boyle’s law experiment
Summary
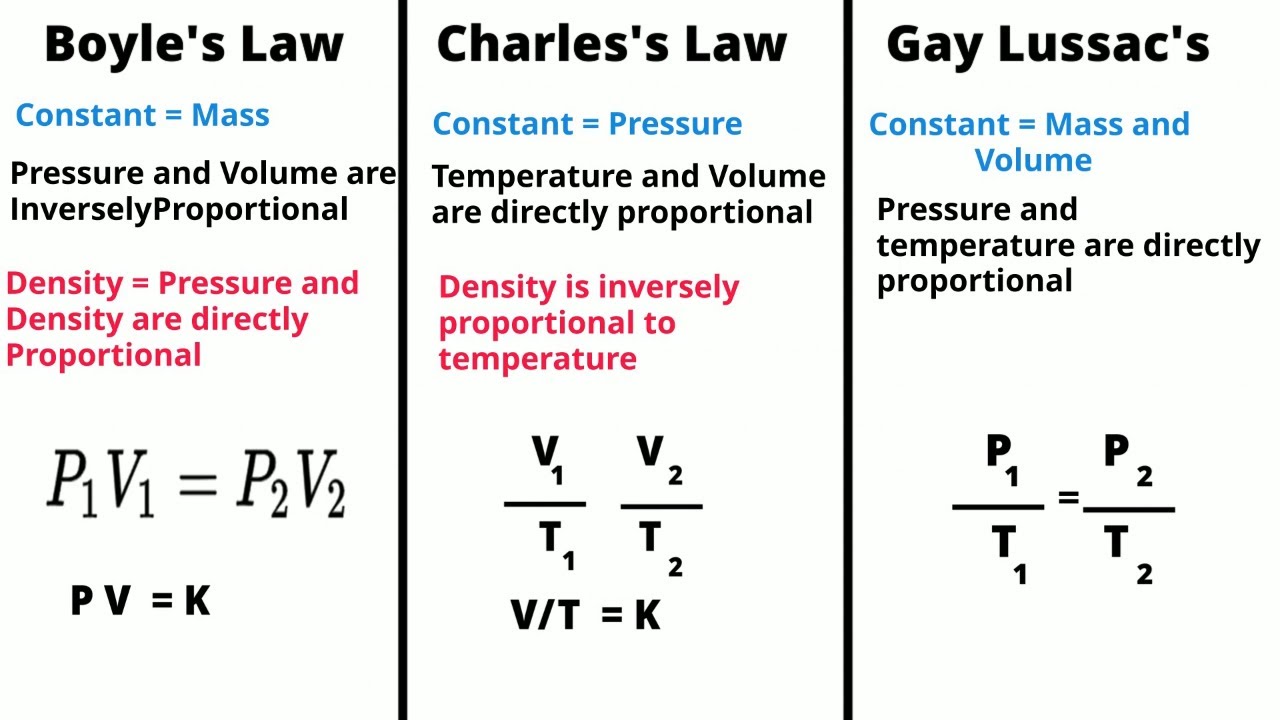
TLDRIn this video, Cassandra Angela from Saint Dominic class demonstrates an experiment illustrating Boyle's Law, which states that pressure and volume are inversely proportional. Using a lung model made from a balloon and a bottle, she shows how inhaling and exhaling affect lung volume and pressure. As pressure inside the bottle increases, the balloon (representing the lung) deflates, and as pressure decreases, the balloon expands. The experiment effectively explains how Boyle's Law applies to breathing and the function of the lungs during inhalation and exhalation.
Takeaways
- 📜 Boyle's Law explains the inverse relationship between pressure and volume in a closed system.
- 🔬 The experiment demonstrates how Boyle's Law works using a balloon as a lung and a bottle as the body.
- 🎈 The balloon in the experiment represents the lung, and its volume changes with pressure applied inside the bottle.
- 🫁 Boyle's Law is applicable to breathing, showing how air pressure inside the lungs changes during inhalation and exhalation.
- ⬆️ When pressure inside the chest cavity decreases during inhalation, the volume of the lungs increases, allowing air to flow in.
- ⬇️ When pressure inside the chest cavity increases during exhalation, the volume of the lungs decreases, pushing air out.
- 🧪 The experiment visually illustrates how the volume of the balloon (lung) decreases when pressure is applied inside the bottle (chest).
- 📉 Boyle's Law is a fundamental principle in understanding lung function during breathing.
- 🚨 Boyle's Law also explains the effects of pressure changes, such as those experienced during diving or high-altitude flying, on the lungs.
- 🎓 This experiment helps demonstrate the practical applications of Boyle's Law in everyday activities like breathing.
Q & A
Who is presenting the Boyle's Law experiment in the video?
-The presenter of the Boyle's Law experiment is Cassandra Angela, a student from Saint Dominic class.
What is Boyle's Law?
-Boyle's Law states that pressure and volume are inversely proportional, meaning when pressure increases, volume decreases and vice versa.
How does Boyle's Law relate to breathing?
-Boyle's Law explains that during inhalation, the volume of the lungs increases, causing pressure to decrease, allowing air to flow into the lungs. During exhalation, the volume of the lungs decreases, increasing pressure and forcing air out of the lungs.
What materials are used in the lung model for the experiment?
-The materials used in the lung model include a balloon to represent the lung, a bottle to represent the body, and a thumbtack to create a hole representing the mouth.
How does the lung model demonstrate Boyle's Law?
-In the lung model, as pressure is applied inside the bottle (representing exhalation), the volume of the balloon (the lung) decreases. When pressure is removed (inhalation), the balloon expands, demonstrating the inverse relationship between pressure and volume.
What happens to the volume of the chest cavity during inhalation?
-During inhalation, the volume of the chest cavity increases as the diaphragm and the muscles between the ribs contract.
What effect does exhalation have on pressure and volume in the lungs?
-During exhalation, the diaphragm and rib muscles relax, reducing the chest cavity's volume, which increases pressure and pushes air out of the lungs.
How does Boyle's Law explain the effect of altitude or diving on lung function?
-Boyle's Law explains that changes in external pressure, such as those experienced during diving or flying at high altitudes, can affect lung function by altering the balance between pressure and volume in the lungs.
What is the significance of Boyle's Law in respiratory physiology?
-Boyle's Law is crucial in respiratory physiology because it explains how the lungs, as air-filled sacs, expand and contract to facilitate breathing through changes in pressure and volume.
Why does air rush into the lungs during inhalation?
-Air rushes into the lungs during inhalation because the increase in chest cavity volume decreases pressure inside the lungs, creating a pressure difference that causes air to flow in.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)