Sistem Kontrol #3b: Analisis Respon Waktu Sistem Orde 1
Summary
TLDRThis lecture discusses first-order system analysis in control systems. The instructor, Khairul Anam from the Department of Electrical Engineering at Universitas Jember, explains the purpose of learning first-order systems, transient and steady-state responses, and how these responses are analyzed using test signals like step, ramp, and impulse inputs. The lecture covers key concepts such as time constants, Laplace transforms, and response characteristics. The session concludes with an emphasis on practical applications, including simulations using Python, providing students with essential tools for analyzing first-order systems.
Takeaways
- 📚 The lecture is about first-order system analysis and its characteristics, presented by Khairul Anam from Universitas Jember.
- 🔍 The primary objectives include understanding first-order systems, transient and steady-state responses using step, ramp, and impulse inputs.
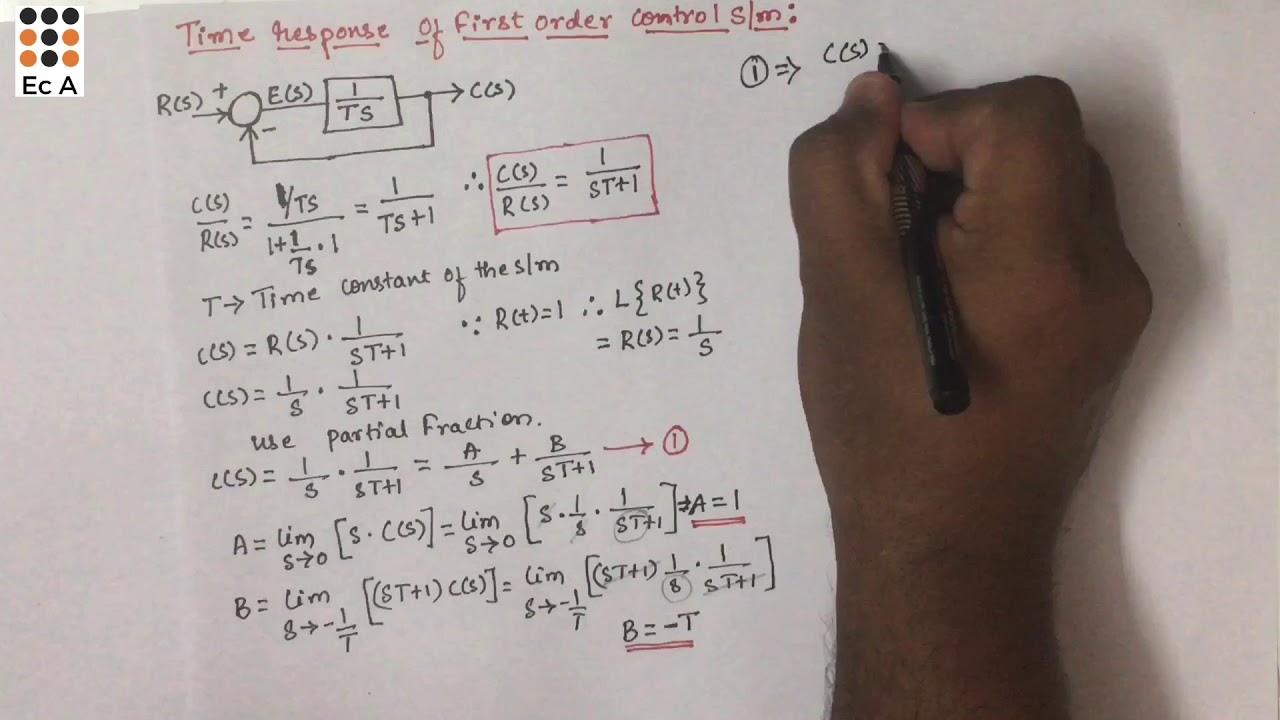
- 📊 The block diagram of a first-order system is simplified, where the transfer function is 1/(τs+1), with τ being the time constant.
