Porter's Five Forces Model | A-Level, IB & BTEC Business
Summary
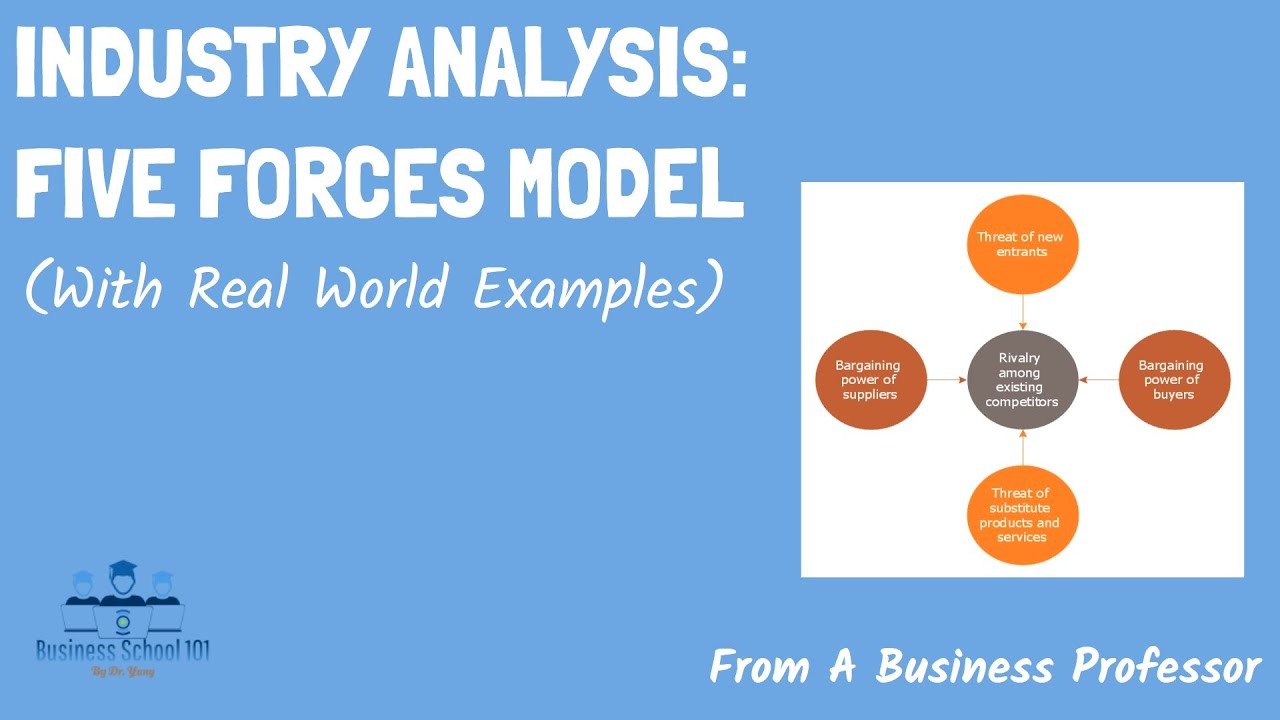
TLDRThis video provides a concise introduction to Porter's Five Forces model, developed by Professor Michael Porter. It explains how the model helps analyze competition and market attractiveness by examining key forces such as the threat of new entrants, bargaining power of suppliers and customers, and rivalry among existing competitors. The video highlights the importance of evaluating industry differences, competitive dynamics, and barriers to entry, using examples like soft drinks, airlines, and pharmaceuticals. It concludes with practical insights for business strategy, exams, and industry analysis using the model.
Takeaways
- 📊 The Five Forces model, devised by Michael Porter, is essential for analyzing the nature of competition and market attractiveness.
- 📉 The model helps explain why profits vary across industries by examining five critical forces affecting competition.
- ⚠️ One major force is the threat of new entrants, which can reduce market share and profits for existing businesses.
- 🏭 Barriers to entry, such as economies of scale, brand loyalty, and industry know-how, affect how easy or difficult it is for new competitors to enter the market.
- 🧪 Some industries, like pharmaceuticals and oil and gas, have high entry barriers, leading to higher profit margins.
- 🐶 Markets with low entry barriers, such as personal tutoring or dog walking, experience more competition and lower profits.
- 🛠 Suppliers with high bargaining power can exert influence over businesses by controlling crucial resources or charging higher prices.
- 🛒 Customers can also have bargaining power, especially in markets like grocery retail, where large chains negotiate tough terms with suppliers.
- 🔄 The availability of substitute products can threaten industries by providing customers with alternative options, thus increasing competition.
- 🤝 Technological change and takeovers can influence competitive dynamics, such as by reducing entry barriers or shifting bargaining power through vertical integration.
Q & A
What is the purpose of Porter's Five Forces model?
-Porter's Five Forces model helps assess market attractiveness and understand the nature of competition within an industry. It explains why certain industries experience high or low profits and can be applied to various industries to analyze competitive dynamics.
Who created the Five Forces model, and what inspired its development?
-The Five Forces model was created by Professor Michael Porter. It was developed as a result of his research into the nature of competition in different industries and markets.
How can Porter's Five Forces model be used in business analysis?
-The model can be used to assess market attractiveness, understand competitive forces, and explain how and why profits vary between industries. It's also used in exam scenarios to support analytical arguments regarding industry structure and competition.
Which force within the Five Forces model is often considered the most important, and why?
-The 'threat of new entrants' is often considered one of the most important forces because it directly affects existing firms in a market. New entrants can reduce market share and drive down profits, especially if barriers to entry are low.
What factors contribute to high barriers to entry in a market?
-Factors such as economies of scale, brand loyalty, industry expertise, and significant research and development costs can contribute to high barriers to entry, making it difficult for new firms to enter the market.
Can you provide examples of industries with high and low barriers to entry?
-Industries like pharmaceuticals and oil and gas exploration have high barriers to entry due to the need for significant R&D investment and technical expertise. In contrast, personal services like hairdressing or dog walking have low barriers to entry, making them highly competitive and low-margin.
How do substitutes affect competition in a market?
-The availability of substitute products increases competition as consumers have alternatives. For example, the rise of digital media has created substitutes for traditional newspapers, forcing those industries to adapt to maintain profitability.
How does technological change influence competition according to Porter’s model?
-Technological change can lower barriers to entry by making it easier for new competitors to enter a market. It can also introduce new substitute products, intensifying competition and reducing profitability for established companies.
How does customer bargaining power impact an industry?
-Customer bargaining power affects the prices and terms businesses can offer. When customers have strong bargaining power, as seen with large supermarkets negotiating with suppliers, it can force businesses to lower prices and reduce profit margins.
How can the Five Forces model be used to evaluate potential diversification strategies?
-The model helps assess the attractiveness of a target market when considering diversification. If the market is highly competitive with intense rivalry, the strategy may be less likely to succeed. The model provides a framework for understanding the competitive landscape before launching new products in new markets.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Porter's Five Forces Explained | Supermarket Industry Examples
Industry Analysis: Porter's Five Forces Model | Strategic Management | From A Business Professor

The Explainer: The 5 Forces That Make Companies Successful

Insight: Ideas for Change - Michael Porter - Creating Shared Value

The Five Competitive Forces That Shape Strategy

COMPETITIVE STRATEGY (BY MICHAEL PORTER)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)