C1.3 Photosynthesis [IB Biology SL/HL]
Summary
TLDRThis script explains the critical role of photosynthesis in energy conversion and food chain formation. It highlights how producers transform light energy into chemical energy, primarily as glucose, using water and carbon dioxide, with oxygen as a byproduct. The script also delves into pigments' role in light absorption, the significance of the oxygen byproduct in Earth's atmosphere, and explores methods to measure photosynthesis rates, including the impact of factors like carbon dioxide concentration, light intensity, and temperature.
Takeaways
- 🌿 Photosynthesis is the process by which producers convert light energy into chemical energy, forming the base of the food chain.
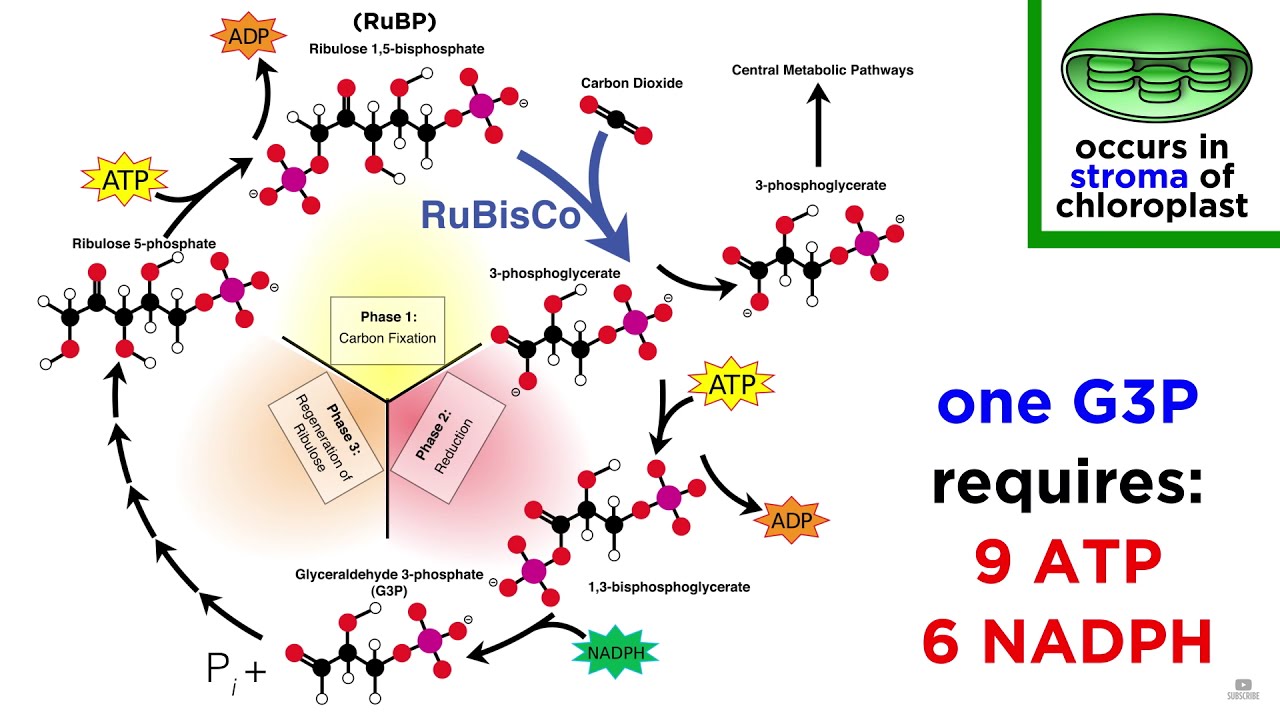
- 🔄 Chemical energy is often in the form of glucose, produced by converting water and carbon dioxide into glucose with oxygen as a byproduct.
- 💧 The oxygen byproduct from photosynthesis is a result of photolysis, where light energy is used to break water molecules.
- 🌱 Producers are essential for both energy conversion and oxygen production, which significantly altered Earth's atmosphere.
- 🌈 Pigments in photosynthetic organisms absorb different wavelengths of light, crucial for the process of photosynthesis.
- 🔬 Chromatography can be used to separate and study different pigments found in plants and algae.
- 📊 The RF value, or retention factor, helps identify pigments by measuring their movement relative to a solvent in chromatography.
- 🌱 Colors are how our brain perceives different wavelengths of light, while pigments absorb and reflect these wavelengths.
