GCSE Biology - How the Eye Works (Part 2) - Accommodation #32
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the eye's accommodation process, which adjusts the lens's refractive power to focus light on the retina for clear vision at varying distances. It explains how the cornea and lens work together, with the ciliary muscles and suspensory ligaments controlling the lens's shape. The video also discusses common vision problems like hyperopia (long-sightedness) and myopia (short-sightedness), and how corrective lenses like convex and concave lenses help.
Takeaways
- 🔍 The process of accommodation is a reflex that adjusts the eye's refractive power to focus on both near and distant objects.
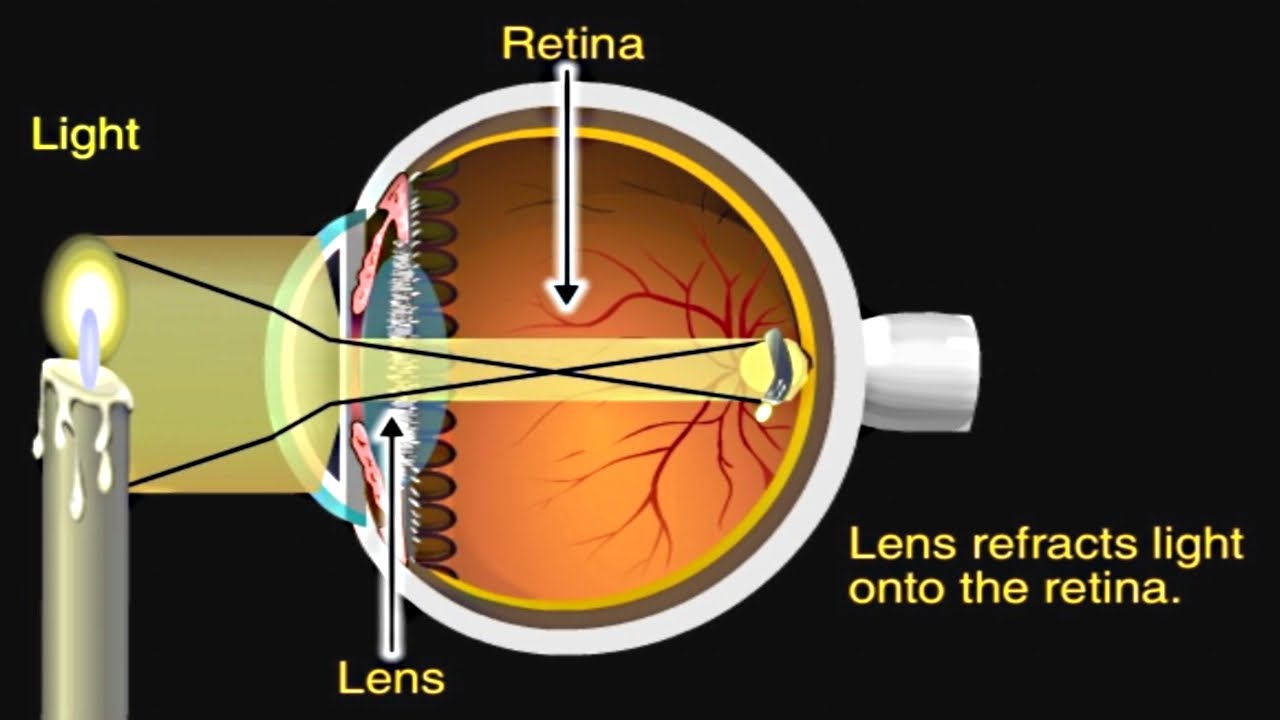
- 👁️ The cornea and the lens are the primary refractive structures in the eye, responsible for bending light to focus it on the retina.
- 💪 The ciliary muscles and suspensory ligaments control the shape of the lens, enabling it to adjust its curvature for focusing.
- 🌐 For near objects, the ciliary muscle contracts, slackening the suspensory ligaments, allowing the lens to become more curved and refract light more strongly.
- 🌌 For distant objects, the ciliary muscle relaxes, tightening the suspensory ligaments, which flattens the lens and reduces its refractive power.
- 🤓 Long-sightedness (hyperopia) occurs when the lens doesn't refract enough, causing nearby objects to appear blurry because the light is not focused on the retina.
- 🤓 Short-sightedness (myopia) happens when the lens refracts too much, causing distant objects to appear blurry as the light focuses in front of the retina.
- 👓 Convex lenses in glasses help long-sighted individuals by providing extra refractive power to focus light on the retina.
- 👓 Concave lenses in glasses correct short-sightedness by refracting light outwards, counteracting the lens's over-refraction and allowing the light to focus properly on the retina.
Q & A
What is the process of accommodation?
-Accommodation is a reflex that changes the refractive power of the lens to enable the eye to focus on both near and distant objects.
What are the key components of the eye involved in accommodation?
-The key components involved in accommodation are the cornea, the lens, the ciliary muscles, and the suspensory ligaments.
How does the cornea contribute to the process of accommodation?
-The cornea is responsible for the initial refraction of light, bending it so that it can be further focused by the lens.
What role do the ciliary muscles and suspensory ligaments play in accommodation?
-The ciliary muscles control the shape of the lens by contracting or relaxing, which in turn affects the tension of the suspensory ligaments, allowing the lens to become more or less curved for focusing.
How does the shape of the lens change when looking at a close object?
-When focusing on a close object, the lens becomes 'short and fat', meaning it is more curved, to refract light more strongly.
What happens to the lens when looking at a distant object?
-For distant objects, the lens needs to be less curved to reduce its refractive power, so the ciliary muscles relax, pulling the suspensory ligaments taut and stretching the lens out.
What is the medical term for long-sightedness?
-The medical term for long-sightedness is hyperopia.
What is the medical term for short-sightedness?
-The medical term for short-sightedness is myopia.
How do convex lenses help in the case of long-sightedness?
-Convex lenses provide additional refractive power to help long-sighted individuals focus light properly onto the retina for nearby objects.
How do concave lenses correct short-sightedness?
-Concave lenses refract light outwards, counteracting the over-refraction of the lens in short-sighted individuals, allowing light to focus correctly on the retina.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Das Auge als optisches Linsensystem

Alat Optik • Part 1: Mata, Gangguan Penglihatan Miopi Hipermetropi, & Kacamata

Akomodasi Mata

Parts of the eye | Human eye & the colourful world | Khan Academy

🥇 Anatomía del OJO 3/3 - Medios de Refracción, Cámaras del Ojo, Humor Acuoso, Cuerpo Vítreo
How the Eye Works Animation - How Do We See Video - Nearsighted & Farsighted Human Eye Anatomy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)