizontal velocity remains unchanged throughout the motion. The video also explains how the shape of a projectile's path is a parabola and why 45 degrees is the optimal angle for maximum range. Despite intuition, the speed given to a stone thrown horizontally has no effect on its descent time compared to one dropped straight down.
Takeaways
- 😀 Objects dropped or thrown horizontally from the same height will land at the same time, regardless of horizontal speed.
- 🌍 Projectile motion describes the curved path an object follows when thrown at an angle, typically a parabolic trajectory.
- 🔄 Gravity acts vertically, so only the vertical component of velocity is affected by gravity, not the horizontal component.
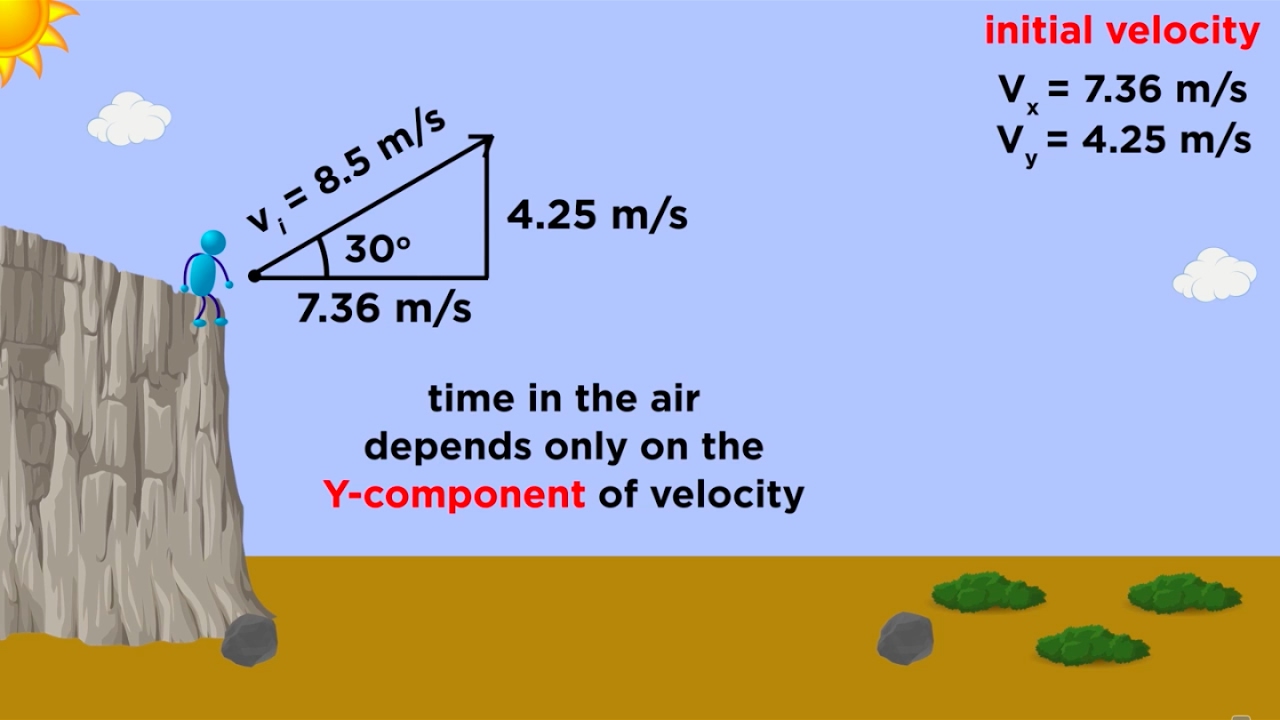
- ↔️ The horizontal velocity remains constant throughout the motion, while the vertical velocity changes due to gravity.
- 📉 Vertical velocity decreases as the object ascends, reaching zero at the highest point of the trajectory.
- 🪂 After reaching the peak, the vertical velocity becomes negative, accelerating the object downward.
- 🏞️ The optimal angle for maximum range in projectile motion is 45 degrees, balancing time in the air and horizontal speed.
- 🔀 Reducing the angle below or increasing it above 45 degrees decreases the horizontal range of the projectile.
- ⏳ Time spent in the air is determined by the vertical velocity, and horizontal speed does not affect this duration.
- 💡 Even when a stone is thrown horizontally with high speed, its vertical velocity starts at zero, just like a dropped stone.
Q & A
What is the main point of the initial example with the two stones?
-The main point is that both stones, regardless of one being dropped vertically and the other being thrown horizontally, will land on the ground at the same time due to gravity only affecting the vertical motion.
Why does horizontal velocity not affect the time taken for the stone to land?
-Horizontal velocity does not affect the time taken for the stone to land because gravity only influences the vertical component of the stone's motion. The horizontal motion remains constant and does not impact the descent time.
What kind of path does an object follow when thrown at an angle?
-When thrown at an angle, an object follows a parabolic path due to the combination of horizontal and vertical components of motion under the influence of gravity.
How does gravity affect the vertical component of velocity?
-Gravity acts vertically and decreases the vertical component of velocity as the object moves upward. At the highest point, the vertical velocity becomes zero, after which the object begins to descend, and its vertical velocity increases.
Why does the horizontal component of velocity remain constant during projectile motion?
-The horizontal component of velocity remains constant because there are no forces acting in the horizontal direction to accelerate or decelerate the object. Gravity only affects the vertical motion.
At what point during the motion does the vertical velocity become zero?
-The vertical velocity becomes zero at the highest point of the object's trajectory, which is also known as the maximum height.
What happens to the vertical velocity during the descent of the object?
-During the descent, the vertical velocity increases as gravity accelerates the object downward. Both the velocity and gravitational force are in the same direction during this phase.
Why is 45 degrees the optimal angle for achieving the maximum range in projectile motion?
-45 degrees is the optimal angle for maximum range because it provides a good balance between horizontal velocity and the time the object spends in the air. At this angle, both factors contribute effectively to maximizing the range.
What happens to the range when the angle of projection is increased beyond 45 degrees?
-When the angle of projection is increased beyond 45 degrees, the range decreases because the time spent in the air increases, but the horizontal velocity decreases, reducing the overall distance the object travels.
In the original example, why do both stones hit the ground at the same time despite different speeds?
-Both stones hit the ground at the same time because their vertical velocities are the same. Gravity affects both stones equally, and the horizontal velocity does not influence the time it takes to hit the ground.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

How Do Horizontally Launched Projectiles Behave? | Physics in Motion

Falling objects | Physics | Khan Academy
Kinematics Part 3: Projectile Motion

Projectile Motion Part II | Quarter 4 Grade 9 Science Week 2 Lesson

Motion Characteristics of a Projectile

QUEDA LIVRE e LANÇAMENTO VERTICAL - [Física do ZERO]
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)