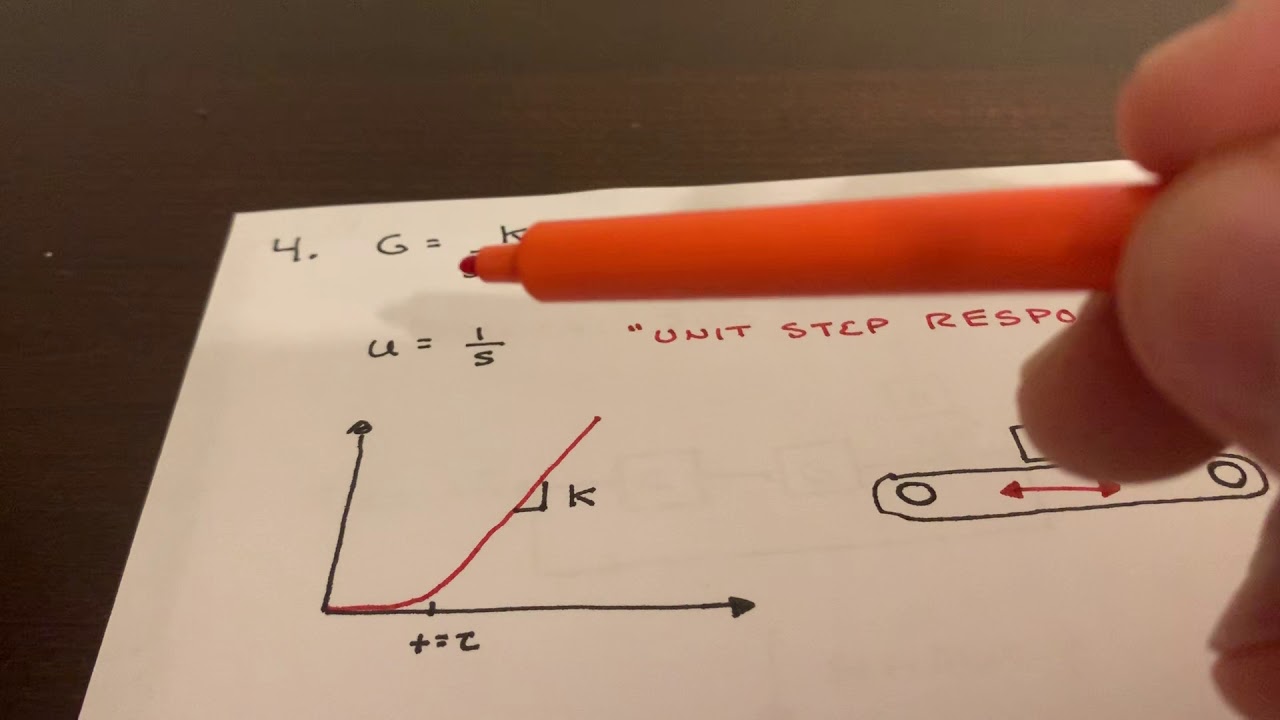
- ⏳ The time constant can be identified by analyzing the system's response to a step input. It is the time when the system output reaches 63.2% of its final value.
- 📈 A unit step response of a first-order system gradually approaches the final value, with the speed of response depending on the time constant.
- ⏲️ The transient response occurs before the system reaches its steady-state, and the system behavior slows down over time as it reaches equilibrium.
- 📐 The slope of the response decreases over time until it reaches zero at steady-state, a typical characteristic of first-order systems.
- 🔄 The response to a unit ramp input and impulse input is also discussed, showcasing how each input leads to different transient and steady-state behaviors.
- 💡 The lecture introduces the importance of steady-state errors, especially in response to ramp and impulse inputs, highlighting that smaller time constants lead to faster systems.
- 💻 The next step in the lecture involves simulating first-order systems using Python to better understand the system's behavior.
Q & A
What is the main topic of this lecture?
-The main topic of this lecture is the analysis of first-order control systems, including their transient response and steady-state response.
Who is the presenter of this lecture?
-The presenter of this lecture is Khairul Anam from the Electrical Engineering Department, Universitas Jember.
What is the objective of learning about first-order systems?
-The objective is for students to understand first-order systems, explain their transient response and steady-state response, and understand their characteristics using test signals such as step, ramp, and impulse.
What is the transfer function of the first-order system discussed in the lecture?
-The transfer function of the first-order system is given by 1 / (Ts + 1), where T represents the time constant.
What is the definition of the time constant in a first-order system?
-The time constant is the time taken by the response to reach approximately 63.2% of its final value after a step input is applied.
How can we determine the time constant graphically?
-To determine the time constant graphically, locate the point where the response reaches 63.2% of its final value, and then read the corresponding time.
What is the difference between transient response and steady-state response?
-The transient response is the part of the system's output from the initial state until it reaches a stable condition, while the steady-state response is the behavior of the system after the transient effects have settled.
What happens to the system response if the time constant decreases?
-If the time constant decreases, the system response becomes faster, meaning it reaches the steady-state value more quickly.
What are the three different types of input signals used for first-order systems in the lecture?
-The three types of input signals are unit step, ramp, and impulse signals.
What is the steady-state error for a unit ramp input in a first-order system?
-The steady-state error for a unit ramp input in a first-order system is equal to the time constant of the system.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)