SPM Mathematics Form 4 (Number Bases) Chapter 2 Complete Revision
Summary
TLDRTeacher Daisy's video script offers an educational exploration into number bases, starting from binary to decimal. It explains the concept of digit representation in various bases and demonstrates counting balls in base 2, 3, and 10. The script delves into place values and digit values, using examples to clarify calculations. It also covers methods for converting numbers between bases, including division by place value and base value, with examples for converting to base 5 and base 8. The educational content is complemented by practical exercises on digit value calculation and number conversion, making the lesson interactive and informative.
Takeaways
- 📚 The chapter introduces various number bases, explaining that each base uses a specific number of digits (e.g., base 2 uses 0 and 1, base 10 uses 0 to 9).
- 🧮 It demonstrates counting balls in base 2, base 3, and base 10 to illustrate how different bases represent quantities.
- 🔢 The concept of place values in number bases is explained, showing how they are calculated as repeated multiplications of the base raised to the position number.
- 📈 An example is provided to calculate the place value of digits in numbers represented in base 8 and base 2.
- 🔑 The script explains digit value as the product of a digit and its place value within a number.
- 💡 Digit values for numbers in base 8 and base 2 are calculated to show how to find the value of each digit in a number.
- 🔄 The script outlines how to determine the numerical value of a number in various bases by summing the digit values.
- 🔀 Two methods for converting numbers from one base to another are discussed: division using place value and division using base value.
- 🗂️ An example shows how to convert the decimal number 563 to base 5 and base 8 using both methods, confirming they yield the same result.
- 🔄 It explains how to convert a number from any base to base 10 and then to another base, using base 6 to base 9 as an example.
- 💻 The use of a calculator for base conversions is briefly mentioned, including how to set the calculator to different base modes.
- ➕➖ The script covers addition and subtraction in different number bases, using both vertical form and conversion to base 10 as methods.
Q & A
What are the digits used in base two?
-Base two uses two digits which are zero and one.
How many digits does base ten have?
-Base ten uses 10 digits which are 0 to 9.
