Iodine Test For Starch Practical Experiment
Summary
TLDRThe iodine test is a biochemical method to differentiate certain polysaccharides like starch and glycogen from monosaccharides and cellulose. It involves using a diluted Lugol's iodine solution, which reacts with helical glucose chains in polysaccharides to produce distinct colors. Amylose in starch shows a blue-black color, while amylopectin gives an orange-yellow hue. This test is also used to confirm starch formation in plants during photosynthesis, with a negative result for cellulose due to its linear structure preventing iodine interaction.
Takeaways
- 🌟 The iodine test is a biochemical test used to detect and distinguish certain polysaccharides from monosaccharides and other types of polysaccharides.
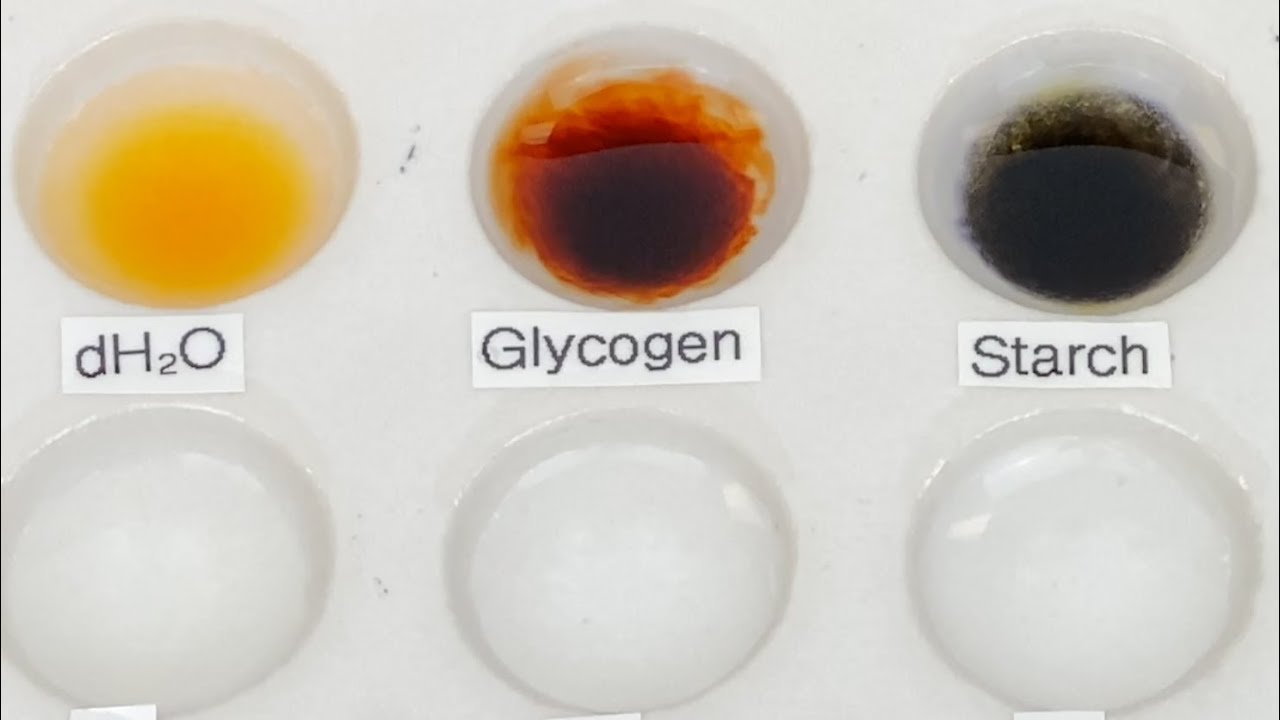
- 🔍 A positive iodine test is indicated by the development of color, which varies depending on the type of polysaccharide: amylose turns blue-black, amylopectin orange-yellow, dextrin red, and glycogen reddish-brown.
- 📚 The iodine test was first described by J.J. Cullen and H.F. Gottierdo in 1814, and independently by F. Stromer in 1815.
- 🧪 The reagent used in the iodine test is a diluted form of Lugol's iodine, an aqueous solution of elemental iodine and potassium iodide.
- 🌿 Polysaccharides like starch, dextrin, and glycogen are made up of many alpha D-glucose units linked by alpha 1-4 glycosidic bonds, forming 3D spiral structures.
- 🍠 Starch is composed of two fractions: amylose (linear chain) and amylopectin (branched chain), with amylose forming a colloidal dispersion in hot water.
- 🧬 The iodine test works on the principle that polyiodide ions form colored absorption complexes with the helical chains of glucose residues in certain polysaccharides.
- 🌈 The color produced in the iodine test depends on factors like glucose chain length, temperature, presence of water-miscible organic compounds, and pH.
- 🌱 The iodine test is used in plant physiology to indirectly check if a plant is photosynthesizing by detecting the presence of starch.
- 🔬 The test involves adding a dilute iodine solution to various test samples and observing any color change, with starch turning blue-black, confirming its presence.
Q & A
What is the iodine test used for?
-The iodine test is a biochemical test used to detect and distinguish certain polysaccharides such as starch, dextrin, and glycogen from monosaccharides, disaccharides, and other polysaccharides like cellulose.
What is the difference between a positive and negative iodine test?
-A positive iodine test is indicated by the development of color depending on the type of polysaccharide, while a negative test shows no color change, retaining the original iodine color.
