Research Methods in Sociology: Quantitative and Qualitative (Sociology Theory & Methods)
Summary
TLDRThis sociology video explores the dichotomy between quantitative and qualitative research methods. It defines both types of data, highlighting quantitative data's objectivity and trend analysis capabilities, and qualitative data's contextual richness and interpretive depth. The video discusses the preference of positivists for quantitative data and interpretivists for qualitative, illustrating how each method is employed to understand social phenomena. It also touches on the application of these methods in various research contexts, from government policy to individual experiences, and advocates for methodological pluralism to achieve a comprehensive understanding of society.
Takeaways
- 📊 Quantitative data is numerical and objective, allowing for reliable analysis and trend identification over time.
- 📘 Qualitative data is contextual and interpretive, providing deeper insights into individuals' lives and experiences.
- 🔍 Positivists favor quantitative data for observing social facts and establishing behavioral patterns.
- 🌟 Interpretivists prefer qualitative data to understand the meanings and motivations behind people's actions.
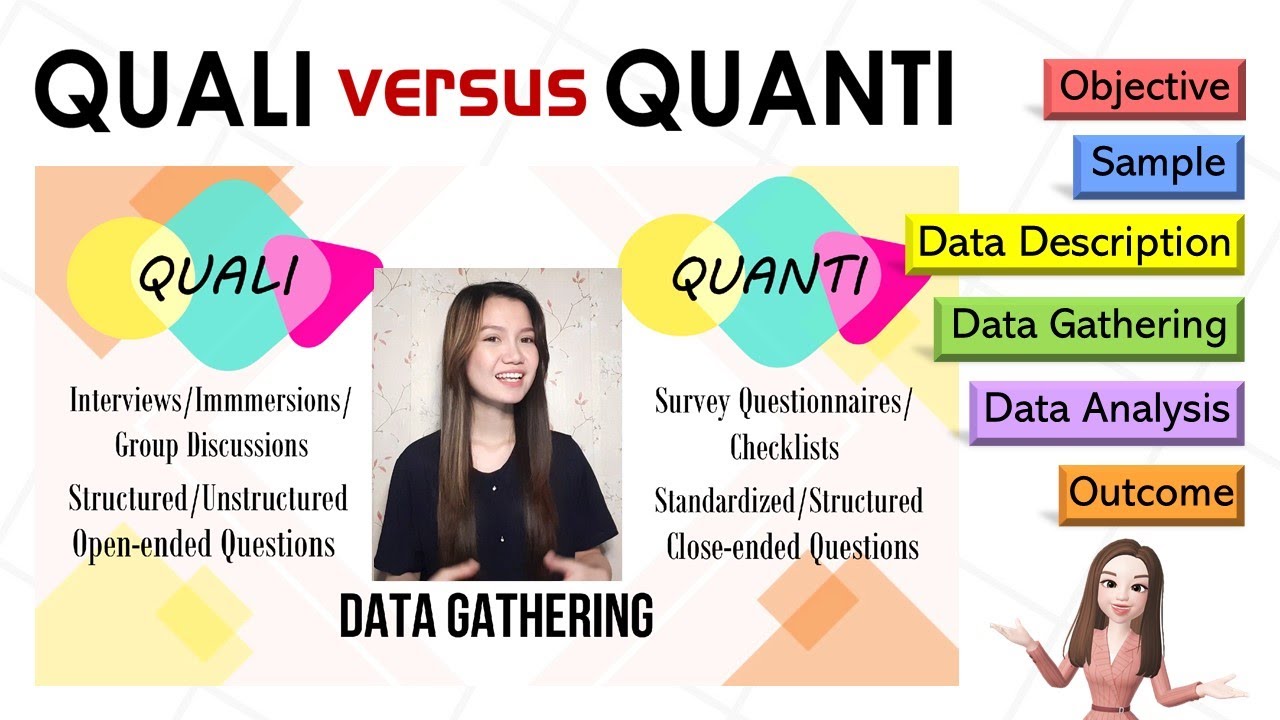
- 🧪 Methods producing quantitative data include experiments, questionnaires, opinion polls, and official statistics.
- 📝 Qualitative data is often collected through participant observation, unstructured interviews, and case studies.
- 🏛️ Quantitative data is crucial for government reporting on social trends and policy-making.
- 🌐 Qualitative data helps understand societal changes and the perspectives of underrepresented groups.
- 🔑 Combining quantitative and qualitative methods, known as methodological pluralism, enhances research validity and reliability.
- 📚 Examples like Willis's 'Learning to Labor' demonstrate the power of mixed methods in sociological research.
Q & A
What is the main difference between quantitative and qualitative data in sociology?
-Quantitative data is numerical and objective, allowing for analysis that is more likely to be reliable and can be repeated to see trends over time. Qualitative data is contextual and often presented in written, verbal, or visual formats, offering more insight into the lives of others and having greater validity.
Which sociological group tends to prefer quantitative data and why?
-Positivists prefer quantitative data as it allows them to observe social facts and establish trends and patterns of behavior. This form of data is also easily replicated for use across different cultures and time periods.
How does the scale of research differ between quantitative and qualitative methods?
-Quantitative methods are generally used on a larger scale to look at wide-ranging social issues, while qualitative methods are smaller in scale due to the individual nature of responses and are less likely to be replicated with similar findings.
What are some common methods that produce quantitative data in sociological research?
-Common methods include experiments, questionnaires with pre-coded questions, opinion polls, non-participant observations in a structured manner, official statistics, and content analysis using qualitative data as input.
How is quantitative data utilized by governments and in the private sector?
-Quantitative data is used by governments to report social trends and to plan budgets and social policies. In the private sector, it is used for marketing, funding projects, and as a discussion point in the media.
What are some methods that produce qualitative data in sociological research?
-Qualitative methods include participant and non-participant observations, unstructured interviews, open-ended questionnaires, secondary sources like personal documents and historical records, case studies, and ethnographic approaches.
How do secondary sources contribute to qualitative research in sociology?
-Secondary sources, particularly historical documents, allow researchers to access views that other methods might not, revealing changes in attitudes over time and aiding in the understanding of social change.
What is the advantage of using qualitative data in sociological research?
-The main advantage is the ability to gain insight into different perceptions, meanings, and motivations behind people's behavior, as well as accessing views of underrepresented or hard-to-reach groups in society.
How can combining quantitative and qualitative methods enhance sociological research?
-Combining methods increases validity through qualitative insights and reliability through quantitative analysis. This approach, known as methodological pluralism, allows for a more comprehensive understanding of social phenomena.
What is an example of a sociological study that used both quantitative and qualitative methods?
-Willis's 'Learning to Labor' is an example that used a mixture of questionnaires, observations, and unstructured interviews to investigate the experiences of working-class boys in an anti-school subculture.
Why might a researcher choose to use both open and closed questions on a questionnaire?
-Using both open and closed questions allows researchers to collect quantitative data illustrating preferences or behaviors, and then use open questions to understand the reasons behind those preferences or behaviors.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Metodologi dalam Sosiologi

Understanding Social Science Research: Research Methods

Research Design (in 3 minutes)

CIRI-CIRI SOSIOLOGI SEBAGAI ILMU PENGETAHUAN DAN METODE ILMIAH - Materi Sosiologi Kelas 10 SMA
PRACTICAL RESEARCH 1 - Qualitative and Quantitative Research - EP.5 (Research Simplified)

Qualitative vs Quantitative Research | Qualitative And Quantitative Research Methods | Simplilearn
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)