- 📈 Chlorophyll, the main pigment in plants, absorbs blue and red light well but not green, which is why it appears green to our eyes.
- 🌡 Limiting factors such as carbon dioxide concentration, temperature, and light intensity can affect the rate of photosynthesis.
- 🌳 Measuring photosynthesis rates can be done through oxygen production or carbon dioxide consumption, with aquatic plants like pondweed being particularly useful for such experiments.
Q & A
What is the primary role of producers in the context of photosynthesis?
-Producers, such as plants, are crucial as they can convert light energy into chemical energy, forming the base of the food chain and providing energy that is passed along to consumers.
What is the significance of the chemical energy produced by producers?
-The chemical energy produced by producers is essential as it is used to form various biomolecules like carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, which are then utilized by other organisms in the food chain.
Why is glucose considered the product of photosynthesis in these examples?
-Glucose is highlighted as the product of photosynthesis because it is a simple sugar that serves as a primary source of energy and a building block for more complex carbohydrates.
What is the role of photolysis in photosynthesis?
-Photolysis is the process where light energy is used to break apart water molecules into hydrogen ions, electrons, and oxygen gas. The hydrogen is crucial for converting carbon dioxide into glucose.
How did the oxygen byproduct from photosynthesis impact Earth's early atmosphere?
-The oxygen byproduct from photosynthesis significantly altered the composition of Earth's atmosphere, leading to substantial changes in the planet's environment and the evolution of life.
What are pigments and how do they relate to photosynthesis?
-Pigments are molecules that absorb specific wavelengths of light. In photosynthesis, they are used to absorb light energy, which is then converted into chemical energy.
What is chromatography and how is it used to study pigments?
-Chromatography is a process used to separate pigments based on their different solubilities in a solvent. It involves transferring pigments onto chromatography paper and allowing the solvent to move up the paper, separating the pigments.
What is the Retention Factor (RF) value and how is it calculated?
-The Retention Factor (RF) value is a ratio calculated by dividing the distance a pigment traveled by the distance the solvent traveled on chromatography paper. It is used to identify different pigments based on their characteristic RF values.
How does the absorption spectrum of chlorophyll relate to the color we perceive in plants?
-Chlorophyll appears green to our eyes because it reflects green light while absorbing blue and red light. The absorption spectrum of chlorophyll shows that it is efficient at absorbing blue and red wavelengths but not green, which is why green light is reflected.
What is the difference between an absorption spectrum and an action spectrum for chlorophyll?
-While both spectra show the wavelengths chlorophyll can absorb, the absorption spectrum measures the percentage of light absorbed, whereas the action spectrum measures the rate of photosynthesis in response to different wavelengths of light.
How can photosynthesis rates be measured and what are some of the limiting factors?
-Photosynthesis rates can be measured through oxygen production or carbon dioxide consumption. Limiting factors include carbon dioxide concentration, light intensity, and temperature, which can affect the rate of photosynthesis until a maximum is reached or the conditions become too extreme.
How can one experimentally manipulate carbon dioxide concentration to study its effect on photosynthesis?
-To manipulate carbon dioxide concentration, one can remove CO2 from water by boiling and then reintroduce it by adding sodium hydrogen carbonate. This allows for testing different concentrations to observe their effect on the rate of photosynthesis.
What is a simple method to measure photosynthesis rates using aquatic plants?
-One can use aquatic plants like pondweed and count the oxygen bubbles produced during photosynthesis as an indicator of the rate. The number of bubbles correlates with the rate of photosynthesis.
How can leaf discs be used to measure photosynthesis rates?
-Leaf discs can be used by observing how quickly they float to the surface of water after photosynthesis begins. As oxygen is produced, the buoyancy of the leaf disc increases, causing it to float, and the time taken to float can indicate the rate of photosynthesis.
What role do pH sensors play in measuring photosynthesis rates?
-pH sensors can measure changes in water pH due to the consumption of carbon dioxide by photosynthesizing organisms. As CO2 is consumed, the water becomes less acidic, leading to an increase in pH, which can be correlated with the rate of photosynthesis.
What are Free Air Carbon dioxide Enrichment (FACE) experiments and why are they important?
-FACE experiments are conducted on plots of land where carbon dioxide levels are manipulated to study the effects on photosynthesis and ecosystem dynamics. They are important for understanding the potential consequences of increased atmospheric CO2 levels on a larger scale.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)