What colors do different polysaccharides produce in a positive iodine test?
-Amylose gives a blue-black color, amylopectin gives an orange-yellow color, dextrin gives a red color, and glycogen gives a reddish-brown color.
Who first described the iodine test?
-The iodine test was first described by J.J. Cullen and H.F. Gottierdo Clubri in 1814, and independently by F. Stormer in 1815.
What is the reagent used in the iodine test?
-The reagent used in the iodine test is a very diluted form of Lugol's iodine, also known as aqueous iodine.
Why was Lugol's iodine created?
-Lugol's iodine was created because elemental iodine is insoluble in water, and the addition of potassium iodide results in a reversible reaction that forms soluble polyiodide ions.
How does the iodine test work with starch?
-The iodine test works with starch because the polyiodide ions present in the iodine solution form colored absorption complexes with the helical chains of glucose residues in starch.
Why does starch appear blue-black with iodine, even though it contains both amylose and amylopectin?
-Starch appears blue-black with iodine because the amylose component forms a very dark blue-black complex that is intense enough to mask the orange-yellow color formed by amylopectin.
What is the role of charge transfer complexes in the iodine test?
-Charge transfer complexes are believed to be responsible for the color changes that occur in the iodine test. They form between the helical amylose and polyiodide ions, resulting in the transfer of charge that excites the electrons of the acceptor molecules, which then emit radiation in the visible spectrum.
Why does cellulose not give a positive iodine test?
-Cellulose does not give a positive iodine test because its beta-D-glucose units are linked by beta-1,4 glycosidic linkages, forming long linear chains instead of a helix, leaving no room for polyiodide ions to slip in and form colored complexes.
How can the iodine test be used in plant physiology experiments?
-The iodine test can be used in plant physiology experiments as an indirect test to check if a plant is photosynthesizing by confirming the presence of starch, which is formed as a reserved food material in the leaves of plants during photosynthesis.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Iodine Test - a qualitative test to find polysaccharides

What are polysaccharides?

Lesson 4: Biomolecules-Carbohydrates (Part 1)
Iodine Test for Polysaccharides 2.0

Uji Karbohidrat - Molisch, Iodium, Barfoed, Benedict, Seliwanoff, dan Osazon

Chemia życia 3 🧪 Węglowodany czyli cukry 🍬 - biologia matura rozszerzona
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)