How Does the Internet Work ?
Summary
TLDRThe internet functions through a series of agreed-upon rules called the Internet Protocol, allowing networks and devices to connect seamlessly. Data is broken into small packets that travel across multiple paths before reaching their destination. The decentralized nature of the internet ensures reliability and resilience. Internet Exchange Points (IXPs) allow organizations to efficiently exchange traffic, reducing costs and improving speed. Peering, where companies agree to share data without selling network space, makes the internet faster and more affordable. Cooperation and neutrality are key to the internet’s success.
Takeaways
- 🌐 The internet works because of agreements and rules, known as the Internet Protocol, which allow devices to communicate seamlessly.
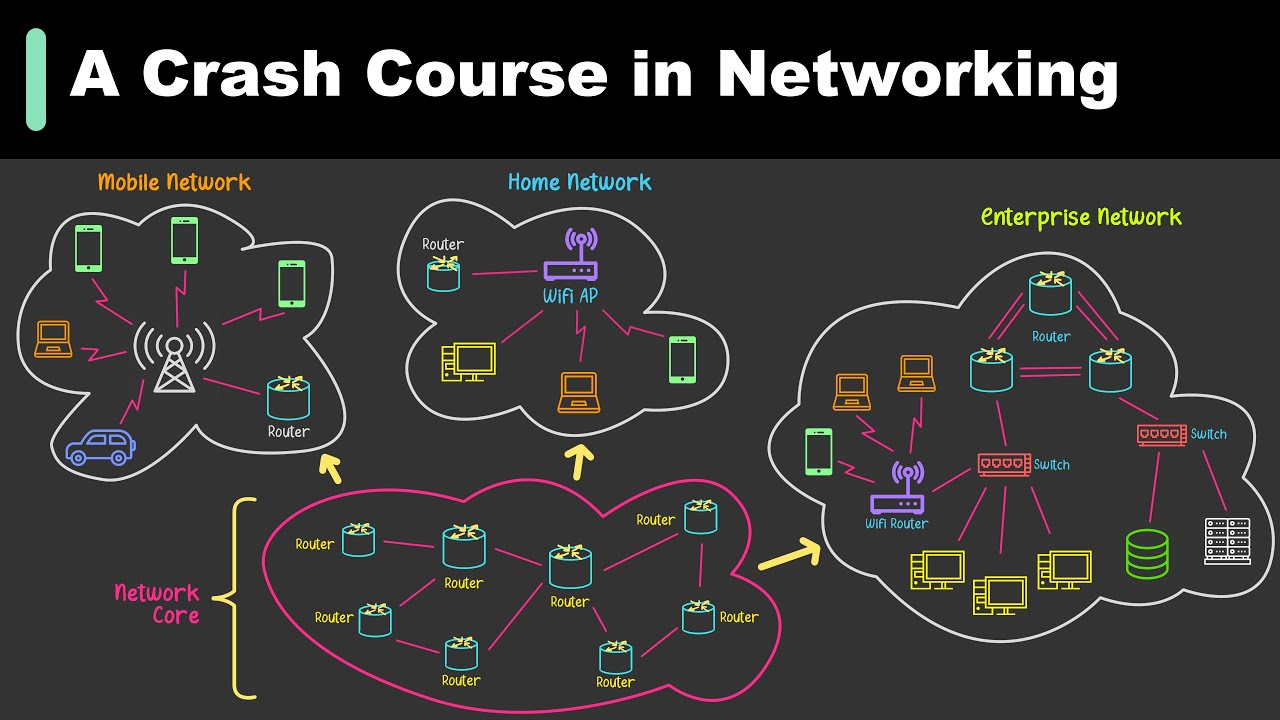
- 💻 A network is formed when two or more computers agree to follow the same rules, and the internet is a network of networks.
- 🔗 Every device on the internet has a unique address, allowing for messages to be sent from one device to another.
- 📦 Messages sent over the internet are broken down into small data packets, which can take different paths to reach their destination.
- 🛤️ The decentralized nature of the internet allows data to reroute through different paths if part of the network is blocked or overloaded.
- 🌍 Internet service providers (ISPs) and networks can connect with each other either privately or through shared platforms like internet exchange points.
- 🤝 Internet exchanges are places where different organizations connect to exchange network traffic more efficiently, saving costs and speeding up data flow.
- 💸 Providers often use a method called peering, where they exchange traffic without the need for purchasing passage, making the internet faster and more cost-effective.
- 🔄 Peering agreements are mutually beneficial and help regulate traffic, ensuring smooth and efficient communication between networks.
- ⚖️ The internet remains open, decentralized, and neutral, with no single organization controlling it, making it resilient and highly functional due to collective cooperation.
Q & A
What is networking and how does it work?
-Networking is the process of connecting two or more computers to communicate with each other. It works by having all computers follow the same rules or protocols, enabling them to exchange data and form a network.
What is the Internet Protocol (IP) and why is it important?
-The Internet Protocol (IP) is a set of rules that govern how devices communicate over the internet. It is important because it ensures that all devices follow the same guidelines, allowing them to connect and share information across the network of networks.
How does data travel across the internet?
-Data sent over the internet is broken into small packets, each containing information about its origin, destination, and content. These packets take different routes to reach their destination and are reassembled once they arrive.
What makes the internet decentralized and resilient?
-The internet is decentralized because it consists of many interconnected networks with no central control point. This structure allows data to reroute through different paths if part of the network fails, making it resilient.
What role do internet service providers (ISPs) play in data transfer between different networks?
-Internet service providers (ISPs) connect different networks by exchanging data between them. Some ISPs have private connections, while others use shared platforms like internet exchange points to make the process faster and more efficient.
What is an internet exchange point (IXP) and why is it important?
-An internet exchange point (IXP) is a physical location where multiple organizations, such as ISPs and content providers, connect their networks to exchange data traffic. IXPs help reduce costs and improve the speed and efficiency of data transfer.
What is peering, and how does it benefit internet service providers?
-Peering is an agreement between internet service providers to exchange data traffic directly without charging each other. It reduces costs for the providers and improves the flow of internet traffic by avoiding intermediary networks.
How do companies benefit from participating in internet exchange points?
-Companies benefit from internet exchange points by saving costs and improving the speed and efficiency of data transfer. By connecting in one place, they reduce the complexity and expense of making multiple connections with other providers.
How is the internet self-regulating through the peering system?
-The peering system is self-regulating because companies negotiate mutual agreements that benefit both parties. By making deals that reduce costs and improve performance, the system naturally balances itself without the need for central control.
Why is the internet considered open, decentralized, and neutral?
-The internet is open because anyone can connect to it, decentralized because no single entity controls it, and neutral because data travels freely between networks without any one organization dominating the system. This design ensures it remains accessible and reliable.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Network Protocols - ARP, FTP, SMTP, HTTP, SSL, TLS, HTTPS, DNS, DHCP - Networking Fundamentals - L6

Network Devices Explained | Hub, Bridge, Router, Switch
How the Internet Works in 9 Minutes

BAB 5 JARINGAN KOMPUTER DAN INTERNET | JARINGAN LOKAL, INTERNET, KONEKTIVITAS INTERNET | INFORMATIKA

Bab 5 - Jaringan Komputer dan Internet (JKI) | INFORMATIKA Fase E

Jaringan Komputer dan Internet (Pengantar dan Koneksi Internet) - Informatika Kelas 7 SMP/ MTs
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)