Overview of Illumina Sequencing by Synthesis Workflow
Summary
TLDRThe Illumina sequencing workflow involves four main steps: sample preparation, cluster generation, sequencing, and data analysis. During sample preparation, adaptors are added to DNA fragments. Cluster generation then amplifies these fragments through bridge amplification on a flow cell. Sequencing uses fluorescently tagged nucleotides to identify bases in a massively parallel process called Sequencing-by-Synthesis. After each cycle, light signals determine the sequence of bases. The process includes multiple reads to sequence different regions of the DNA, resulting in a comprehensive analysis of hundreds of millions of clusters simultaneously.
Takeaways
- 🧬 The Illumina sequencing workflow consists of 4 main steps: sample preparation, cluster generation, sequencing, and data analysis.
- 🔗 Sample preparation involves attaching adaptors to the ends of DNA fragments, with additional motifs introduced through reduced cycle amplification.
- 🧪 Clustering is the isothermal amplification of each DNA fragment molecule on a flow cell, which is a glass slide with lanes coated with two types of oligos.
- 🔄 Hybridization occurs when one of the oligos binds to the adapter region of the DNA fragment, enabling polymerase to create a complementary strand.
- 🔬 Clonal amplification is performed through bridge amplification, where the strand folds over and hybridizes to a second oligo, forming a double-stranded bridge.
- 🔄 The double-stranded bridge is denatured to produce two single-stranded DNA molecules tethered to the flow cell, repeating this process for millions of clusters.
- 🧹 After amplification, reverse strands are cleaved and washed away, leaving only forward strands with their three prime ends blocked to prevent unwanted priming.
- ✨ Sequencing-by-Synthesis begins by extending a sequencing primer with fluorescently tagged nucleotides, which emit light signals based on the base calls.
- 📊 Hundreds of millions of clusters are sequenced in parallel, generating massive amounts of data.
- 🔄 After completing the first read, index reads are performed for further sequencing, and the process repeats with read 2 until the desired read length is achieved.
Q & A
What are the four basic steps of the Illumina sequencing workflow?
-The four basic steps of the Illumina sequencing workflow are sample preparation, cluster generation, sequencing, and data analysis.
What is the purpose of adding adaptors to DNA fragments during sample preparation?
-Adaptors are added to the ends of DNA fragments during sample preparation to enable the binding of DNA to the flow cell and to introduce motifs necessary for sequencing, such as sequencing binding sites and indices.
What is bridge amplification, and why is it important in Illumina sequencing?
