Tableau Data Modeling and Layers (Physical & Logical) | #Tableau Course #33
Summary
TLDRThe video provides an introduction to data modeling in Tableau, explaining how to work with both the physical and logical layers of data. It covers four methods to combine tables: joins, unions, relationships, and data blending. The physical layer allows joins and unions between tables, while the logical layer uses relationships to abstract data and simplify visualizations. The video also touches on how to navigate between these layers and introduces data blending for combining data from different sources at the visualization level.
Takeaways
- 📊 **Data Modeling in Tableau**: Tableau allows creating a data model from a data source which can include multiple tables.
- 🔗 **Four Methods of Combining Tables**: Tableau offers relationships, joins, unions, and data blending to combine tables.
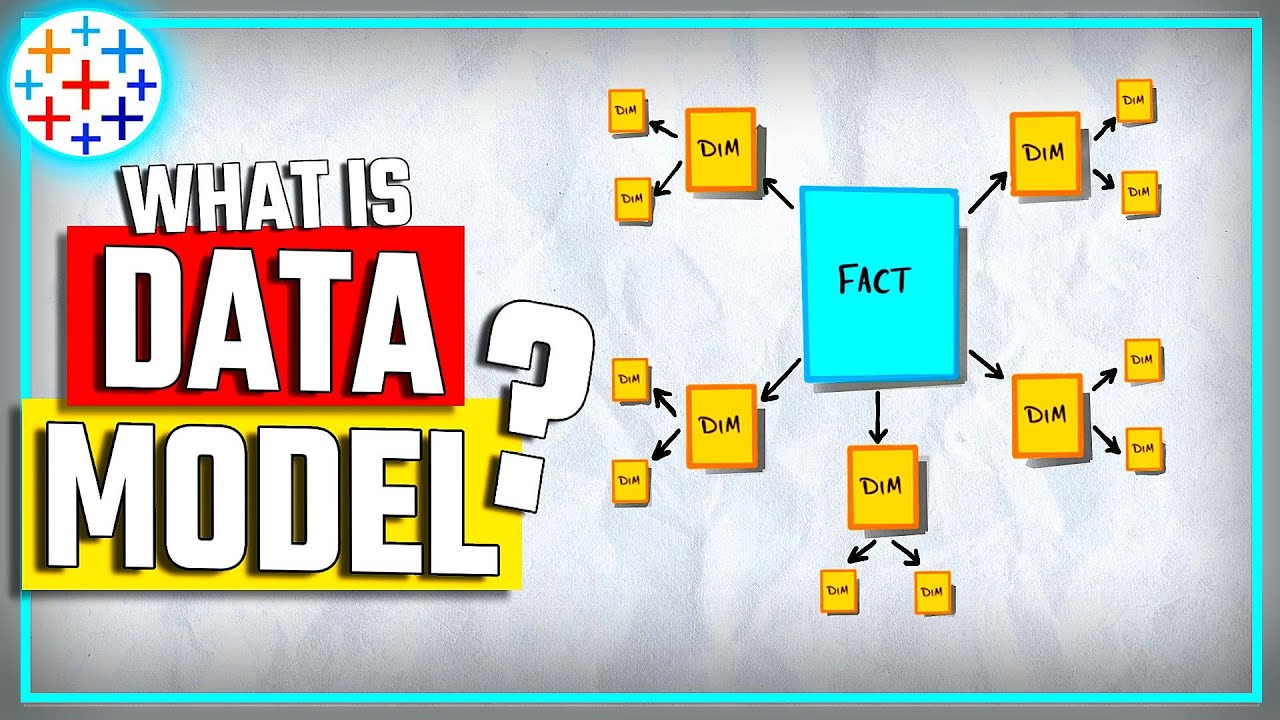
- 🏗️ **Physical and Logical Layers**: Tableau's data model consists of a physical layer with the actual data tables and a logical layer that abstracts these details.
- 🔄 **Joins and Unions in the Physical Layer**: In the physical layer, tables can be combined using joins or unions.
- 📚 **Logical Layer Abstraction**: The logical layer presents a single table (logical table) that can represent multiple physical tables, simplifying the data for visualizations.
- 🔗 **Relationships in the Logical Layer**: Relationships are used in the logical layer to connect logical tables, but they do not merge them into one.
- 🌐 **Data Blending at Visualization Level**: Data blending is used to combine data from different data sources for a single visualization.
- 📑 **Navigating Layers**: Users can navigate between the physical and logical layers within Tableau's data source page.
- 🔍 **Understanding Table Composition**: By hovering over icons in Tableau, users can see how logical tables are composed of physical tables.
- 🎥 **Supporting the Channel**: The script encourages viewers to like, comment, and support the content to help with YouTube algorithm visibility.
Q & A
What is a data model in Tableau?
-A data model in Tableau is a structure that defines how different tables in a data source are connected, helping organize and manage the relationships between tables for visualization.
What happens when your data contains only one table in Tableau?
-When your data contains only one table, the data model is very simple, with a single table representing the entire data source.
What are the four methods Tableau offers for connecting and combining tables?
-Tableau offers four methods for connecting and combining tables: relationships, joins, union, and data blending.
What is the difference between the physical layer and the logical layer in Tableau's data model?
-The physical layer consists of physical tables that can be joined or combined using unions, while the logical layer abstracts these physical tables into logical tables to simplify visualization by hiding underlying details.
How can tables be combined in the physical layer in Tableau?
-In the physical layer, tables can be combined using either joins or unions.
What is the role of relationships in the logical layer?
-In the logical layer, relationships are used to connect logical tables without merging them into one table, which allows each logical table to maintain its own structure.
How do joins and unions work in the physical layer?
-Joins in the physical layer combine rows from multiple tables based on a common field, while unions stack data from similar tables vertically, adding rows from one table to another.
What is data blending in Tableau?
-Data blending in Tableau is a method used to combine data from different data sources or data models at the visualization level, allowing for unified analysis.
How can you navigate between the physical and logical layers in Tableau?
-To navigate between the physical and logical layers, you can double-click on a logical table to enter the physical layer, and close it to return to the logical layer.
What are the steps involved in adding tables to the logical and physical layers?
-In the logical layer, tables are added as logical tables and connected using relationships. In the physical layer, tables can be added and combined using joins or unions.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)