Pertemuan 2 : Citra Digital, Sampling, dan Quantization - Part 3 : Komponen fundamental dalam PCD
Summary
TLDRThe video discusses the steps involved in digital image processing, dividing them into two main categories: low-level processes like image acquisition, filtering, and enhancement, and higher-level tasks such as object segmentation and recognition. It highlights key components, including sensors and digitizers, which capture and convert energy into digital data. The video explains the hardware and software required for processing, storing, and transmitting digital images, making comparisons to general digital data handling. Lastly, it outlines methods such as color processing, compression, and morphological processing to enhance or manipulate images.
Takeaways
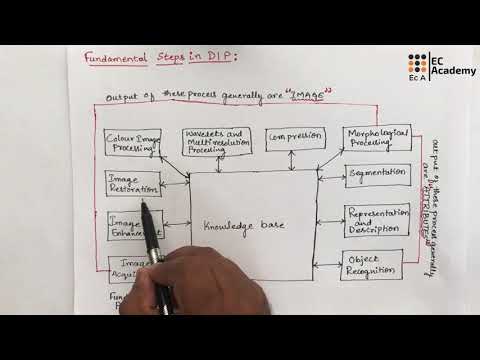
- 🖼️ Image processing involves various steps and sub-processes, categorized into three paradigms.
- 📸 The process begins with image acquisition, which is influenced by the problems to be solved in digital image processing.
- 🔍 Low-level processing includes fundamental steps like image filtering, enhancement, and restoration.
- 🎨 Color image processing involves changes in color space and includes techniques like color splash.
- 🔄 Multi-resolution and frequency domain processing techniques are used for specific image types.
- 🗜️ Compression is a fundamental step to manage large digital image sizes for efficient storage and transmission.
- 🔧 Morphological processing is a type of low-level or bit-level processing.
- 📏 High-level processing aims to extract attributes and descriptions from images, moving from image improvement to object recognition.
- 💻 A complete digital image processing system includes components for capturing, processing, displaying, storing, and transmitting images.
- 🔄 The system requires specialized hardware and software to handle digital image data effectively.
- 🔎 To capture digital images, physical sensors and digitizers are essential to convert energy emitted by objects into digital form.
Q & A
What is the first step in digital image processing as mentioned in the script?
-The first step in digital image processing is image acquisition, which involves capturing the image digitally, influenced by the problem domain being addressed.
How are digital image processing steps categorized?
-Digital image processing steps are categorized into two levels: low-level processing, which includes operations like image filtering and enhancement, and high-level processing, which includes tasks such as segmentation and object recognition.
What are some fundamental processes in the low-level stage of digital image processing?
-Fundamental processes in the low-level stage include image filtering, image enhancement, image restoration, color image processing, and multi-resolution analysis using methods like wavelets.
Why is image compression important in digital image processing?
-Image compression is important to reduce the size of digital images, making storage and transmission more efficient, especially when dealing with large amounts of data.
What role does morphological processing play in image processing?
-Morphological processing is used to extract image components useful for representation and description, such as boundaries and skeletons of objects.
What is image segmentation, and why is it important?
-Image segmentation is the process of separating different regions or objects in an image. It is important because it helps isolate and identify meaningful objects within the image for further analysis or recognition.
What happens after the segmentation stage in image processing?
-After segmentation, the process moves to object representation and description, where the attributes of the segmented objects are analyzed, followed by object recognition, where the system attempts to identify or classify these objects.
What are the components of a complete digital image processing system?
-A complete digital image processing system consists of sensors for image capture, hardware capable of processing the image data, software for manipulating the images, display systems for visualization, storage components, and networking systems for transmission of images.
What is the function of a sensor in digital image acquisition?
-A sensor detects the energy (such as light) emitted by an object, which is then converted into a digital form by a digitizer for further processing.
How does a digitizer work in the context of image acquisition?
-A digitizer converts the signals received from a sensor (e.g., light intensity captured by a camera sensor) into digital data that can be processed by a computer to form a digital image.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Pertemuan 2 : Citra Digital, Sampling, dan Quantization - Part 1 : Apa itu citra digital ?

Parallel Computing Final project
DIP#3 Fundamental steps in Digital image processing || EC Academy

PENGANTAR PERKULIAHAN PENGOLAHAN CITRA DIGITAL [Pert. 1]

Tutorial Geobia for ArcGIS

Konsep Dasar Citra Digital - Perkuliahan Pengolahan Citra Digital #01
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)