-Bridge amplification is a process where single-stranded DNA folds over and hybridizes with oligos on the flow cell, allowing for the amplification of DNA fragments. It is important because it generates clonal amplification, creating millions of identical copies of each DNA fragment for sequencing.
What is the purpose of the two types of oligos on the flow cell?
-The two types of oligos on the flow cell serve to bind the adapter regions of the DNA fragments. One oligo hybridizes to the adapter region on the fragment strand, while the other facilitates the folding and amplification process during bridge amplification.
How does the Sequencing-by-Synthesis (SBS) method work in Illumina sequencing?
-Sequencing-by-Synthesis (SBS) is a method where fluorescently tagged nucleotides are incorporated into the growing DNA strand one at a time, based on the template sequence. After each nucleotide is added, a fluorescent signal is emitted, which is used to determine the base call.
What role do fluorescently tagged nucleotides play in the sequencing process?
-Fluorescently tagged nucleotides are used to identify the specific base incorporated into the DNA strand during sequencing. As each nucleotide is added, it emits a characteristic fluorescent signal, allowing the sequencing machine to determine the sequence of bases in the DNA fragment.
What is the significance of blocking the three prime ends of the forward strands after bridge amplification?
-Blocking the three prime ends of the forward strands prevents unwanted priming during sequencing, ensuring that only the desired strands are extended during the sequencing process.
How is the index read performed in Illumina sequencing?
-The index read is performed by introducing an index read primer, which hybridizes to the template. The sequencing steps are then carried out in a similar manner as the first read to generate the index sequence, which helps in identifying and differentiating samples.
What happens to the DNA fragments after the first read is completed?
-After the first read is completed, the read product is washed away, and a new primer is introduced for the index read. Once the index read is completed, the process is repeated for the second read, after which the reverse strand is cleaved and washed away.
Why is clonal amplification essential for Illumina sequencing?
-Clonal amplification is essential because it creates millions of identical copies of each DNA fragment, ensuring that the sequencing signal is strong and clear. This allows for accurate base calling during the sequencing process.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Introduction to Next Generation Sequencing
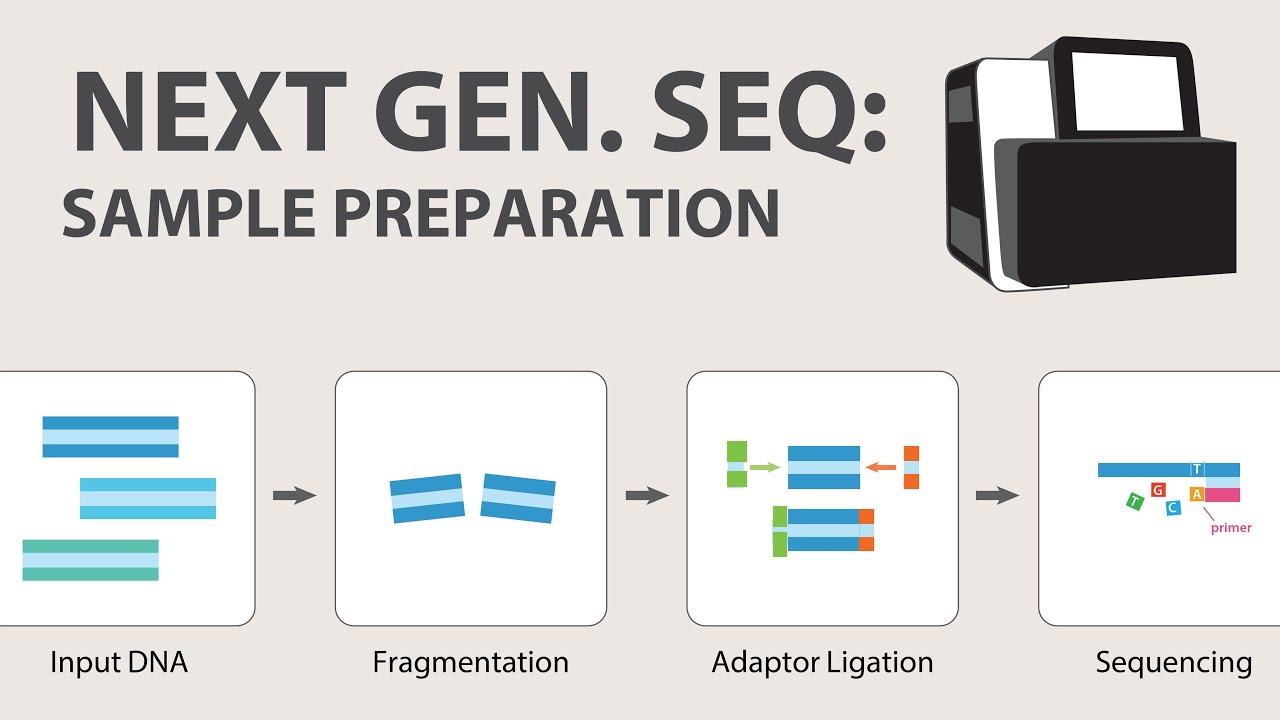
2) Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) - Sample Preparation

Illumina sequencing | DNA sequencing by synthesis
Next Generation Sequencing - A Step-By-Step Guide to DNA Sequencing.

Illumina Experts: Preventing Contamination

5) CRISPR Cas9 - Screening and Validation Strategies
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)