Addison's vs Cushing's | Endocrine System (Part 2)
Summary
TLDRThis educational video delves into the endocrine system, contrasting Addison's and Cushing's diseases. Addison's disease is characterized by insufficient corticosteroid production, leading to symptoms like fatigue and hypotension, and is treated with steroid replacement. Conversely, Cushing's syndrome results from corticosteroid excess, often caused by tumors, and manifests as weight gain, hypertension, and muscle weakness. Treatment options include surgery, hormone regulation, and radiation therapy.
Takeaways
- 🔎 The video discusses Addison's and Cushing's syndromes, two disorders related to the endocrine system's corticosteroid production.
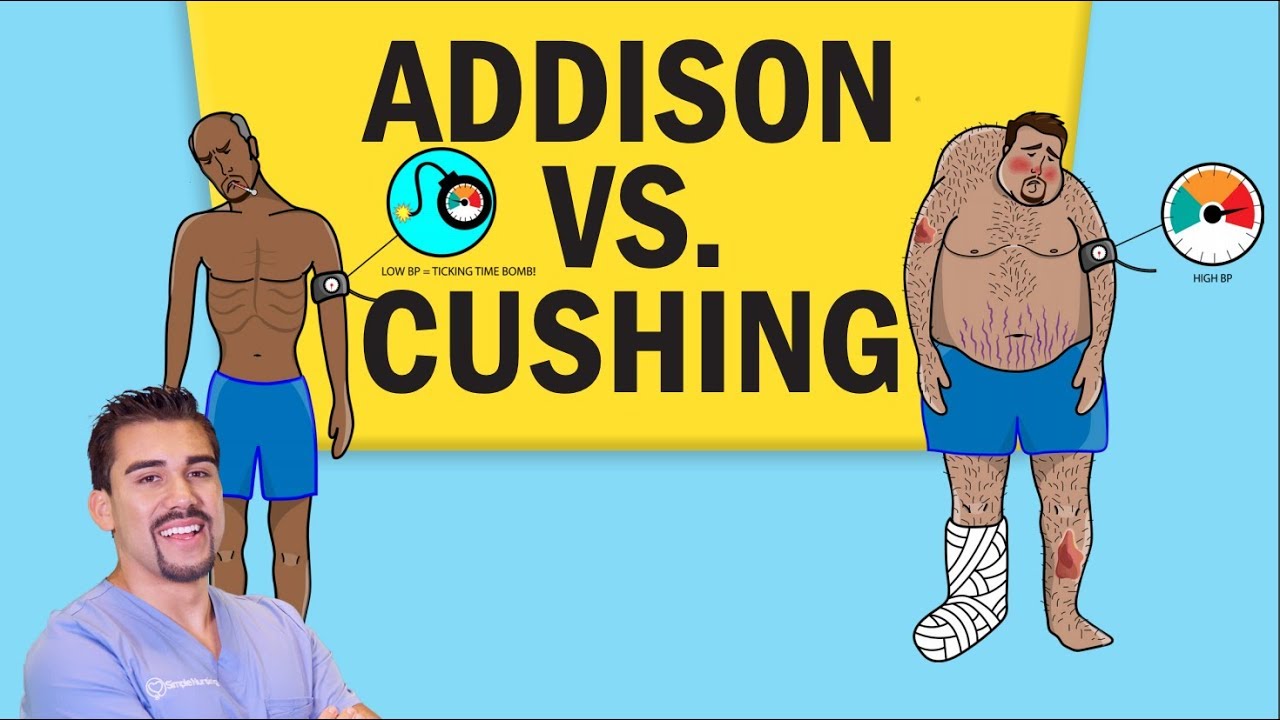
- 🌟 Addison's disease is characterized by insufficient production of cortisol and aldosterone, leading to chronic adrenal dysfunction.
- 🏥 Primary causes of Addison's include damage to adrenal cortex from autoimmune diseases, cancer, trauma, and drugs.
- 🧬 Secondary causes involve interference with hormone secretion, often due to pituitary or hypothalamic disorders.
- 💊 Long-term steroid use can lead to tertiary Addison's, where the adrenal glands fail to resume cortisol production.
- 📉 Addison's symptoms include fatigue, hypotension, and hypoglycemia, often requiring a cosyntropin stimulation test for diagnosis.
- 💊 Treatment for Addison's involves steroid replacement, fluid and glucose replacement to prevent cardiovascular collapse.
- 🆚 Cushing's syndrome is the opposite, with excessive production of corticosteroids, often due to tumors or long-term steroid use.
- 📈 Cushing's symptoms include hypertension, osteoporosis, immune suppression, and a characteristic 'moon face' appearance.
- 🧪 Diagnosis of Cushing's involves a 24-hour urine cortisol test and dexamethasone suppression test to evaluate cortisol levels.
- 🩺 Treatment for Cushing's aims to control the cause, which may include surgery, radiation therapy, or adjusting steroid dosages.
Q & A
What are the two main disorders discussed in the video?
-The two main disorders discussed in the video are Addison's disease and Cushing's syndrome.
How do Addison's disease and Cushing's syndrome differ in terms of corticosteroid production?
-Addison's disease is characterized by inadequate secretion of glucocorticoids (cortisol) and mineral corticoids (aldosterone), while Cushing's syndrome is marked by an overproduction of these hormones.
What is the role of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and adrenal glands in the endocrine system as discussed in the video?
