The Intertidal | UnderH2O | PBS Digital Studios
Summary
TLDRThe video explores the challenging environment of the intertidal zone, the area between the highest and lowest tides. Organisms here face extreme fluctuations in salinity, temperature, and wave energy. Tide pools, formed during low tide, are home to various species, including small fish and algae. These organisms must adapt to survive in the harsh conditions, as water evaporates and salinity rises. As the tide recedes, space becomes limited, forcing fish to migrate within the pools until the tide returns. The video emphasizes the resilience and unique adaptations of marine life in this dynamic habitat.
Takeaways
- 🌊 The marine environment presents significant challenges for animal survival.
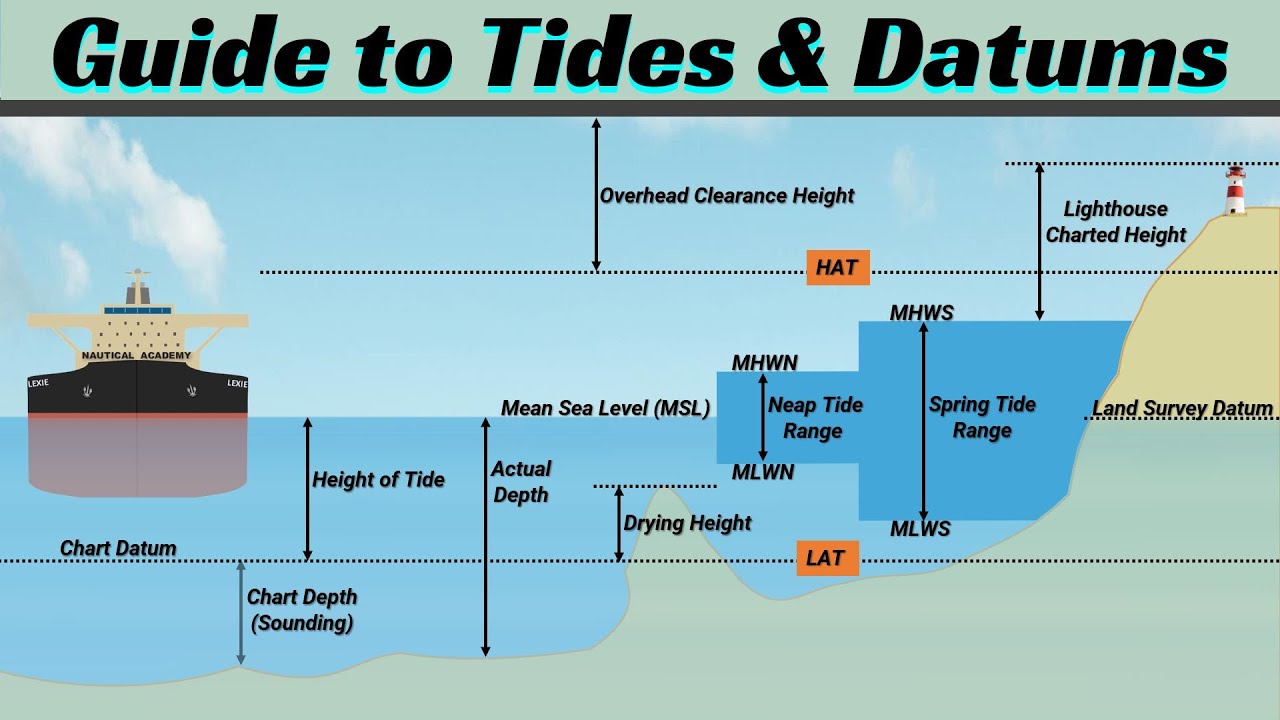
- 🌍 The intertidal zone, between the lowest low tide and the highest high tide, is one of the harshest marine environments.
- ⚡ Organisms in the intertidal zone face extreme fluctuations in salinity, temperature, and intense wave energy.
- 🐠 Tide pools are formed when the tide goes out, leaving behind shallow water areas on the shore.
- 🔥 As the tide pools become cut off from the ocean, water evaporation increases salinity and temperature, creating stressful conditions for organisms.
- 🪸 Coral reefs do not thrive in tide pools due to these harsh conditions, and the substrate is usually bare rock or covered in algae.
- 🐟 Some fish, especially small-bodied and juvenile species, are able to survive in tide pools.
- 🧭 Certain species, like the blenny, spend their entire adult life in tide pools.
- 💧 As water evaporates during low tide, fish must migrate within the tide pools to find the remaining water habitats.
- 🌊 Once the incoming tide replenishes the water, the tide pool environment changes, and it becomes dangerous to remain due to strong waves.
Q & A
What is the intertidal zone?
-The intertidal zone is the area between the lowest low tide and the highest high tide, characterized by extreme fluctuations in environmental conditions.
Why is the intertidal zone considered one of the most challenging marine environments?
-The intertidal zone is subjected to harsh conditions like wild fluctuations in salinity, temperature, and constant wave energy, making it a highly challenging environment for organisms.
What are some adaptations organisms in the intertidal zone have developed?
-Organisms in the intertidal zone have adaptations that allow them to tolerate extreme salinity and temperature changes, as well as the physical stress of wave action.
What happens to tide pools during low tide?
-During low tide, tide pools are cut off from the ocean, and the sun heats the water, causing evaporation. This increases the salinity, making the environment stressful for organisms.
Why can't corals survive in tide pools?
-Corals cannot survive in tide pools because they are unable to handle the fluctuating conditions, such as changes in salinity and temperature.
What types of organisms typically inhabit tide pools?
-Tide pools are generally inhabited by small-bodied fishes, algae, and some species like blennies that are adapted to these extreme conditions. Many juvenile fish also live in tide pools before moving to the coral reefs.
What happens to the fish in tide pools as water evaporates?
-As the water evaporates, habitat availability shrinks, causing fish to migrate to the last remaining tide pools, where space becomes highly competitive.
How do fish survive in such small and often isolated tide pools?
-Fish that live in tide pools are often small-bodied and have adaptations to withstand the extreme conditions like high salinity, heat, and reduced space.
Why is the tide pool environment different from a coral reef?
-Unlike coral reefs, tide pools have harsher conditions that corals cannot tolerate. Instead of coral, the substrate in tide pools is often bare rock or covered with algae.
What does the incoming tide signify for the tide pool environment?
-The incoming tide replenishes the water supply in tide pools, but it also marks the end of human exploration of the area, as it brings back stronger wave energy.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)