What is the place value of each digit in the number 6231 in base eight?
-The place values from right to left are eight to the power of zero, eight to the power of one, eight to the power of two, and eight to the power of three.
How do you calculate the digit value of a particular digit in a number?
-The digit value is calculated by multiplying the digit by its place value.
What is the number value of the number 6231 in base eight?
-The number value is calculated by summing the digit values: 6 * 512 + 2 * 64 + 3 * 8 + 1 * 1 which equals 3220.
How do you convert a base 10 number to a different base using division by place value?
-You write down the place values of the target base, starting from the rightmost digit. Then you determine how many times each place value fits into the number, writing down the quotient and carrying over the remainder to the next place value.
What is the base 5 representation of the number 563 in base 10?
-The base 5 representation of 563 in base 10 is 4223.
How can you convert a number from base 6 to base 10?
-You multiply each digit by its corresponding place value and sum up all the products to get the base 10 number.
What is the process of converting a number from base 8 to base 2?
-Each digit in base 8 is equivalent to three digits in base 2. You convert each digit into three binary digits using the values 4, 2, and 1, and then combine them.
How do you perform addition in different number bases?
-You can either write the numbers vertically and add them digit by digit, carrying over as necessary, or convert the numbers to base 10, perform the addition, and then convert the result back to the original base.
Can you provide an example of subtracting numbers in base 6?
-Yes, to subtract numbers in base 6, you can either perform the operation directly in base 6 by borrowing as necessary, or convert both numbers to base 10, perform the subtraction, and then convert the result back to base 6.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Tutorial Lengkap: Cara Konversi Bilangan Desimal ke Biner, Oktal dan Hexadesimal
Pre-Algebra 3 - Decimal, Binary, Octal & Hexadecimal
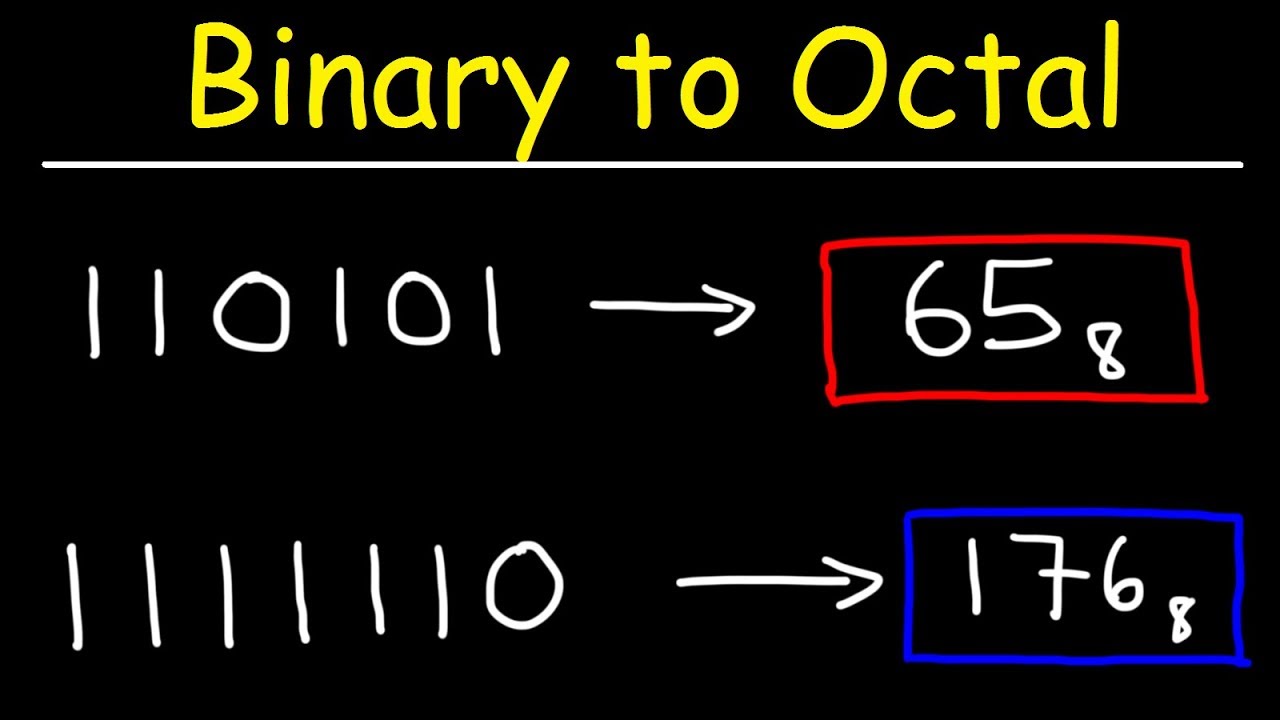
Binary to Octal Conversion
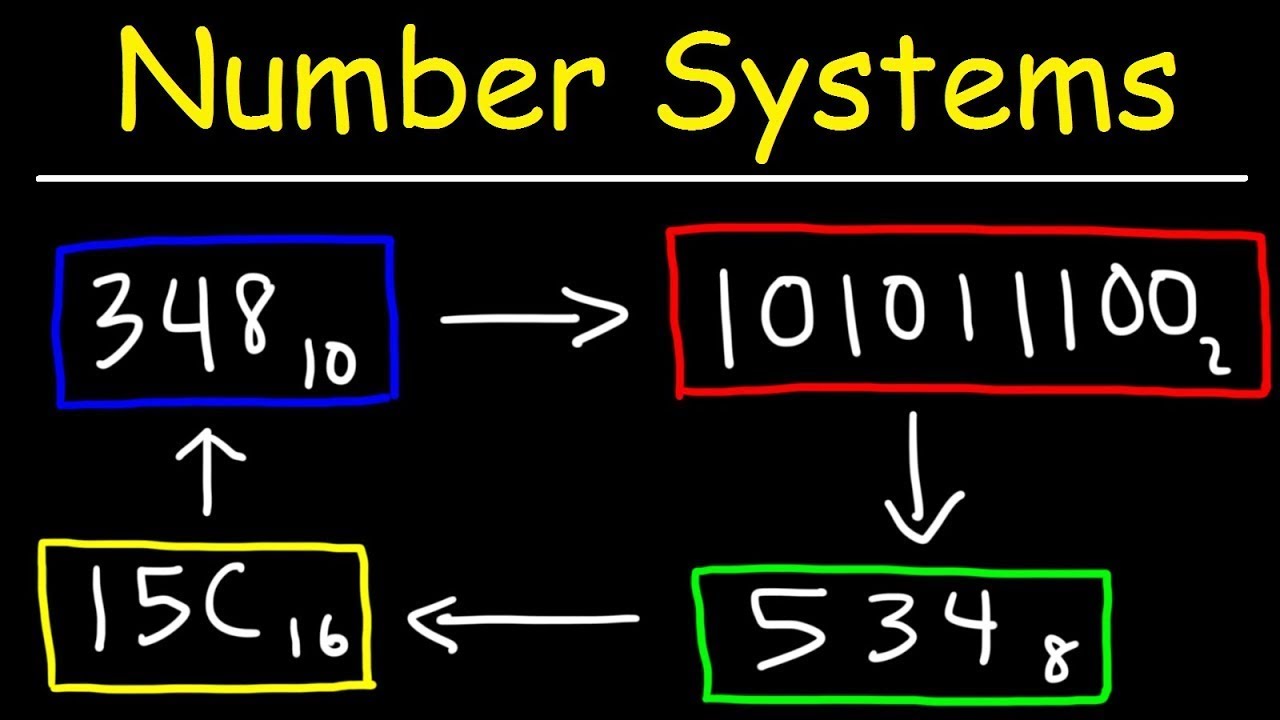
Number Systems Introduction - Decimal, Binary, Octal & Hexadecimal

[Part 1] Unit 2.1 - Binary Numbers
W2_L2_Binary representation of decimal numbers
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)