Muscles of the face and scalp: Anatomy
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the muscles responsible for facial expressions, beginning with an overview of the scalp's structure and layers. It details key muscles like the occipitofrontalis, orbicularis oculi, and buccinator, explaining their origins, functions, and innervation by the facial nerve. Viewers learn how these muscles enable expressions like smiling, frowning, and eyebrow movement. The video also discusses muscles involved in lip and chin movements, emphasizing how each contributes to non-verbal communication. This informative guide aids in understanding facial anatomy, especially for students and clinicians.
Takeaways
- 😀 Facial expressions are an essential way of communication, revealing emotions like happiness or curiosity.
- 🧠 The scalp consists of five layers: Skin, Connective tissue, Aponeurosis, Loose connective tissue, and Pericranium.
- 🧍 Facial muscles originate from the mesoderm of the second pharyngeal arch and are innervated by branches of the facial nerve.
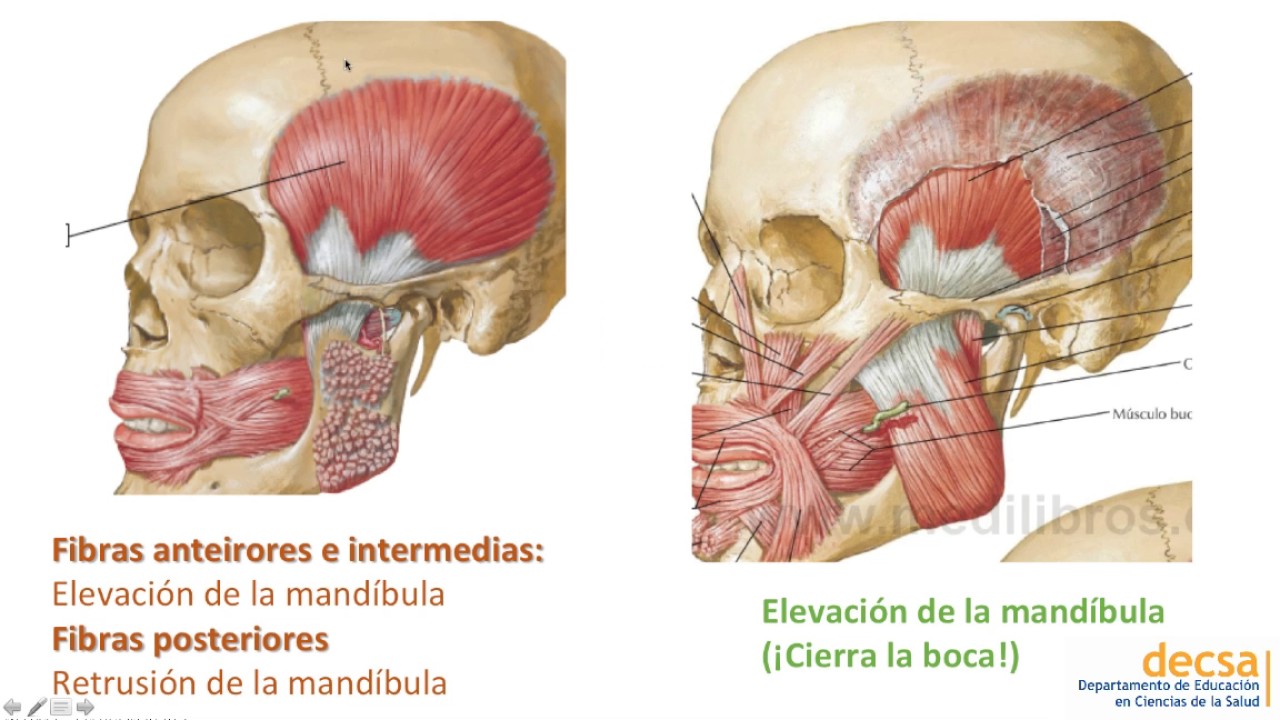
- 😲 The occipitofrontalis muscle, with its frontal and occipital bellies, elevates the eyebrows and wrinkles the forehead, showing surprise.
- 👁 The orbicularis oculi muscle has two parts: palpebral for gentle eyelid closure (blinking/sleeping) and orbital for tight closure (winking/squeezing).
- 🤔 The corrugator supercilii muscle draws the eyebrows downward and inward, creating vertical wrinkles during frowning.
- 👃 Muscles of the nose include the procerus, nasalis, and levator labii superioris alaeque nasi, which control nostril movements.
- 👄 The orbicularis oris encircles the mouth, helping close and protrude the lips (e.g., for kissing or whistling).
- 😁 Upper lip muscles like the zygomaticus major and minor elevate the lip to create a smile.
- 😐 Lower lip muscles, such as the depressor anguli oris, pull the mouth downward to express sadness or pout.
Q & A
What are facial expressions, and why are they important for communication?
-Facial expressions are movements of the facial muscles that convey emotions and reactions. They are essential for communication as they allow us to express feelings such as happiness, curiosity, or surprise without using words.
What are the five layers of the scalp, and how can they be remembered?
-The five layers of the scalp are Skin, Connective tissue, Aponeurosis (or epicranial aponeurosis), Loose connective tissue, and Pericranium. These layers can be remembered using the acronym 'SCALP,' which corresponds to the first letter of each layer.
Which cranial nerve innervates all facial muscles, and what are its branches?
-All facial muscles are innervated by the facial nerve, also known as Cranial Nerve VII. Its branches are the Posterior Auricular, Temporal, Zygomatic, Buccal, Marginal Mandibular, and Cervical nerves.
What is the function of the occipitofrontalis muscle, and how are its two bellies connected?
-The occipitofrontalis muscle functions to elevate the eyebrows and wrinkle the forehead, giving an expression of surprise. It has two bellies: the frontal and occipital bellies, which are connected by the epicranial aponeurosis.
What is the role of the orbicularis oculi muscle, and what are its two parts?
-The orbicularis oculi muscle is responsible for closing the eyelids. It has two parts: the palpebral part, which closes the eyelids gently (e.g., during blinking or sleeping), and the orbital part, which closes the eyelids tightly (e.g., when winking or squeezing the eyes shut).
Which muscle is responsible for frowning, and where is it located?
-The corrugator supercilii muscle is responsible for frowning. It is located deep in the eyebrow and pulls the eyebrows medially and inferiorly, creating vertical wrinkles at the root of the nose.
What are the three muscles of the nose, and what are their functions?
-The three muscles of the nose are the procerus, nasalis, and levator labii superioris alaeque nasi. The procerus depresses the medial ends of the eyebrows, creating transverse wrinkles on the nose. The nasalis has two parts: the transverse part narrows the nostrils, and the alar part flares the nostrils. The levator labii superioris alaeque nasi also flares the nostrils and raises the upper lip.
Which muscle encircles the mouth, and what are its functions?
-The orbicularis oris muscle encircles the mouth. It functions to close the mouth and protrude the lips, such as during kissing or whistling.
What are the muscles of the upper lip, and what are their general functions?
-The muscles of the upper lip include the risorius, levator anguli oris, zygomaticus major, zygomaticus minor, levator labii superioris, and levator labii superioris alaeque nasi. These muscles primarily elevate the upper lip and are involved in smiling, grinning, and other lip movements.
What is the function of the buccinator muscle, and where is it located?
-The buccinator muscle is located deep in the cheek and functions to press the cheek against the teeth, which is useful when drinking from a straw or during chewing. It helps maintain tension in the cheeks.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)