SRAM vs DRAM : How SRAM Works? How DRAM Works? Why SRAM is faster than DRAM?
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the two main types of random access memory (RAM) used in computers: SRAM (Static RAM) and DRAM (Dynamic RAM). It highlights their key differences, including speed, cost, density, and power consumption. SRAM is faster and used as cache memory due to its stability but is more expensive and has lower density. DRAM, while slower and requiring periodic refresh cycles, is more cost-effective and has higher density, making it suitable for main memory. The video delves into the internal structure, read/write operations, and advantages of each, providing a thorough comparison between SRAM and DRAM.
Takeaways
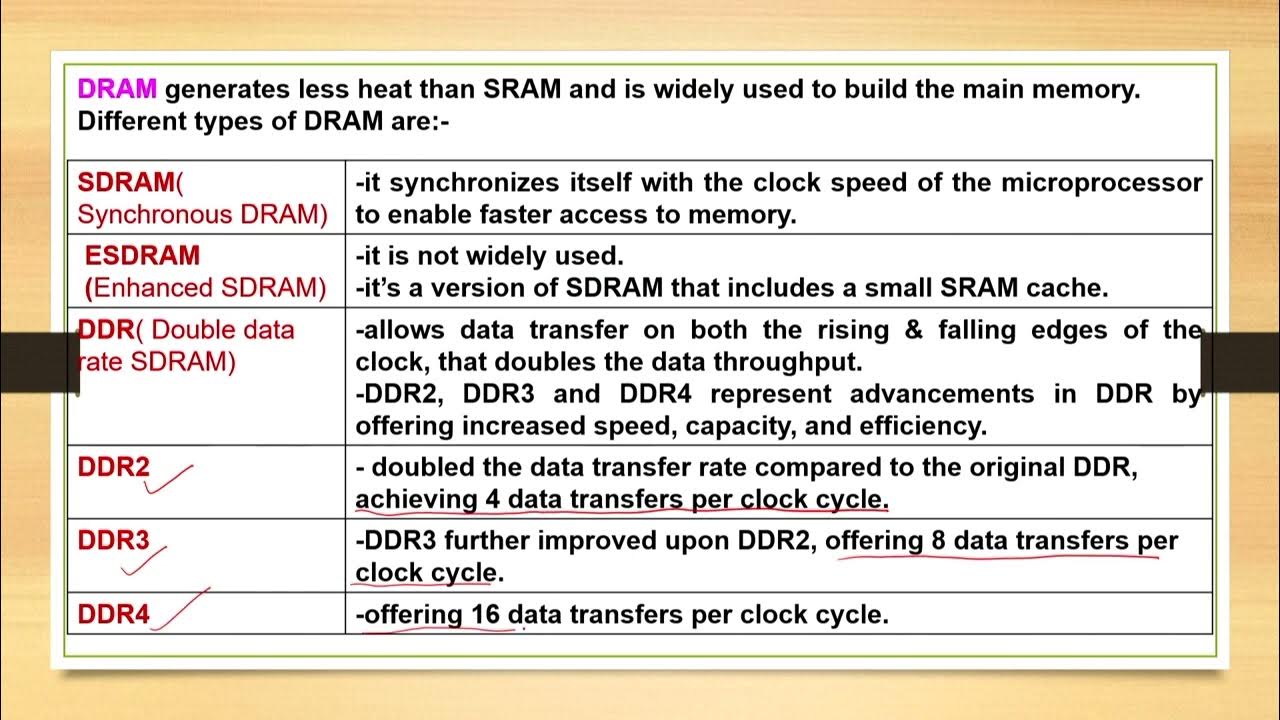
- 💻 SRAM stands for Static RAM, while DRAM stands for Dynamic RAM, with DRAM requiring periodic refresh cycles due to capacitor charge leakage.
- ⚡ SRAM is faster and used as cache memory, while DRAM is slower and used as main memory inside computers.
- 💰 SRAM is more expensive than DRAM due to its complexity and lower density, which leads to higher costs per memory bit.
- 🔋 SRAM consumes less power than DRAM, but at higher frequencies, their power consumption becomes comparable.
- 🧠 DRAM stores memory bits using one transistor and one capacitor, requiring refresh cycles to maintain data due to charge leakage.
- 🔄 DRAM read operations are destructive, meaning the data must be refreshed after every read to avoid data loss.
- ⏱️ Precharging DRAM bit lines helps reduce read time by starting the read process closer to the target voltage.
- 🔧 SRAM uses six transistors to store each memory bit, which does not require refresh cycles, making it faster than DRAM.
- 🔁 Two bit lines in SRAM improve the speed of both read and write operations by differentiating and amplifying voltages quickly.
- 🏎️ The lack of capacitors in SRAM allows for faster transitions between logic states, making SRAM faster than DRAM in terms of speed.
Q & A
What are the two common types of RAM discussed in the video?
-The two common types of RAM discussed are SRAM (Static RAM) and DRAM (Dynamic RAM).
Why is DRAM called 'Dynamic' RAM?
-DRAM is called 'Dynamic' because it requires periodic refresh cycles to retain data due to charge leakage from the capacitors storing the memory bits.
Where are SRAM and DRAM typically used in computers?
-SRAM is typically used as cache memory because of its speed, while DRAM is used as the main memory in computers.
Why is SRAM faster than DRAM?
-SRAM is faster because it does not involve capacitors that need to charge and discharge. Instead, it uses cross-coupled inverters for memory storage, which enables faster read/write operations.
What is the main reason SRAM is more expensive than DRAM?
-SRAM is more expensive because it requires six transistors per memory cell, whereas DRAM uses only one transistor and one capacitor per cell, making SRAM's cost per bit higher.
What are the primary differences in power consumption between SRAM and DRAM?
-SRAM consumes less power than DRAM under typical conditions, but when operated at higher frequencies, the power consumption of SRAM and DRAM becomes comparable.
How does DRAM store data, and what challenge arises from this method?
-DRAM stores data in the form of charge across a capacitor. The challenge is that capacitors gradually lose their charge due to leakage, requiring periodic refresh cycles to retain data.
What makes the read operation in DRAM 'destructive,' and how is this problem addressed?
-The read operation in DRAM is 'destructive' because reading the stored charge causes the capacitor to lose its charge. To address this, a refresh operation is performed after every read cycle to restore the charge.
What role do pass transistors play in DRAM and SRAM?
-In DRAM, the pass transistor controls access to the capacitor, allowing data to be read or written. In SRAM, the pass transistors provide access to the bit lines for reading and writing data from the cross-coupled inverters.
Why is the density of DRAM higher than that of SRAM?
-The density of DRAM is higher because each DRAM cell uses only one transistor and one capacitor, whereas SRAM requires six transistors per cell, which increases the area and reduces the density.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)