The Carbon Cycle Process
Summary
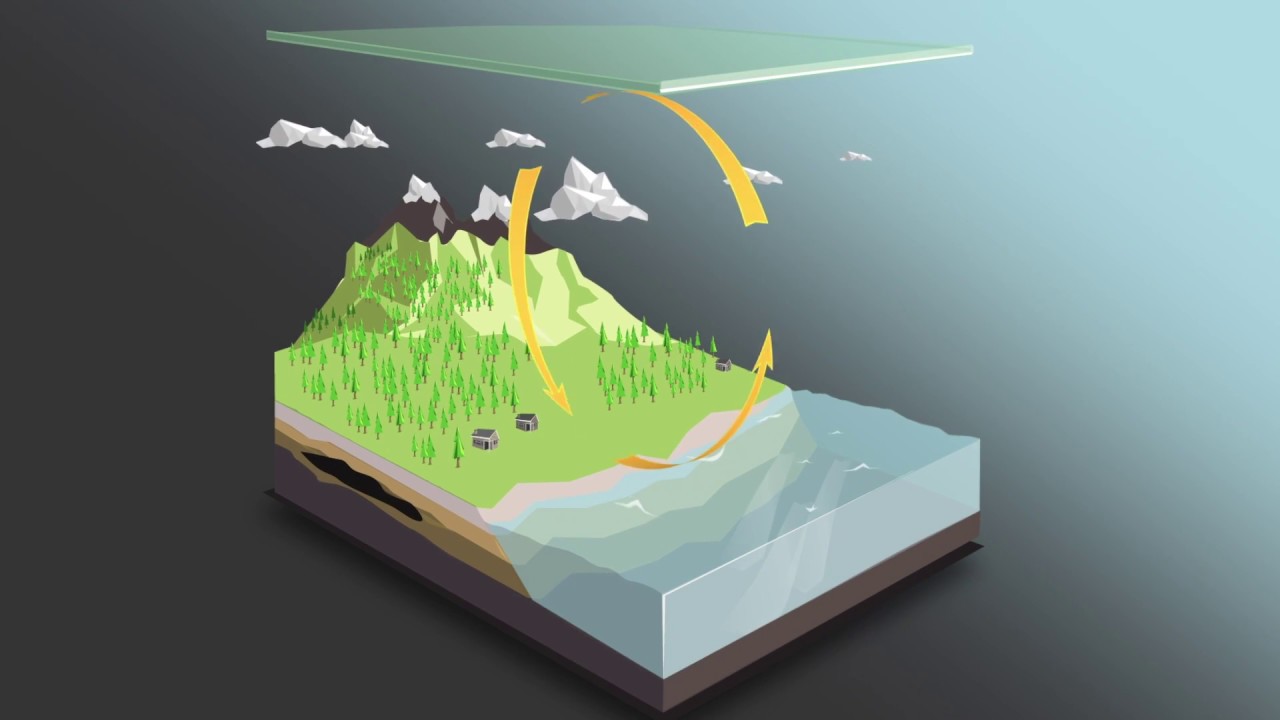
TLDRThe video script delves into the carbon cycle, highlighting carbon's journey through five key locations: the atmosphere, terrestrial biosphere, earth's interior, ocean, and human influence. It explains how carbon exists in various forms, such as CO2 and methane, and its absorption by plants and plankton for photosynthesis. The script also addresses human activities like burning fossil fuels and deforestation, which significantly impact the carbon cycle.
Takeaways
- 🌿 Carbon is essential for life on Earth and is a significant part of our atmosphere.
- 🌍 Carbon cycles through various reservoirs including the atmosphere, land, ocean, and Earth's interior.
- 🌳 Autotrophs like plants and plankton absorb atmospheric carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
- 💧 The ocean absorbs carbon dioxide and converts it into carbonic acid.
- 🐘 Animals release carbon dioxide through respiration and methane during digestion.
- 🌱 Plants and animals exchange carbon through the process of photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
- 🌋 Volcanic eruptions can release carbon stored in the Earth's lithosphere.
- 🌊 The ocean plays a critical role in carbon sequestration and has a large carbon cycle exchange.
- 🔥 Human activities such as burning fossil fuels and cement production increase atmospheric carbon dioxide.
- 🌲 Deforestation contributes to the rise in atmospheric carbon levels.
- 🌐 The carbon cycle is a complex system involving both natural processes and human influence.
Q & A
What is the significance of carbon in the context of the carbon cycle?
-Carbon is a vital element for most living organisms on Earth and a key component of our atmosphere. It cycles through various components of the Earth system, including the atmosphere, ocean, and terrestrial biosphere.
In what forms does carbon exist in the atmosphere?
-Carbon is found in the atmosphere primarily in the forms of carbon dioxide and methane.
How does the ocean absorb carbon?
-When carbon is absorbed by the ocean, it reacts with water to create carbonic acid.
What is the role of autotrophs in the carbon cycle?
-Autotrophs, such as plants and plankton, absorb atmospheric carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
What are the different paths of carbon in the terrestrial biosphere?
-In the terrestrial biosphere, carbon is exchanged between plants and animals, absorbed by plants for photosynthesis, released by animals during respiration, and stored in the soil by decomposers.
How does carbon get stored in the earth's interior?
-Carbon is stored in the earth's interior in the form of fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas, as well as in deposits such as limestone.
What is the impact of volcanic eruptions on the carbon cycle?
-Volcanic eruptions can release carbon that was previously stored in the lithosphere back into the atmosphere.
How does the ocean contribute to the carbon cycle?
-The ocean plays a significant role in the carbon cycle by absorbing carbon dioxide and hosting plankton that uses carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
How do human activities affect the carbon cycle?
-Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and producing cement, release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Deforestation also contributes to an increase in atmospheric carbon.
What is the role of plankton in the ocean's carbon cycle?
-Plankton absorbs carbon dioxide for photosynthesis, which helps in the sequestration of carbon in the ocean.
How does the carbon cycle relate to global climate change?
-The carbon cycle is closely related to global climate change as the increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide due to human activities contributes to global warming.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)