-The hypothalamus releases corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), which signals the pituitary gland to release adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). ACTH then stimulates the adrenal cortex to release cortisol, aldosterone, and androgens.
What are the primary causes of Addison's disease?
-Primary causes of Addison's disease include damage to the adrenal cortex due to idiopathic autoimmune diseases, metastatic cancer, trauma, sepsis, AIDS, and certain drugs.
What is an Addisonian crisis?
-An Addisonian crisis is an acute exacerbation of adrenal insufficiency that can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
What are the signs and symptoms of Addison's disease mentioned in the video?
-Signs and symptoms of Addison's disease include headache, fatigue, anorexia, depression, nausea, vomiting, fever, hair loss, hyperpigmentation, hypotension, and shock.
How is Addison's disease diagnosed?
-Addison's disease is diagnosed through a combination of symptoms, lab tests (CBC, CMP, ABG, cortisol, and aldosterone levels), and the cosyntropin stimulation test.
What are the treatment approaches for Addison's disease?
-Treatment for Addison's disease involves steroid replacement, fluid and glucose replacement, and sometimes the use of vasopressors until volume is restored.
What are the causes of Cushing's syndrome?
-Causes of Cushing's syndrome include adrenal cortex tumors, pituitary tumors leading to excessive ACTH production, long-term steroid use, and ectopic ACTH production from non-endocrine tumors.
What is the significance of the acronym 'BIG' in the context of Cushing's syndrome?
-The acronym 'BIG' stands for Blood pressure elevation, Inhibition of bone formation, Immune suppression, and Gluconeogenesis, lipolysis, and protein lysis, which are key features of Cushing's syndrome.
How is Cushing's syndrome diagnosed?
-Cushing's syndrome is diagnosed through tests such as the 24-hour urine free cortisol test, dexamethasone suppression test, and imaging studies like MRI.
What are the treatment options for Cushing's syndrome?
-Treatment options for Cushing's syndrome depend on the cause and may include reducing steroid dosage, surgery to remove tumors, radiation therapy, and lifelong hormone replacement therapy.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Addisons vs Cushing's Disease for NCLEX RN

Overview and Anatomy & Physiology | Endocrine System (Part 1)

gangguan pada sistem endokrin/hormonal | biologi sma kelas 11 bab.sistem endokrin utbk

SISTEM ENDOKRIN : BIOLOGI SMA KELAS 11

IPD 2.1 Peny Kelenjar Adrenal dr. aron (8/5/25)

The Mindmap Method- Exposing My Full Process for Effective Studying
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)