Blue-White Screen & Transformation
Summary
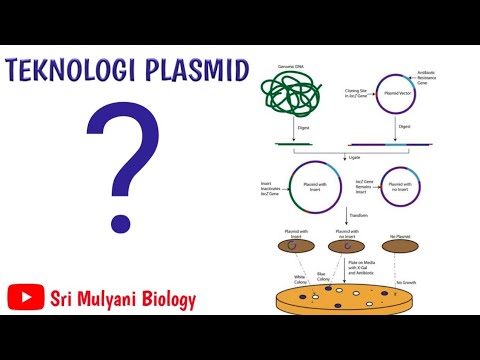
TLDRThis video explains DNA transformation and the blue-white screening technique used to detect recombinant bacteria. It covers how plasmids with genes of interest are introduced into bacteria like E. coli via heat shock. The blue-white screen uses the beta-galactosidase enzyme; blue colonies indicate non-recombinant bacteria, while white colonies show successful transformation with recombinant DNA. The video also discusses plasmid design, including ampicillin resistance and lacZ gene for screening.
Takeaways
- 🧬 DNA transformation is the process of transferring a plasmid with a gene of interest into another cell, often bacteria like E. coli.
- 🔵 The blue/white screening technique is used to detect recombinant bacteria and determine if the transformation was successful.
- 🌡️ Heat shock is a common method used to insert the plasmid into bacteria like E. coli.
- 🧬 Beta-galactosidase is an enzyme composed of two subunits, one from the bacterial genome and the other from the plasmid.
- 🌐 The presence of functional beta-galactosidase results in white colonies on X-gal plates, indicating successful transformation.
- 💊 Ampicillin resistance is a common feature of plasmids, allowing bacteria to survive on ampicillin-containing media.
- 🔄 The lacZ gene on the plasmid produces beta-galactosidase, but when the gene is cut by restriction enzymes, it produces blue colonies if intact, and white if the insert is successful.
- 🧪 Restriction sites on the plasmid allow for precise cutting to insert foreign DNA, creating recombinant DNA.
- 🌀 The blue/white screen uses X-gal and IPTG to identify successful transformations; blue dots indicate non-recombinant bacteria, white dots indicate recombinant bacteria.
- 📍 Selective media containing antibiotics and X-gal is used to isolate and culture recombinant bacteria for further study.
Q & A
What is DNA transformation?
-DNA transformation is the process during which a plasmid or vector carrying a specific gene of interest is introduced into another cell, often bacteria.
Why is E. coli commonly used for transformation?
-E. coli is commonly used for transformation because it is easy to manipulate and can be induced to take up foreign DNA through methods like heat shock.
What is the purpose of the blue/white screening technique?
-The blue/white screening technique is used to detect recombinant bacteria and determine if the transformation process was successful.
How does the blue/white screening work?
-It works by using the fact that the enzyme beta-galactosidase is composed of two subunits, one from the bacterial genome and one from the plasmid. Only when both subunits are present does the enzyme become active, leading to blue colonies on an X-gal plate.
What does the color of the colonies on an X-gal plate indicate?
-White colonies indicate the presence of a functional beta-galactosidase enzyme, suggesting successful transformation with recombinant DNA. Blue colonies indicate the absence of recombinant DNA.
What is the role of ampicillin resistance in the plasmid?
-Ampicillin resistance allows bacteria containing the plasmid to survive on ampicillin-containing media, which helps in identifying bacteria that have taken up the plasmid.
What is the lacZ gene and why is it important in the blue/white screening?
-The lacZ gene encodes for beta-galactosidase. It is important because the presence of a functional lacZ gene leads to blue colonies on X-gal plates, while a disrupted lacZ gene due to the insertion of foreign DNA leads to white colonies.
How is the restriction site used in the plasmid design?
-The restriction site in the plasmid design allows for the specific cutting of DNA by restriction enzymes, enabling the insertion of foreign DNA into the plasmid.
What happens to the lacZ gene when foreign DNA is inserted?
-When foreign DNA is inserted, part of the lacZ gene is often removed, disrupting its ability to produce functional beta-galactosidase, leading to white colonies on X-gal plates.
How can you select for recombinant bacteria using the blue/white screening?
-You can select for recombinant bacteria by picking white colonies from the X-gal plate, as they indicate successful transformation with the insertion of foreign DNA.
What is the significance of the blue dots on the X-gal plate?
-Blue dots on the X-gal plate indicate colonies that have not been successfully transformed with recombinant DNA, as they still have a functional lacZ gene.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

pembuatan hormon insulin sintetis / buatan - bioteknologi modern materi sma biologi kelas 12
TEKNOLOGI PLASMID (KLONING GEN/DNA REKOMBINAN)
Bioteknologi: Rekayasa Genetika | Biologi SMA | Alternatifa

Recombinant DNA

TEKNIK DNA REKOMBINAN (Bioteknologi Modern)

PROSES TRANSFORMASI BAKTERI (REPRODUKSI BAKTERI)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)