03 02 Fisika Dasar 1- Operasi Vektor
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into vector operations, focusing on vector addition through graphical and analytical methods. It explains how to graphically add vectors by drawing and aligning their representations, emphasizing precision in depiction. The script also covers vector subtraction and the concept of scalar multiplication. Analytically, it introduces vector addition by components and the importance of direction in vector operations. Further, the script explores vector multiplication, including scalar-vector multiplication and the two types of vector-vector multiplication: dot product, resulting in a scalar, and cross-product, yielding another vector. The tutorial is designed to aid understanding in kinematics and dynamics, using clear examples and step-by-step explanations.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video script is a tutorial on vector operations, focusing on vector addition and multiplication.
- 📏 Two methods for vector addition are discussed: graphical and analytical, with an emphasis on precision in graphical representation.
- 🖼️ The graphical method involves drawing vectors accurately according to their magnitude and direction without any analytical calculations.
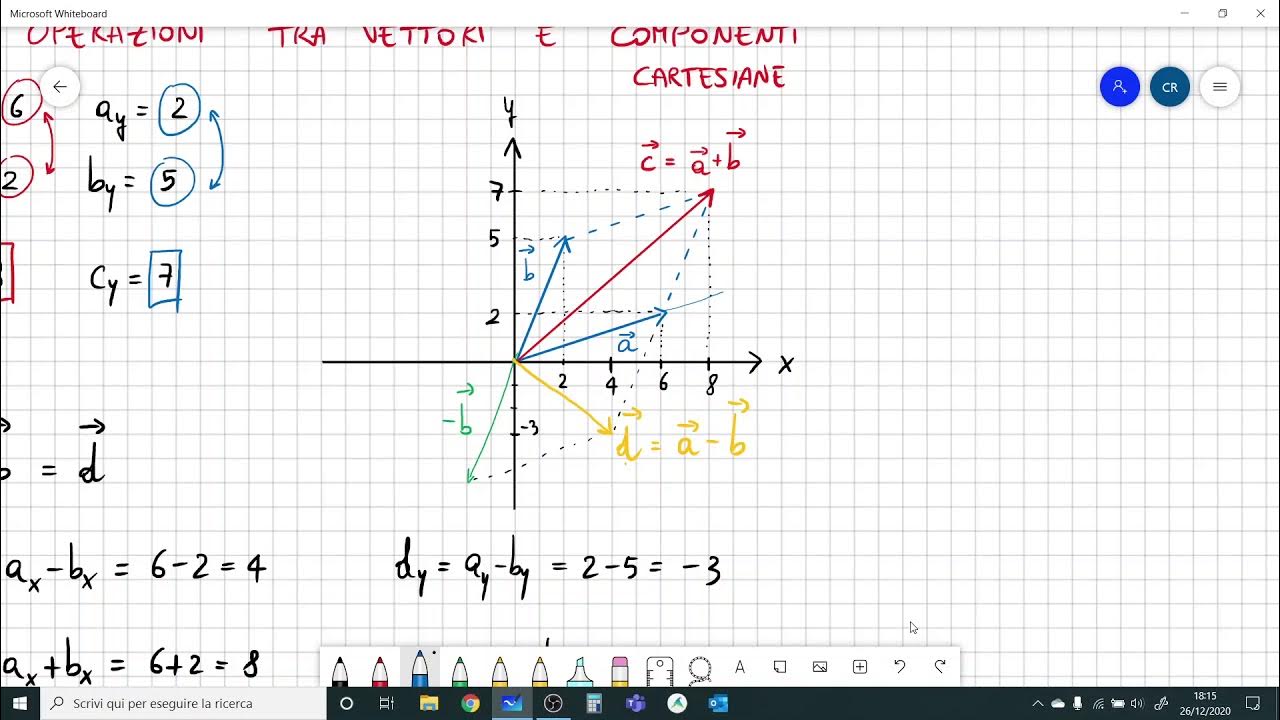
- ✏️ Analytical addition of vectors requires understanding the components of vectors and performing calculations based on their projections onto the coordinate axes.
- 🔄 The script explains that vector addition is commutative, meaning the order of addition does not change the result.
- ➖ Subtraction of vectors is covered, illustrating that subtracting a vector is equivalent to adding its negative.
- 🔢 The tutorial highlights the importance of performing vector operations only on vectors with the same direction and clarifies common mistakes in vector addition.
- 📐 The script introduces vector multiplication, including scalar multiplication and the two types of vector-vector multiplication: dot product and cross product.
- 📉 For scalar multiplication, the tutorial shows how a vector is scaled by a constant factor, which can be positive, negative, or zero.
- 📌 The dot product is explained as a scalar result of the multiplication of two vectors, calculated as the product of their magnitudes and the cosine of the angle between them.
- 📚 The cross product is introduced as a vector result of the multiplication of two vectors, associated with rotation and the right-hand rule in three-dimensional space.
Q & A
What are the two methods discussed for vector addition?
-The two methods discussed for vector addition are the graphical method and the analytical method.
What tools are required for the graphical method of vector addition?
-For the graphical method of vector addition, tools such as a ruler, protractor, and graph paper are required.
How is the resultant vector found using the graphical method?
-In the graphical method, the resultant vector is found by drawing vector B and then from the tip of vector B, drawing vector C. The resultant vector is then drawn from the initial point of vector B to the tip of vector C.
What property of vector addition is demonstrated when adding vector B and vector C in a specific order?
-The property of commutativity is demonstrated when adding vector B and vector C, as the order in which they are added does not change the resultant vector.
How is the subtraction of vectors represented graphically?
-The subtraction of vectors is represented graphically by reversing the direction of the vector being subtracted. For example, to subtract vector C from B, you would reverse the direction of vector C and add it to vector B.
What is the significance of the dot product in vector operations?
-The dot product is significant in vector operations as it results in a scalar value, representing the product of the magnitudes of the vectors and the cosine of the angle between them.
What is the physical interpretation of the cross product in three-dimensional space?
-The cross product in three-dimensional space is related to rotational systems or rotations and is often associated with the right-hand rule, which is used to determine the direction of the resulting vector.
How are the components of the cross product calculated in Cartesian coordinates?
-In Cartesian coordinates, the components of the cross product are calculated using the determinant of a matrix formed by the unit vectors i, j, and k, and the corresponding components of the vectors being multiplied.
What is the result of the dot product when two vectors are orthogonal?
-When two vectors are orthogonal (perpendicular), the result of the dot product is zero because the cosine of the angle between them is zero.
Why is it important to consider the direction of the vectors when performing vector operations?
-The direction of the vectors is important in vector operations because it affects the outcome of operations like addition, subtraction, and the cross product, which depend on the relative orientation of the vectors.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)