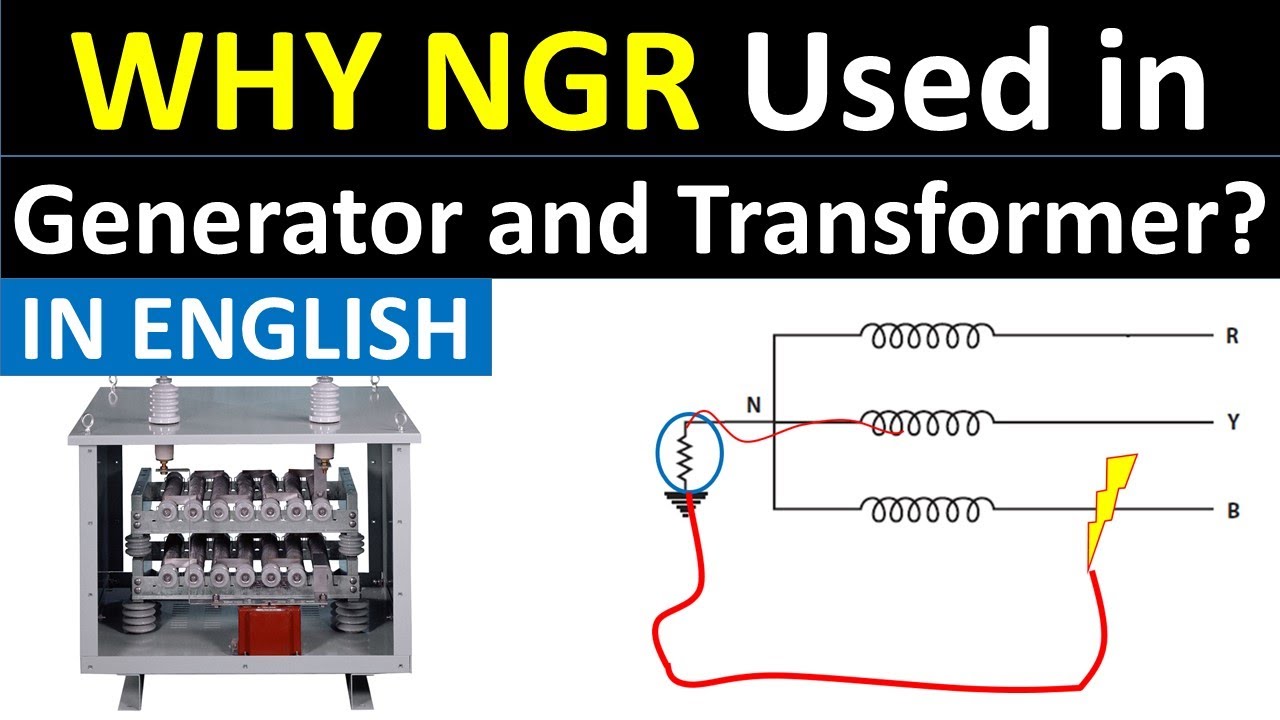
What is the reason for using NGR (Neutral Grounding Resistor) in a power transformer?
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the role of the neutral grounding resistor (NGR) in power transformers. It explains how NGRs limit fault currents, stabilize voltage, reduce transients, and aid in fault detection, ensuring the safe and reliable operation of electrical systems. NGRs connect the neutral point of a transformer to the ground, preventing dangerous fault currents that could damage equipment or pose safety hazards. The video emphasizes the importance of selecting and designing NGRs correctly to protect transformers and maintain system stability.
Takeaways
- ⚡ Power transformers are essential for stepping up or stepping down voltage levels for efficient power transmission.
- 🛡️ Neutral grounding resistors (NGRs) connect the neutral point of a transformer to the ground to ensure safe operation.
- ⚙️ The primary purpose of an NGR is to limit fault current during single-line-to-ground faults in low and medium voltage systems.
- 🌍 NGRs protect generators and transformers from damaging currents during earth faults, offering advantages over direct earthing or insulated systems.
- 🔥 NGRs prevent overheating by acting as current-limiting devices, reducing fault current to manageable levels.
- 📉 NGRs help stabilize voltage and reduce transients, which protects connected equipment from sudden voltage changes.
- 🔎 NGRs assist in fault detection by allowing engineers to monitor voltage drops and locate faults quickly.
- 🛠️ NGRs provide the benefits of both ungrounded and solidly grounded systems by controlling fault current to safe levels.
- 💡 Properly designed NGR systems absorb and dissipate energy during fault events without exceeding temperature limits.
- ✅ NGRs are crucial for maintaining a safe, stable, and reliable electrical power system while minimizing damage to transformers and equipment.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of a power transformer?
-The primary purpose of a power transformer is to step up or step down voltage levels, facilitating the efficient transmission and distribution of electricity.
What is a neutral grounding resistor (NGR) and where is it used?
-A neutral grounding resistor is a resistor that connects the neutral point of a transformer to the ground. It is used in low and medium voltage (LV and MV) distribution networks to protect transformers and generators from damaging currents during ground faults.
Why is the neutral grounding resistor important in power transformers?
-The neutral grounding resistor is important because it limits fault currents during a single line-to-ground fault, protects transformers and generators from damage, stabilizes voltage, reduces transient overvoltages, and aids in fault detection.
What are the disadvantages of using direct earthing or insulated neutral systems?
-Direct earthing or insulated neutral systems can lead to transient overvoltages, damaging fault currents, arc blasts, and difficulties in locating ground faults.
How does a neutral grounding resistor help stabilize voltage in power transformers?
-A neutral grounding resistor helps stabilize voltage by creating a grounding path for fault currents, which reduces voltage transients and ensures that the output voltage remains within acceptable limits.
What role does a neutral grounding resistor play in fault detection?
-A neutral grounding resistor aids in fault detection by experiencing a voltage drop when a fault occurs. By monitoring this voltage drop, engineers can accurately detect and locate the fault, allowing for quick corrective actions.
How does a neutral grounding resistor limit fault current?
-A neutral grounding resistor limits fault current by providing a resistance path for the current to flow to the ground. This reduces the fault current to a safe level, preventing damage to the transformer and other electrical components.
What happens to the energy absorbed by the neutral grounding resistor during a fault?
-The neutral grounding resistor absorbs and dissipates a large amount of energy during a fault event, ensuring that the temperature does not exceed the designed limitations.
Why is the design and selection of neutral grounding resistors important?
-The design and selection of neutral grounding resistors are important to ensure that they can handle the fault current, dissipate energy effectively, and protect electrical equipment and personnel from harm.
What are the main benefits of using a neutral grounding resistor in power transformers?
-The main benefits of using a neutral grounding resistor are limiting fault currents, stabilizing voltage, reducing transients, aiding in fault detection, and improving the overall safety and reliability of the power system.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)